Placating communication seeks to avoid conflict through agreement and submission, while aggressive communication imposes one's views forcefully, often escalating tension. Understand the key differences between placating and aggressive behaviors to improve your relationship dynamics by exploring this article.
Table of Comparison
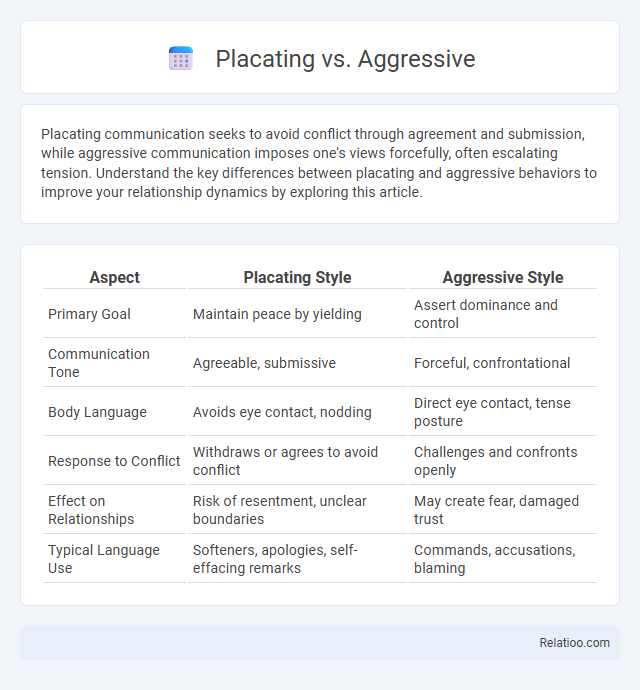
| Aspect | Placating Style | Aggressive Style |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maintain peace by yielding | Assert dominance and control |
| Communication Tone | Agreeable, submissive | Forceful, confrontational |
| Body Language | Avoids eye contact, nodding | Direct eye contact, tense posture |
| Response to Conflict | Withdraws or agrees to avoid conflict | Challenges and confronts openly |
| Effect on Relationships | Risk of resentment, unclear boundaries | May create fear, damaged trust |
| Typical Language Use | Softeners, apologies, self-effacing remarks | Commands, accusations, blaming |
Understanding Placating and Aggressive Behaviors
Understanding placating and aggressive behaviors is crucial for improving communication and conflict resolution. Placating behavior involves prioritizing others' needs over your own, often leading to suppressed emotions and resentment, while aggressive behavior focuses on dominating or controlling interactions, potentially causing hostility and damaged relationships. Recognizing these patterns helps you develop more balanced assertiveness, fostering healthier and more effective interpersonal dynamics.
Key Differences Between Placating and Aggressive Responses
Placating responses prioritize harmony by agreeing or yielding to others, often at the expense of your own needs, while aggressive responses assert opinions forcefully, sometimes disregarding others' feelings or viewpoints. Placating aims to avoid conflict through compliance, whereas aggressive behavior can provoke confrontation and resistance. Understanding these key differences helps in choosing balanced communication strategies that respect both your boundaries and others' perspectives.
Psychological Roots of Placating Tendencies
Placating behaviors often stem from deep psychological needs for approval, fear of conflict, or low self-esteem, driving individuals to prioritize others' feelings over their own. Understanding these roots helps differentiate placating from aggressive styles, which are driven by dominance and control, and passive-aggressive tendencies characterized by indirect resistance. Your awareness of these patterns can improve emotional intelligence and interpersonal communication, fostering healthier interactions.
Triggers and Causes of Aggressive Behavior
Triggers of aggressive behavior often stem from perceived threats, frustration, or unmet needs, leading individuals to react defensively or with hostility. Aggressive behavior can be caused by stress, past trauma, or feelings of powerlessness, which provoke fight-or-flight responses. Understanding these triggers helps differentiate aggression from placating responses, where individuals attempt to avoid conflict by appeasing others.
Effects of Placating on Personal Relationships
Placating often leads to unresolved conflicts and suppressed emotions in your personal relationships, creating imbalance and resentment over time. Individuals who consistently placate may sacrifice their own needs to maintain harmony, causing emotional fatigue and undermining genuine connection. This behavior can hinder authentic communication and trust, ultimately weakening the foundation of healthy relationships.
Consequences of Aggressiveness in Communication
Aggressive communication often results in damaged relationships, heightened conflicts, and reduced collaboration as it can provoke defensiveness and resentment in others. Your message may get lost in the hostility, causing misunderstandings and decreased trust. Choosing assertive communication instead can foster respect and more effective interactions.
Recognizing Placating vs Aggressive Patterns
Recognizing placating versus aggressive patterns involves identifying distinct communication styles rooted in emotional responses and behavioral tendencies. Placating behavior often features appeasement, excessive agreement, and avoiding conflict to maintain harmony, while aggressive patterns exhibit dominance, assertiveness, and confrontational language to control or intimidate. Awareness of these contrasting dynamics enhances interpersonal effectiveness and conflict resolution by promoting balanced, assertive communication.
Strategies to Balance Assertion and Empathy
Strategies to balance assertion and empathy involve recognizing when to employ placating behaviors that validate others' feelings without sacrificing personal boundaries. Aggressive tactics may assert dominance but risk alienating collaboration, so integrating assertiveness with empathetic listening ensures clear communication and mutual respect. Effective interpersonal dynamics rely on modulating between placating, assertiveness, and controlled aggression to maintain constructive dialogue and emotional connection.
Overcoming Placating and Aggressive Habits
Overcoming placating and aggressive habits requires recognizing the underlying need for validation and control in your interactions. Developing assertiveness skills helps you express your needs respectfully and confidently without resorting to submission or dominance. Practicing clear communication and setting healthy boundaries fosters balanced relationships and reduces conflict.
Building Healthy Communication Skills
Building healthy communication skills requires balancing placating, aggressive, and assertive behaviors to foster mutual respect and understanding. Placating often involves appeasing others at the expense of one's own needs, while aggressive communication disregards others' feelings, leading to conflict. Developing assertive communication enables expressing thoughts clearly and respectfully, promoting effective problem-solving and stronger relationships.
Infographic: Placating vs Aggressive
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com