Accessible communication ensures everyone, including those with disabilities, can receive and understand information, while inclusive communication actively involves diverse perspectives and fosters a sense of belonging. Explore this article to discover how balancing both enhances relationship dynamics.
Table of Comparison
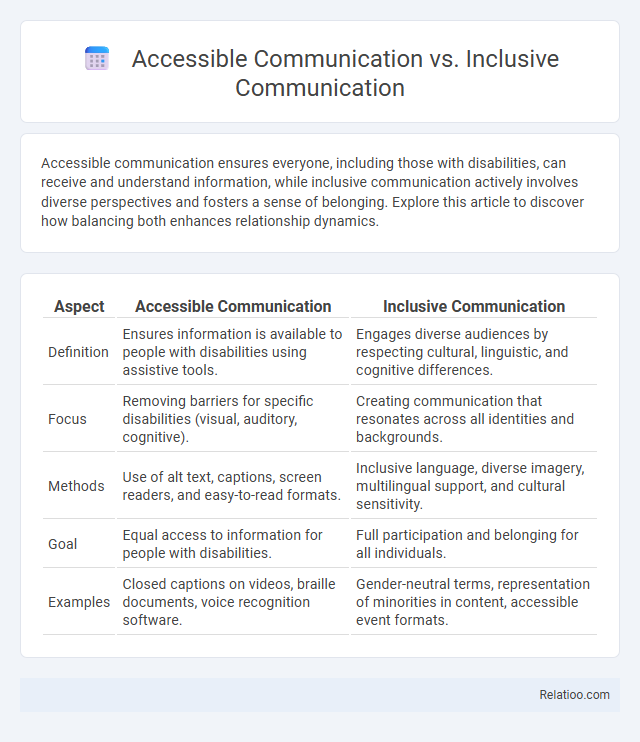
| Aspect | Accessible Communication | Inclusive Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ensures information is available to people with disabilities using assistive tools. | Engages diverse audiences by respecting cultural, linguistic, and cognitive differences. |
| Focus | Removing barriers for specific disabilities (visual, auditory, cognitive). | Creating communication that resonates across all identities and backgrounds. |
| Methods | Use of alt text, captions, screen readers, and easy-to-read formats. | Inclusive language, diverse imagery, multilingual support, and cultural sensitivity. |
| Goal | Equal access to information for people with disabilities. | Full participation and belonging for all individuals. |
| Examples | Closed captions on videos, braille documents, voice recognition software. | Gender-neutral terms, representation of minorities in content, accessible event formats. |
Introduction to Accessible and Inclusive Communication
Accessible communication ensures your messages are understandable and usable by people with disabilities, involving tools like captions, screen readers, and easy-to-read formats. Inclusive communication goes beyond accessibility by actively respecting and reflecting diverse cultural, linguistic, and social backgrounds to engage all audiences effectively. Understanding the differences and connections between accessible and inclusive communication helps you create content that fosters genuine inclusion and equal participation.
Defining Accessible Communication
Accessible communication ensures that information is conveyed in ways that all individuals, including those with disabilities, can perceive, understand, and respond to effectively. It involves adapting formats, technologies, and language to address diverse sensory, cognitive, and physical needs, thereby removing barriers to information access. Your ability to implement accessible communication is essential for fostering inclusive environments where everyone can participate fully.
Understanding Inclusive Communication
Inclusive communication prioritizes clear, respectful, and equitable interaction that accommodates diverse audiences, ensuring everyone can engage meaningfully. Accessible communication focuses specifically on removing barriers related to disabilities by using tools like screen readers, captions, and simplified language. Understanding inclusive communication involves recognizing diverse needs beyond accessibility, incorporating cultural sensitivity, diverse perspectives, and adaptable communication styles to foster full participation and belonging.
Key Differences Between Accessible and Inclusive Communication
Accessible communication ensures information is available and understandable to people with disabilities by using tools like captions, braille, and plain language. Inclusive communication goes beyond accessibility by fostering a sense of belonging and engagement for all individuals, considering diverse cultural, linguistic, and social backgrounds. While accessibility focuses on removing barriers, inclusion emphasizes actively inviting participation and valuing every person's unique contributions.
Importance of Accessibility in Communication
Accessible communication ensures information is available to people with diverse abilities, using tools like screen readers, captions, and plain language. Inclusive communication goes further by considering cultural, linguistic, and cognitive differences, fostering engagement and understanding among all audiences. Emphasizing accessibility in communication is crucial for promoting equality, removing barriers, and enabling full participation in social, educational, and professional environments.
Value of Inclusivity in Communication
Accessible communication ensures information is available to people with disabilities by removing barriers such as visual, auditory, or cognitive challenges. Inclusive communication goes beyond accessibility by fostering a sense of belonging and respect for diverse backgrounds, cultures, and perspectives, creating an environment where everyone feels valued. Embracing the value of inclusivity in your communication enhances collaboration, drives innovation, and strengthens relationships across diverse teams and audiences.
Common Barriers to Accessible Communication
Common barriers to accessible communication include lack of alternative formats, inadequate use of assistive technologies, and unawareness of diverse communication needs. Your efforts to implement inclusive communication must address language simplicity, visual clarity, and cultural sensitivity to ensure everyone can participate fully. Overcoming these barriers fosters genuine inclusion, moving beyond mere accessibility to create environments where every individual feels valued and understood.
Overcoming Challenges in Inclusive Communication
Overcoming challenges in inclusive communication requires recognizing diverse needs and eliminating barriers such as language, cultural differences, and disabilities. Accessible communication ensures information is available to all, while inclusive communication actively involves every individual, respecting unique perspectives for meaningful engagement. Your efforts to combine accessibility with inclusiveness drive true inclusion, fostering environments where everyone feels valued and empowered.
Best Practices for Combining Accessibility and Inclusivity
Accessible communication ensures content is usable by people with disabilities through tools like screen readers, captions, and clear language, while inclusive communication encompasses diverse cultural, linguistic, and cognitive needs to create a sense of belonging. Best practices for combining accessibility and inclusivity include using plain language, providing multiple formats (audio, visual, text), and implementing universal design principles that accommodate various abilities and backgrounds. Organizations should regularly involve diverse user feedback and employ assistive technologies to continuously improve communication strategies and foster genuine inclusion.
Future Trends in Accessible and Inclusive Communication
Future trends in accessible and inclusive communication emphasize the integration of advanced technologies like AI-driven real-time transcription, adaptive interfaces, and multilingual support to enhance user experience for individuals with diverse needs. Your organization can leverage these innovations to foster equitable participation, ensuring all voices are heard and reducing communication barriers. Emphasizing inclusive design principles alongside accessibility standards will shape the evolution of communication practices, promoting a truly inclusive environment where everyone's contribution is valued.
Infographic: Accessible Communication vs Inclusive Communication
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com