Assurance guarantees coverage for events certain to happen, like death, while insurance protects against uncertain risks, such as accidents or theft. Explore the key differences between assurance and insurance in this article.
Table of Comparison
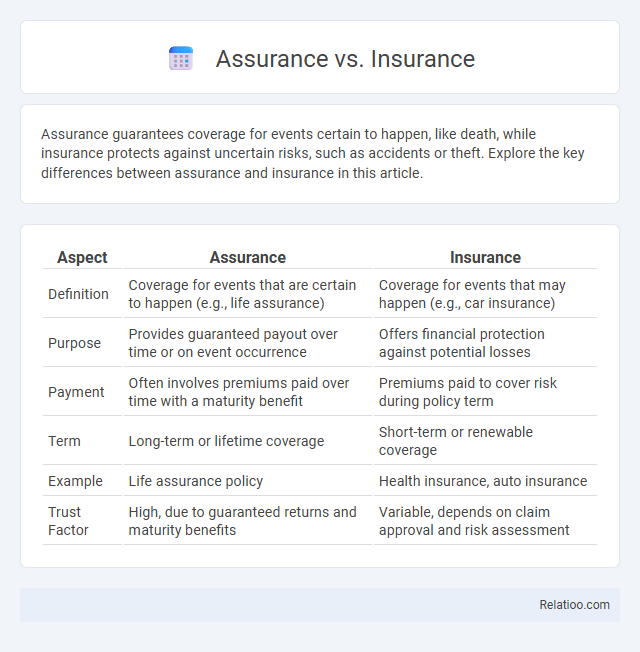
| Aspect | Assurance | Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coverage for events that are certain to happen (e.g., life assurance) | Coverage for events that may happen (e.g., car insurance) |
| Purpose | Provides guaranteed payout over time or on event occurrence | Offers financial protection against potential losses |
| Payment | Often involves premiums paid over time with a maturity benefit | Premiums paid to cover risk during policy term |
| Term | Long-term or lifetime coverage | Short-term or renewable coverage |
| Example | Life assurance policy | Health insurance, auto insurance |
| Trust Factor | High, due to guaranteed returns and maturity benefits | Variable, depends on claim approval and risk assessment |
Understanding Assurance and Insurance: Key Definitions
Assurance refers to coverage for events that are certain to happen, such as life assurance providing financial protection upon death, while insurance covers uncertain events like accidents or theft. Understanding the difference helps you choose the right policy based on predictable versus unpredictable risks. Your decisions should focus on whether the event is guaranteed, in which case assurance applies, or uncertain, requiring insurance.
Historical Background: Origins of Assurance and Insurance
Assurance traces its origins to the 17th century, primarily linked to life insurance contracts that guarantee payment upon death, reflecting a promise or "assurance" of future benefit. Insurance, with roots dating back to ancient civilizations such as Babylon and Greece, initially developed to protect merchants against losses from trade and shipping hazards. Understanding these historical differences helps you appreciate how modern financial protection products evolved from distinct legal and commercial traditions.
Main Differences Between Assurance and Insurance
Assurance typically refers to coverage for events that are certain to happen, such as life assurance, which provides a payout upon death. Insurance covers risks or events that might happen, like car or health insurance, offering financial protection against unforeseen losses. The main difference lies in assurance being a guarantee of payment upon a guaranteed event, while insurance involves risk management for possible future occurrences.
Policy Duration: Term vs Lifetime Coverage
Assurance policies provide lifetime coverage, ensuring payout upon the occurrence of an event such as death, regardless of when it happens, while insurance policies like term insurance offer coverage only for a specified period, usually 10, 20, or 30 years. Term insurance is cost-effective and ideal for covering temporary financial obligations, whereas assurance suits long-term protection needs, such as estate planning or lifelong income replacement. Understanding policy duration is critical for selecting a plan that matches financial goals and risk tolerance.
Types of Assurance Policies
Types of assurance policies primarily include life assurance, which guarantees payment upon death or after a specified term, and endowment assurance, combining insurance with savings for a predetermined maturity benefit. Assurance differs from insurance by providing coverage that is certain to happen, such as life assurance, unlike insurance, which covers events that might occur, like health or property insurance. Your choice of assurance policy should align with long-term financial goals, focusing on guaranteed benefits rather than risk protection.
Types of Insurance Policies
Types of insurance policies include term life, whole life, health, auto, and property insurance, each designed to cover specific risks or assets. Assurance typically refers to life insurance that guarantees a payout upon death, such as whole life or endowment plans, providing financial security for your beneficiaries. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right coverage to protect your financial future effectively.
Premium Payments and Payout Structures
Premium payments for insurance policies are typically paid regularly, such as monthly or annually, and provide coverage for a specified term, expiring without payout if no claim occurs. Assurance policies involve premium payments that often continue until a defined event, like death, ensuring a guaranteed payout regardless of when the event happens. Insurance payout structures depend on the occurrence of uncertain events, whereas assurance guarantees outcomes, influencing how premiums and returns are managed over time.
Common Use Cases: When to Choose Assurance or Insurance
Insurance is commonly chosen for risk management involving unexpected events, such as auto accidents, health emergencies, or property damage, providing financial protection against potential losses. Assurance applies to long-term commitments or outcomes, like life assurance policies that guarantee a payout upon death or maturity, ensuring financial security over time. Selecting insurance suits situations requiring coverage against uncertainty, while assurance fits scenarios involving certainty of an event occurring.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Legal and regulatory considerations for assurance and insurance differ primarily in risk coverage and contractual obligations; assurance typically involves long-term commitments for events that are certain to occur, such as life assurance, while insurance covers risks for uncertain events, like property or health insurance. Regulatory bodies enforce strict compliance on insurance providers to maintain solvency, transparency, and consumer protection, whereas assurance products are often governed by financial service regulations focusing on policyholder rights and long-term guarantees. Understanding these distinctions ensures your choice aligns with legal requirements and regulatory protections specific to your financial and risk management needs.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
Choosing between assurance and insurance involves understanding their distinct purposes: assurance typically covers events that will happen, such as death, while insurance protects against uncertain events, like accidents or theft. Key factors to consider include the nature of the risk, financial goals, and the duration of coverage needed, with assurance often suited to long-term commitments and insurance for short-term contingencies. Evaluating policy terms, premium costs, and payout conditions helps ensure the best fit for personal or business protection needs.
Infographic: Assurance vs Insurance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com