Aggressive behavior in relationships involves overt confrontation and dominance, while manipulative behavior relies on subtle control and deception to influence others. Understand the key differences between aggressive and manipulative tactics to foster healthier connections by exploring this article.
Table of Comparison
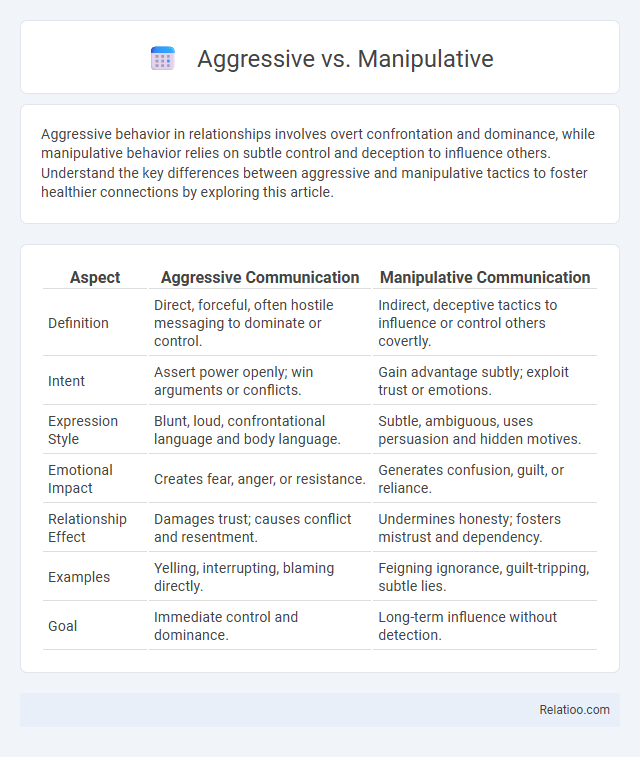
| Aspect | Aggressive Communication | Manipulative Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct, forceful, often hostile messaging to dominate or control. | Indirect, deceptive tactics to influence or control others covertly. |
| Intent | Assert power openly; win arguments or conflicts. | Gain advantage subtly; exploit trust or emotions. |
| Expression Style | Blunt, loud, confrontational language and body language. | Subtle, ambiguous, uses persuasion and hidden motives. |
| Emotional Impact | Creates fear, anger, or resistance. | Generates confusion, guilt, or reliance. |
| Relationship Effect | Damages trust; causes conflict and resentment. | Undermines honesty; fosters mistrust and dependency. |
| Examples | Yelling, interrupting, blaming directly. | Feigning ignorance, guilt-tripping, subtle lies. |
| Goal | Immediate control and dominance. | Long-term influence without detection. |
Understanding Aggressive Behavior
Aggressive behavior manifests through direct actions intended to dominate or injure others, often characterized by hostility and physical or verbal attacks. Manipulative behavior, in contrast, involves indirect, covert tactics aimed at controlling or influencing others for personal gain without overt confrontation. Understanding aggressive behavior requires recognizing its triggers, such as perceived threats or frustration, and differentiating it from manipulation to effectively address and manage interpersonal conflicts.
Defining Manipulative Actions
Manipulative actions involve covert strategies aimed at influencing others' behavior or emotions to serve hidden agendas, often through deception, guilt-tripping, or emotional exploitation. Unlike aggressive behaviors that are overt and confrontational, manipulation is subtle and calculated, leveraging psychological tactics to control or undermine without direct confrontation. Understanding your interactions requires distinguishing these manipulative techniques to avoid being exploited or coerced in personal and professional relationships.
Key Differences Between Aggression and Manipulation
Aggression involves direct and often overt behaviors intended to cause harm or assert dominance, typically marked by physical or verbal hostility. Manipulation, by contrast, relies on covert tactics to influence or control others subtly, using deception or exploitation without overt confrontation. Key differences lie in the visibility of intent and interaction style: aggression is confrontational and immediate, whereas manipulation is indirect and strategic.
Psychological Motivations Behind Each Behavior
Aggressive behavior stems from a desire to assert dominance or protect oneself, often triggered by fear or frustration, while manipulative behavior is driven by the intent to control or influence others covertly to achieve personal gain. Passive-aggressive actions reflect underlying resentment or avoidance of direct confrontation, manifesting through indirect resistance or subtle sabotage. Understanding these psychological motivations helps you recognize the root causes behind each behavior and respond more effectively to interpersonal conflicts.
Common Signs of Aggression
Common signs of aggression include hostile body language, such as clenched fists, intense eye contact, and a raised voice. Manipulative behavior often manifests through deceit, exploitation of others' weaknesses, and persistent guilt-tripping. Recognizing these distinct patterns helps differentiate between aggressive, manipulative, and passive-aggressive actions.
Recognizing Manipulation Tactics
Recognizing manipulation tactics involves identifying subtle psychological strategies that exploit your emotions and decision-making processes to control your behavior without your awareness. Manipulative individuals often use guilt-tripping, gaslighting, passive-aggressiveness, and deception to gain advantage, distinguishing their tactics from overt aggression, which is direct and confrontational. Understanding these differences enables you to protect your boundaries and respond effectively to both aggressive and manipulative behaviors.
Effects on Relationships and Communication
Aggressive behavior often leads to conflict and defensiveness, causing breakdowns in communication and strained relationships due to its confrontational nature. Manipulative actions undermine trust by covertly influencing others for personal gain, which damages emotional bonds and creates suspicion. Your awareness of these patterns can help foster healthier interactions by promoting openness and respect in relationships.
Dealing With Aggressive Individuals
Dealing with aggressive individuals requires firm boundaries and calm assertiveness to prevent escalation while maintaining control of the situation. Recognizing the difference between aggressive behavior, which is direct and confrontational, and manipulative tactics, which are covert and psychologically coercive, helps tailor responses effectively. Employing clear communication and de-escalation techniques can defuse tension and promote respectful interaction without compromising personal safety.
Strategies to Handle Manipulative People
Handling manipulative people requires clear boundaries and assertive communication to protect your emotional well-being while minimizing conflict. Identify manipulation tactics such as guilt-tripping or gaslighting, and respond with factual statements and refusal to engage in distorted narratives. Developing self-awareness and maintaining a support network enhances your ability to recognize and counteract manipulative behaviors effectively.
Building Healthy Boundaries and Assertiveness
Aggressive behavior disregards others' feelings and violates boundaries, while manipulative tactics subtly exploit and control without clear confrontation. Building healthy boundaries requires recognizing these patterns and confidently asserting Your needs without aggression or manipulation. Developing assertiveness empowers You to communicate honestly, maintain respect, and protect emotional well-being in relationships.
Infographic: Aggressive vs Manipulative
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com