Critical listening involves analyzing and evaluating the message for accuracy and logic, essential for effective problem-solving in relationships. Appreciative listening focuses on enjoying and valuing the speaker's expression, enhancing emotional connection and bonding. Discover more about how these listening types impact your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
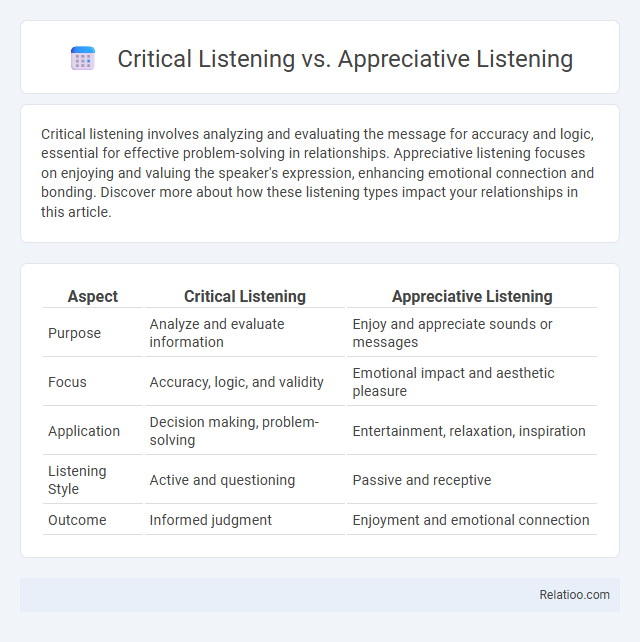
| Aspect | Critical Listening | Appreciative Listening |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Analyze and evaluate information | Enjoy and appreciate sounds or messages |
| Focus | Accuracy, logic, and validity | Emotional impact and aesthetic pleasure |
| Application | Decision making, problem-solving | Entertainment, relaxation, inspiration |
| Listening Style | Active and questioning | Passive and receptive |
| Outcome | Informed judgment | Enjoyment and emotional connection |
Understanding Critical Listening
Critical listening involves actively analyzing and evaluating the information presented to distinguish fact from opinion, identify biases, and assess the credibility of sources. This skill requires heightened attention to detail and logical reasoning to make informed judgments, which is essential in academic, professional, and everyday decision-making contexts. Appreciative listening, in contrast, centers on enjoying and valuing the auditory experience, such as music or storytelling, while general listening skills encompass the foundational ability to process and comprehend spoken language effectively.
Defining Appreciative Listening
Appreciative listening involves engaging with audio or speech for enjoyment and emotional enrichment, often focusing on music, poetry, or storytelling. This type of listening contrasts with critical listening, which requires analyzing and evaluating the content for accuracy or logic, and with general listening skills aimed at effective communication. Your ability to practice appreciative listening enhances your emotional connection and personal satisfaction while experiencing auditory content.
Key Differences Between Critical and Appreciative Listening
Critical listening involves analyzing and evaluating information for accuracy, logic, and relevance, emphasizing judgment and decision-making. Appreciative listening focuses on enjoyment and emotional response, such as appreciating music, storytelling, or speeches without scrutinizing content critically. The key difference lies in the purpose: critical listening demands active assessment to form opinions, whereas appreciative listening centers on pleasure and entertainment.
Purposes and Goals of Each Listening Style
Critical listening aims to evaluate and analyze information for accuracy, logic, and relevance, helping you make informed decisions or judgments. Appreciative listening focuses on enjoyment, emotional connection, and aesthetic pleasure, often experienced through music, poetry, or storytelling. Listening skill encompasses the overall ability to effectively receive and interpret messages, adapting to different contexts to meet diverse communication goals.
Techniques for Effective Critical Listening
Effective critical listening involves techniques such as active engagement, questioning assumptions, and evaluating the credibility of the speaker's message to analyze and interpret information accurately. This skill contrasts with appreciative listening, which focuses on enjoying and responding to aesthetic or emotional content, and general listening skills that emphasize comprehension and retention. Practicing note-taking, focusing on key points, and reflecting on underlying arguments enhances critical listening for better decision-making.
Techniques for Enhancing Appreciative Listening
Enhancing appreciative listening involves techniques such as focusing on the emotional tone, rhythm, and nuances in speech or music to deepen your enjoyment and engagement. Utilizing active listening strategies like maintaining eye contact, nodding, and providing non-verbal feedback helps you fully immerse in the experience. You can improve your listening skill by setting aside distractions and practicing mindfulness to better appreciate the subtleties in sounds and presentations.
Common Challenges in Critical Listening
Critical listening requires focused attention to evaluate and analyze information, often challenged by distractions, personal biases, and emotional interference. Appreciative listening centers on enjoying and valuing audio experiences, posing fewer demands on judgment but still requiring active engagement. Developing listening skills involves overcoming barriers like selective hearing and misinterpretation to improve comprehension and communication effectiveness.
Obstacles to Appreciative Listening
Obstacles to appreciative listening include environmental distractions, personal biases, and lack of interest, which hinder the ability to enjoy or value the speaker's message fully. Unlike critical listening that demands analysis and evaluation, appreciative listening requires emotional engagement and openness, making it more vulnerable to interruptions and preconceived notions. Strengthening listening skills involves overcoming these barriers by fostering focus, empathy, and an active mindset to better appreciate music, speeches, or other enjoyable auditory experiences.
When to Use Critical vs Appreciative Listening
Critical listening is essential when evaluating information for decision-making, detecting biases, or analyzing arguments, while appreciative listening suits occasions where you seek enjoyment or emotional connection, such as music or storytelling. Your listening skills adapt based on context, employing critical listening during work meetings or debates, and appreciative listening in leisure or cultural experiences. Developing expertise in distinguishing when to use each type sharpens comprehension and enhances communication effectiveness.
Real-World Examples of Both Listening Styles
Critical listening involves analyzing and evaluating information, such as when a manager assesses a business proposal to make informed decisions. Appreciative listening focuses on enjoying and valuing the experience, like attending a live concert or listening to a favorite podcast for entertainment. Developing strong listening skills enhances both styles, enabling individuals to effectively interpret feedback during performance reviews and savor nuanced storytelling in audiobooks.
Infographic: Critical Listening vs Appreciative Listening
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com