Positive criticism fosters growth and understanding in relationships by offering constructive feedback, while negative criticism often leads to resentment and conflict. Explore this article to learn how to effectively use criticism to strengthen your relationships.
Table of Comparison
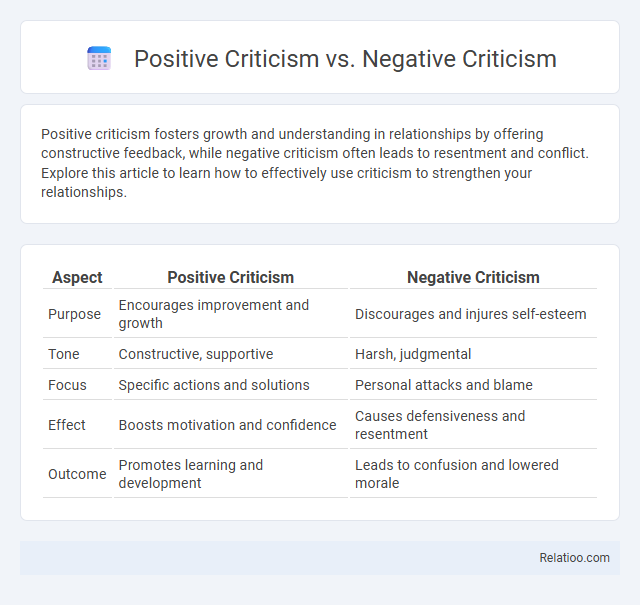
| Aspect | Positive Criticism | Negative Criticism |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Encourages improvement and growth | Discourages and injures self-esteem |
| Tone | Constructive, supportive | Harsh, judgmental |
| Focus | Specific actions and solutions | Personal attacks and blame |
| Effect | Boosts motivation and confidence | Causes defensiveness and resentment |
| Outcome | Promotes learning and development | Leads to confusion and lowered morale |
Understanding Positive and Negative Criticism
Positive criticism highlights constructive feedback aimed at improvement, focusing on specific behaviors and offering actionable solutions that support your growth. Negative criticism often centers on personal faults or generalized complaints, which may hinder motivation and create defensiveness. Understanding the distinction between positive and negative criticism enables you to effectively evaluate feedback and use it to enhance your skills and performance.
Defining Positive Criticism: Constructive Feedback
Positive criticism, also known as constructive feedback, focuses on offering actionable suggestions that help improve performance or behavior without damaging self-esteem. Unlike negative criticism, which highlights faults without solutions, positive criticism provides clear, specific guidance to foster growth and development. Your ability to receive and apply constructive feedback is essential for continuous improvement and achieving personal or professional goals.
Characteristics of Negative Criticism
Negative criticism often focuses on highlighting faults without offering constructive solutions, leading to defensiveness or discouragement. It tends to be subjective, overly harsh, and aimed more at attacking rather than improving performance or behavior. Your ability to recognize the characteristics of negative criticism helps in filtering out unproductive feedback and fostering a healthier response to critique.
Psychological Impact of Different Types of Criticism
Positive criticism enhances motivation and self-esteem by focusing on constructive feedback and actionable suggestions for improvement, fostering a growth mindset. Negative criticism often triggers defensive reactions, anxiety, and reduced self-confidence due to its focus on faults and personal shortcomings without supportive guidance. Overall, the psychological impact of criticism depends on its delivery style, with balanced, empathetic criticism promoting emotional resilience and negative criticism potentially leading to stress and diminished performance.
Benefits of Embracing Positive Criticism
Positive criticism fosters growth by highlighting constructive feedback that encourages improvement and skill development, helping you to embrace challenges and learn from mistakes. Unlike negative criticism, which can demoralize and hinder progress, positive criticism builds confidence and motivation by focusing on strengths and specific areas for enhancement. Embracing positive criticism cultivates a growth mindset, enabling continuous personal and professional development.
Detrimental Effects of Negative Criticism
Negative criticism often leads to decreased motivation, lower self-esteem, and increased stress, significantly impacting mental well-being and productivity. Unlike positive criticism, which encourages growth and improvement through constructive feedback, negative criticism tends to focus on faults without offering solutions, creating a hostile environment. Understanding these differences helps you foster a more supportive atmosphere that minimizes the detrimental effects of harsh judgments.
How to Transform Negative Criticism into Constructive Feedback
Negative criticism often highlights flaws without offering solutions, which can demotivate and confuse the recipient. By reframing negative criticism into constructive feedback, you focus on specific behaviors and suggest actionable improvements that empower growth. Your ability to transform criticism into a positive learning experience fosters development and enhances communication effectiveness.
Effective Strategies for Giving Positive Criticism
Effective strategies for giving positive criticism involve delivering feedback that highlights strengths while offering constructive suggestions for improvement, fostering motivation and growth. Emphasizing specific behaviors and outcomes rather than personal traits ensures clarity and encourages receptiveness. This approach contrasts with negative criticism, which often focuses on faults without guidance, and general criticism that may lack constructive elements, reducing its impact on development.
Responding Productively to Negative Criticism
Responding productively to negative criticism involves actively listening to the feedback, identifying actionable points, and maintaining a calm, open-minded attitude to foster personal or professional growth. Unlike general criticism, which may be neutral or unspecified, negative criticism specifically highlights weaknesses or errors, requiring a balanced approach to separate constructive elements from mere negativity. Embracing this mindset enhances problem-solving skills, builds resilience, and promotes continuous improvement in various contexts.
Building a Positive Criticism Culture in the Workplace
Building a positive criticism culture in the workplace enhances employee growth by focusing on constructive feedback that emphasizes strengths and areas for improvement. Unlike negative criticism, which often highlights faults without solutions, positive criticism fosters open communication, trust, and continuous development. Encouraging a culture where criticism is viewed as an opportunity for learning rather than blame leads to higher job satisfaction and improved team performance.
Infographic: Positive Criticism vs Negative Criticism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com