Trustee negligence occurs when a trustee fails to fulfill their fiduciary duties through carelessness or oversight, whereas fraud involves intentional deception for personal gain. Explore this article to understand the critical differences between trustee negligence and fraud and their legal implications.
Table of Comparison
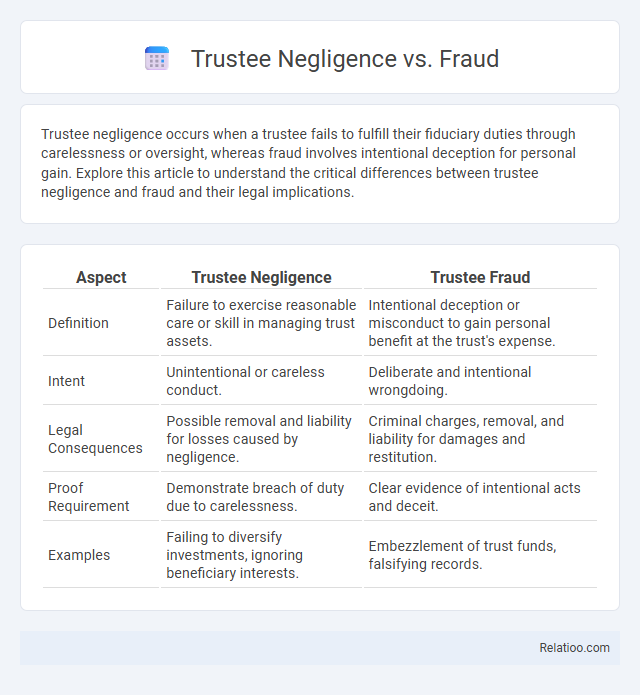
| Aspect | Trustee Negligence | Trustee Fraud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Failure to exercise reasonable care or skill in managing trust assets. | Intentional deception or misconduct to gain personal benefit at the trust's expense. |
| Intent | Unintentional or careless conduct. | Deliberate and intentional wrongdoing. |
| Legal Consequences | Possible removal and liability for losses caused by negligence. | Criminal charges, removal, and liability for damages and restitution. |
| Proof Requirement | Demonstrate breach of duty due to carelessness. | Clear evidence of intentional acts and deceit. |
| Examples | Failing to diversify investments, ignoring beneficiary interests. | Embezzlement of trust funds, falsifying records. |
Understanding Trustee Duties and Responsibilities
Trustee negligence occurs when a trustee fails to perform their fiduciary duties with the care and skill expected, while trustee fraud involves intentional deception for personal gain. Understanding your trustee duties and responsibilities means recognizing the obligation to act in the best interests of beneficiaries, maintain transparency, and avoid conflicts of interest. Differentiating between negligence and fraud is crucial, as negligence reflects carelessness, but fraud implies deliberate misconduct harming your rightful claims.
Defining Trustee Negligence
Trustee negligence occurs when a trustee fails to fulfill their fiduciary duties with the care and prudence expected, leading to financial harm or mismanagement of the trust assets. Unlike fraud, which involves intentional deceit or wrongful acts for personal gain, trustee negligence is characterized by carelessness or failure to act responsibly. Understanding the distinction helps protect your rights by identifying whether a trustee's improper conduct stems from omission or deliberate misconduct.
What Constitutes Trustee Fraud?
Trustee fraud occurs when a trustee intentionally deceives or misappropriates trust assets for personal gain, breaching their fiduciary duty with deliberate dishonesty. Trustee negligence, however, involves a failure to exercise reasonable care or diligence in managing the trust, which may result in unintentional losses but lacks intent to defraud. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for protecting your rights and ensuring trustees fulfill their obligations responsibly.
Key Differences: Negligence vs. Fraud
Trustee negligence involves a failure to exercise reasonable care or diligence in managing a trust, resulting in potential harm to beneficiaries, whereas trustee fraud requires intentional deceit or dishonesty for personal gain. The key difference between negligence and fraud lies in the element of intent: negligence is characterized by carelessness or omission without intent to deceive, while fraud involves purposeful misrepresentation or concealment of facts. Proving fraud demands clear evidence of intentional misconduct, whereas negligence can be established through the breach of the standard duty of care, regardless of intent.
Legal Consequences of Trustee Negligence
Trustee negligence involves the failure to exercise reasonable care in managing trust assets, resulting in potential financial loss to beneficiaries, while trustee fraud entails intentional deception for personal gain. Legal consequences of trustee negligence typically include liability for damages and removal from trustee duties, whereas fraud can lead to criminal charges in addition to civil penalties. Your ability to hold a trustee accountable depends on proving breach of fiduciary duty stemming from negligence or fraudulent actions.
Legal Consequences of Trustee Fraud
Trustee fraud involves intentional deception or misappropriation of trust assets, leading to severe legal consequences such as criminal charges, civil liability, and removal from trusteeship. Trustee negligence, by contrast, arises from failure to exercise reasonable care, resulting in civil liability but typically lacking criminal penalties. Courts impose stricter remedies for trustee fraud to protect beneficiaries' interests and maintain trust integrity.
Warning Signs of Trustee Misconduct
Trustee misconduct often exhibits warning signs such as unexplained financial discrepancies, failure to provide transparent accountings, and unauthorized transactions that may indicate negligence or fraud. You should be alert to unusual delays in reporting, lack of communication, and decisions that do not align with your best interests. Recognizing these red flags early can help protect your assets from breaches of fiduciary duty involving trustee negligence, fraud, or other forms of misconduct.
Remedies for Beneficiaries: Negligence vs. Fraud
Trustee negligence typically results in remedies such as monetary compensation or removal of the trustee to restore the beneficiary's interests. In cases of fraud, beneficiaries can pursue more severe remedies including punitive damages, rescission of transactions, and possible criminal charges against the trustee. While negligence focuses on breaches of duty without intent, fraud involves intentional deception, making the legal consequences and available remedies significantly more stringent for fraudulent actions.
Preventing Trustee Negligence and Fraud
Trustee negligence involves a failure to act with due care, while trustee fraud entails intentional deceit or misappropriation of trust assets, both harming your financial interests. Preventing trustee negligence and fraud requires thorough vetting of trustees, regular audits, and clear communication of fiduciary duties. Implementing strict oversight mechanisms ensures your trust is managed ethically and in alignment with legal standards.
Seeking Legal Advice in Trustee Disputes
Seeking legal advice in trustee disputes is crucial for understanding the distinctions between trustee negligence, fraud, and general negligence, each carrying different legal implications and remedies. Your lawyer can assess whether the trustee's actions were a breach of fiduciary duty through carelessness (negligence), intentional deceit (fraud), or less specific negligence, guiding you toward appropriate claims and compensation. Prompt consultation with a qualified attorney ensures your interests are protected and improves the chances of a favorable resolution in complex trust litigation.
Infographic: Trustee Negligence vs Fraud
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com