Avoidant and disorganized attachment styles both impact relationship dynamics, with avoidant individuals showing emotional distance and disorganized individuals exhibiting erratic behavior due to unresolved trauma. Explore this article to understand how these attachment styles influence intimacy and communication.
Table of Comparison
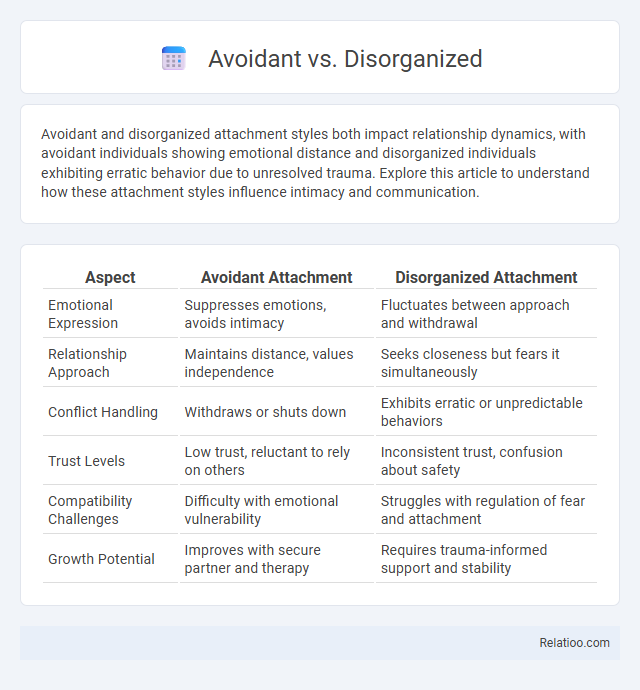
| Aspect | Avoidant Attachment | Disorganized Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Expression | Suppresses emotions, avoids intimacy | Fluctuates between approach and withdrawal |
| Relationship Approach | Maintains distance, values independence | Seeks closeness but fears it simultaneously |
| Conflict Handling | Withdraws or shuts down | Exhibits erratic or unpredictable behaviors |
| Trust Levels | Low trust, reluctant to rely on others | Inconsistent trust, confusion about safety |
| Compatibility Challenges | Difficulty with emotional vulnerability | Struggles with regulation of fear and attachment |
| Growth Potential | Improves with secure partner and therapy | Requires trauma-informed support and stability |
Understanding Attachment Styles: Avoidant vs Disorganized
Avoidant attachment style is characterized by a strong desire for independence and emotional distance, often leading individuals to suppress feelings and avoid intimacy. Disorganized attachment combines both anxious and avoidant behaviors, resulting in unpredictable responses to close relationships and a lack of coherent coping strategies. Understanding these styles helps in recognizing patterns of attachment-related behavior and addressing emotional regulation challenges in therapeutic settings.
Core Characteristics of Avoidant Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by a strong desire for independence and emotional distance, often leading individuals to suppress feelings and avoid closeness in relationships. People with this attachment style typically struggle with trust and may prioritize self-reliance over seeking support from others. Your ability to recognize these core characteristics can help foster healthier connections and improve emotional intimacy.
Key Traits of Disorganized Attachment
Disorganized attachment is characterized by a lack of clear attachment behavior, often displaying contradictory actions such as seeking comfort yet showing fear or avoidance simultaneously. Your behavior may include difficulty trusting others, inconsistent emotional responses, and heightened anxiety in relationships, stemming from early experiences of trauma or neglect. Unlike avoidant attachment, where emotional distance is maintained, disorganized attachment involves confusion and conflict in bonding, making stable relationships challenging.
Childhood Origins of Attachment Differences
Avoidant attachment often stems from caregivers who are emotionally unavailable or unresponsive, leading children to suppress their need for closeness. Disorganized attachment arises from inconsistent or frightening caregiving, causing children to experience fear and confusion in relationships. These early caregiving patterns critically shape children's internal working models, influencing their adult interpersonal dynamics and emotional regulation.
Emotional Regulation in Avoidant vs Disorganized Individuals
Avoidant attachment style is characterized by emotional regulation through suppression and distancing, where individuals minimize emotional expression to maintain self-reliance and avoid vulnerability. Disorganized attachment involves inconsistent emotional regulation, marked by fluctuating behaviors between approach and avoidance, often stemming from unresolved trauma or fear. Understanding your emotional regulation patterns can help differentiate these styles and guide more effective coping strategies.
Relationship Patterns and Challenges
Avoidant attachment style often leads to emotional distancing and difficulty trusting others, resulting in challenges with intimacy and vulnerability in relationships. Disorganized attachment combines fear and confusion, causing unpredictable behaviors and a struggle to maintain stable connections, which can create intense relationship instability. Understanding your attachment style can help you recognize patterns of avoidance, fear, or inconsistency and work toward healthier, more secure relational dynamics.
Coping Mechanisms: Avoidant vs Disorganized
Avoidant attachment involves coping mechanisms characterized by emotional withdrawal and self-reliance to minimize dependency and vulnerability, often leading You to suppress feelings and avoid intimacy. Disorganized attachment presents more chaotic coping strategies, marked by oscillation between approach and avoidance behaviors, reflecting internal conflict and fear of rejection. Understanding these distinct patterns helps tailor therapeutic approaches to improve emotional regulation and relational stability.
Impact on Mental Health and Well-being
Avoidant, disorganized, and other attachment styles shape your mental health by influencing emotional regulation and interpersonal dynamics. Avoidant attachment often leads to emotional suppression and difficulty forming close relationships, increasing anxiety and depression risks. Disorganized attachment is linked to greater vulnerability to trauma, dissociation, and complex PTSD, heavily impacting overall well-being and stability.
Therapeutic Approaches and Healing
Therapeutic approaches for avoidant attachment focus on building trust and fostering emotional expression through techniques like cognitive-behavioral therapy and emotion-focused therapy, helping You develop healthier relational patterns. Disorganized attachment requires trauma-informed care and integrated therapies such as dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) to address fear and confusion stemming from inconsistent caregiving. Repairing attachment styles involves consistent relational safety, mindfulness practices, and gradual exposure to intimacy, promoting healing and secure bonding.
Building Secure Attachments: Strategies for Growth
Building secure attachments requires consistent emotional availability and responsiveness to foster trust and safety, addressing patterns seen in avoidant and disorganized attachment styles. Employing techniques such as reflective listening, emotional validation, and gradual exposure to vulnerability strengthens connection and reduces fear of intimacy. Therapeutic interventions like attachment-based therapy and mindful self-compassion support regulation of attachment-related anxieties, promoting healthier relational dynamics.
Infographic: Avoidant vs Disorganized
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com