Selective listening involves focusing only on specific parts of a conversation that interest you, potentially missing important information, whereas critical listening requires evaluating and analyzing the entire message for deeper understanding. Explore this article to learn how mastering both listening styles can improve your relationships.
Table of Comparison
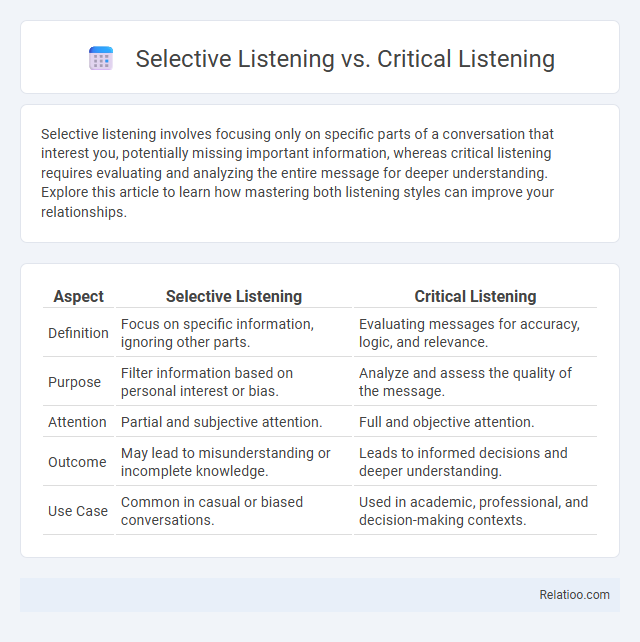
| Aspect | Selective Listening | Critical Listening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on specific information, ignoring other parts. | Evaluating messages for accuracy, logic, and relevance. |
| Purpose | Filter information based on personal interest or bias. | Analyze and assess the quality of the message. |
| Attention | Partial and subjective attention. | Full and objective attention. |
| Outcome | May lead to misunderstanding or incomplete knowledge. | Leads to informed decisions and deeper understanding. |
| Use Case | Common in casual or biased conversations. | Used in academic, professional, and decision-making contexts. |
Introduction to Selective Listening and Critical Listening
Selective listening involves focusing on specific sounds or information while ignoring others, often influenced by personal interests or biases. Critical listening requires actively analyzing and evaluating the meaning, credibility, and logic of the message to form reasoned judgments. Both listening types play crucial roles in communication, enhancing comprehension and decision-making by addressing different cognitive engagement levels.
Defining Selective Listening
Selective listening involves focusing on specific sounds or information while ignoring others, which can limit your understanding and lead to miscommunication. Critical listening requires analyzing and evaluating the content carefully to form a judgment or response. Understanding the distinction between selective listening and critical listening helps improve your communication skills by ensuring you are not only filtering information but also engaging thoughtfully with it.
Understanding Critical Listening
Critical listening involves actively evaluating and analyzing the message for accuracy, logic, and validity, which distinguishes it from selective listening that filters information based on personal biases or preferences. It requires high cognitive engagement and careful assessment of evidence to make informed decisions or judgments. Understanding critical listening enhances effective communication by encouraging listeners to discern underlying meanings and intentions beyond surface-level content.
Key Differences Between Selective and Critical Listening
Selective listening involves focusing on specific parts of a message that align with personal interests or biases, often ignoring other information. Critical listening requires actively analyzing and evaluating the content for accuracy, logic, and relevance, promoting deeper understanding. Key differences lie in selective listening's tendency toward confirmation bias, while critical listening emphasizes objective assessment and informed judgment.
Cognitive Processes Involved in Both Listening Types
Selective listening involves focusing on specific sounds or information while ignoring others, relying heavily on attention control and memory filtering to prioritize relevant stimuli. Critical listening engages deeper cognitive processes such as analysis, evaluation, and reasoning, enabling you to assess the validity and implications of the message. Your brain activates different neural pathways during these listening types, with selective listening emphasizing sensory processing and selective attention, and critical listening involving higher-order functions like judgment and inference.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Selective Listening
Selective listening allows individuals to focus on specific information from a conversation, enhancing efficiency in filtering relevant data but risks missing important context and nuances. This focused approach can improve productivity in noisy environments or multitasking scenarios but often leads to misunderstandings or biased interpretations. Balancing selective listening with critical listening is essential to ensure comprehensive comprehension and avoid the drawbacks of overlooking essential details.
Advantages and Challenges of Critical Listening
Critical listening enhances your ability to evaluate information objectively, fostering better decision-making and problem-solving skills. This listening mode promotes deeper understanding by analyzing arguments and detecting biases, but it requires significant mental effort and concentration, which can be challenging in distracting environments. Unlike selective listening, which involves focusing only on specific information, critical listening demands full attention to all details for comprehensive assessment.
Real-Life Scenarios: Selective vs Critical Listening
In real-life scenarios, selective listening involves focusing on specific sounds or words while filtering out background noise, such as ignoring side conversations to concentrate on a speaker in a crowded room. Critical listening requires analyzing and evaluating the message's content for accuracy, logic, and relevance, often used in debates or when assessing news for credibility. Selective listening prioritizes certain information based on interest or relevance, whereas critical listening demands active judgment and reflection to understand deeper meanings and implications.
Strategies to Improve Critical Listening Skills
Critical listening requires analyzing and evaluating the speaker's message for accuracy, relevance, and logic, unlike selective listening, which filters information based on personal biases or interests. Strategies to improve critical listening skills include focusing on the speaker's evidence, questioning assumptions, and avoiding premature judgments to fully understand and assess the message. You can enhance your critical listening by practicing active engagement, taking notes, and reflecting on the content for deeper comprehension and informed decision-making.
Practical Tips to Minimize Selective Listening Bias
Minimizing selective listening bias involves actively engaging in critical listening techniques such as asking clarifying questions and summarizing key points to ensure accurate understanding. Practicing mindfulness and focusing on the speaker's entire message rather than isolating familiar or comfortable segments enhances comprehensive auditory processing. Utilizing note-taking strategies during conversations can further reduce cognitive filtering and promote unbiased information retention.
Infographic: Selective Listening vs Critical Listening
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com