Objective perspectives in relationships emphasize measurable behaviors and factual observations, while subjective views focus on personal feelings and individual experiences. Explore the nuances between objective and subjective approaches to deepen your understanding of relationship dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
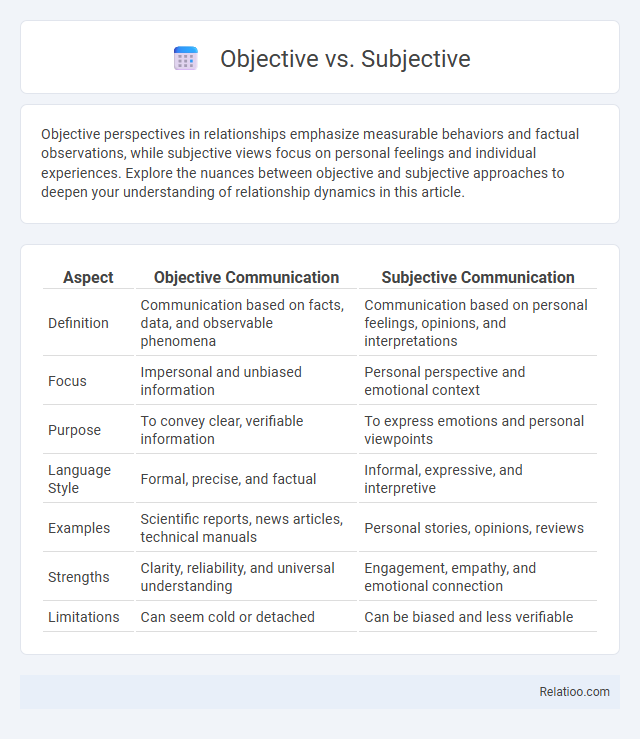
| Aspect | Objective Communication | Subjective Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Communication based on facts, data, and observable phenomena | Communication based on personal feelings, opinions, and interpretations |
| Focus | Impersonal and unbiased information | Personal perspective and emotional context |
| Purpose | To convey clear, verifiable information | To express emotions and personal viewpoints |
| Language Style | Formal, precise, and factual | Informal, expressive, and interpretive |
| Examples | Scientific reports, news articles, technical manuals | Personal stories, opinions, reviews |
| Strengths | Clarity, reliability, and universal understanding | Engagement, empathy, and emotional connection |
| Limitations | Can seem cold or detached | Can be biased and less verifiable |
Understanding Objective vs Subjective
Objective information is based on factual, unbiased data that can be verified through evidence, ensuring reliability and neutrality. Subjective information reflects personal opinions, feelings, or interpretations, which introduces bias and varies between individuals. Understanding the distinction between objective and subjective content is essential for critical analysis, enabling precise evaluation and effective communication of information.
Defining Objective: Facts and Impartiality
Objective information relies on verifiable facts and remains free from personal bias or emotions, ensuring accuracy and impartiality in presenting data. It emphasizes measurable evidence and observable phenomena to maintain credibility in analysis or reporting. This contrasts with subjective viewpoints, which incorporate personal opinions and interpretations.
Unpacking Subjective: Opinions and Perspectives
Subjective content reflects personal opinions, feelings, and perspectives, often influenced by individual experiences and biases. Your interpretation of subjective information requires critical thinking to distinguish between fact-based evidence and personal viewpoints. Understanding this helps in analyzing texts where personal judgment shapes the message rather than objective data or neutral summarization.
Key Differences Between Objective and Subjective
Objective information is based on factual, measurable, and verifiable data, ensuring impartiality and accuracy without personal feelings or opinions. Subjective information reflects personal perspectives, emotions, and biases, which can influence interpretation and vary between individuals. Your understanding of key differences emphasizes that objective content provides a universal truth, while subjective content offers individual experiences, making summarization a tool to blend or highlight both as needed.
The Importance of Context in Objectivity and Subjectivity
Objectivity and subjectivity hinge on the contextual framework in which information is interpreted, with objectivity emphasizing unbiased, fact-based perspectives and subjectivity reflecting personal interpretations influenced by emotions and experiences. The importance of context lies in shaping how facts are perceived and articulated, as the same data may be viewed differently depending on cultural, situational, or individual factors. Summarization compiles essential points by balancing objective facts and subjective insights, ensuring that context-driven nuances are preserved for accurate, comprehensive understanding.
Examples of Objective Statements
Objective statements present facts that are verifiable and free from personal feelings, such as "Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius." These statements provide clear, unbiased information, enabling your audience to assess data without emotional influence. For example, "The company's revenue increased by 15% in the last quarter" is a precise, objective statement useful for factual analysis.
Examples of Subjective Statements
Subjective statements express personal feelings, opinions, or beliefs, such as "I believe the movie was thrilling" or "The weather feels cold today." These statements contrast with objective statements, which provide factual information like "The movie lasts two hours" or "The temperature is 5 degrees Celsius." When summarizing, your goal is to concisely capture the essential points without personal bias or detailed examples.
Objective vs Subjective in Media and Journalism
Objective reporting in media and journalism emphasizes unbiased facts and verifiable information to provide a clear and accurate account of events, ensuring Your trust in the content. Subjective reporting incorporates personal opinions, emotions, and interpretations, which can introduce bias and influence public perception. Summarization distills lengthy reports into concise overviews, maintaining the core facts while omitting detailed analysis or opinion.
Impact on Decision Making: Objective vs Subjective Approaches
Objective approaches rely on quantified data and empirical evidence, ensuring decisions are based on verifiable facts that reduce bias and increase reliability. Subjective approaches incorporate personal judgment and intuition, which can offer nuanced insights but may introduce emotional bias impacting consistency. Your decision-making benefits from combining objective data with subjective perspectives to balance accuracy and contextual understanding.
Choosing the Right Approach: When to Be Objective or Subjective
Choosing the right approach between objective and subjective perspectives depends on your goal and audience. Objective analysis relies on factual, unbiased information ideal for academic research or data reporting, ensuring credibility and clarity. Subjective viewpoints allow personal interpretation and emotional connection, useful in creative writing or opinion pieces, while summarization condenses essential information for quick understanding without detailed analysis.
Infographic: Objective vs Subjective
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com