Balancing privacy and security is crucial in modern relationships to maintain trust while protecting personal information from potential threats. Discover effective strategies to safeguard both privacy and security in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
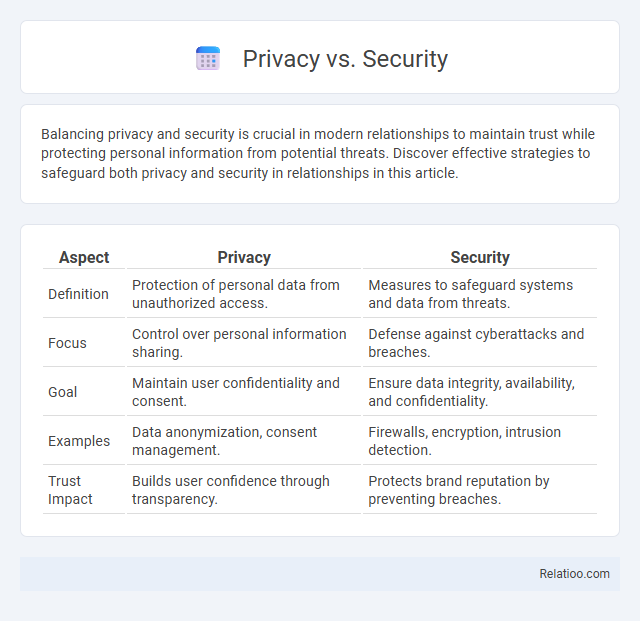
| Aspect | Privacy | Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protection of personal data from unauthorized access. | Measures to safeguard systems and data from threats. |
| Focus | Control over personal information sharing. | Defense against cyberattacks and breaches. |
| Goal | Maintain user confidentiality and consent. | Ensure data integrity, availability, and confidentiality. |
| Examples | Data anonymization, consent management. | Firewalls, encryption, intrusion detection. |
| Trust Impact | Builds user confidence through transparency. | Protects brand reputation by preventing breaches. |
Understanding Privacy and Security: Key Differences
Privacy involves controlling how your personal information is collected, used, and shared, ensuring your data remains confidential. Security focuses on protecting systems and data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats through technical measures like encryption and firewalls. Understanding the key differences helps you make informed decisions to safeguard both your privacy and security effectively.
Historical Context of Privacy and Security
Privacy and security have evolved as fundamental concepts shaped by historical events such as the rise of digital communication and government surveillance. The development of cryptographic techniques and privacy laws in the late 20th century marked key milestones in balancing state control and individual freedoms. Understanding this historical context helps you navigate modern challenges in protecting personal data while ensuring security.
Why Privacy Matters in the Digital Age
Privacy matters in the digital age because personal data is constantly collected, stored, and potentially exploited by corporations, governments, and malicious actors. Without strong privacy protections, individuals face risks such as identity theft, surveillance, and loss of autonomy over their personal information. Ensuring privacy supports freedom of expression, safeguards personal dignity, and prevents abuse in increasingly connected online environments.
The Importance of Security in a Connected World
In a connected world, the importance of security cannot be overstated as it protects sensitive data from cyber threats and unauthorized access, ensuring your digital safety. Balancing privacy with robust security measures helps prevent data breaches while maintaining confidentiality. Implementing advanced encryption and multi-factor authentication enhances both security and privacy, safeguarding your personal and organizational information effectively.
Balancing Privacy and Security: The Ongoing Debate
Balancing privacy and security requires carefully managing the trade-offs between protecting personal data and ensuring safety against threats. Organizations must implement robust security measures without compromising your privacy rights, using encryption, access controls, and transparent policies. The ongoing debate centers on finding solutions that uphold individual freedoms while maintaining effective security frameworks in an increasingly digital world.
Common Privacy Threats and How They Evolve
Common privacy threats include data breaches, identity theft, and unauthorized data tracking, which continuously evolve due to advances in technology and increased cybercriminal sophistication. Threat actors exploit vulnerabilities in software, social engineering, and IoT device weaknesses to gain unauthorized access to personal information. Emerging threats like AI-driven profiling and deepfake technology further complicate privacy protection, requiring adaptive security measures to mitigate risks effectively.
Security Measures: Protecting Data and Infrastructure
Security measures encompass encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication, and advanced firewalls to protect data and infrastructure from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Regular security audits and continuous monitoring systems identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with industry standards like ISO/IEC 27001 and NIST frameworks. Implementing robust access control policies and endpoint protection safeguards critical assets while maintaining operational integrity against evolving cyberattacks.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Privacy and Security
Technology plays a crucial role in shaping both privacy and security by enabling advanced data encryption, secure communication channels, and real-time threat detection systems. Your digital footprint is constantly monitored and protected through innovations like multi-factor authentication and privacy-enhancing technologies that limit unauthorized data access. Balancing privacy and security requires continuous adaptation of technological tools to address emerging cyber threats while respecting individual rights.
Legal and Ethical Implications of Privacy vs Security
Balancing privacy and security presents significant legal and ethical challenges, as laws must protect individual data rights while enabling robust security measures to prevent harm. Regulatory frameworks like GDPR emphasize user consent and data minimization, enforcing strict guidelines on data collection and usage to safeguard privacy. Ethical considerations demand transparency, accountability, and respect for autonomy to ensure security practices do not infringe on personal freedoms or lead to unjust surveillance.
Future Trends: Navigating Privacy and Security Challenges
Emerging technologies like AI and IoT are reshaping the landscape of privacy and security, requiring innovative solutions to protect personal data from evolving cyber threats. Your ability to balance data transparency with robust encryption methods will be critical in navigating these future challenges. Prioritizing adaptive security frameworks ensures resilience against increasingly sophisticated breaches while maintaining user trust and regulatory compliance.
Infographic: Privacy vs Security
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com