Trust forms the foundation of strong relationships, enabling open communication and emotional connection, while security provides the stability and safety that reinforce trust over time. Discover how balancing trust and security can transform your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
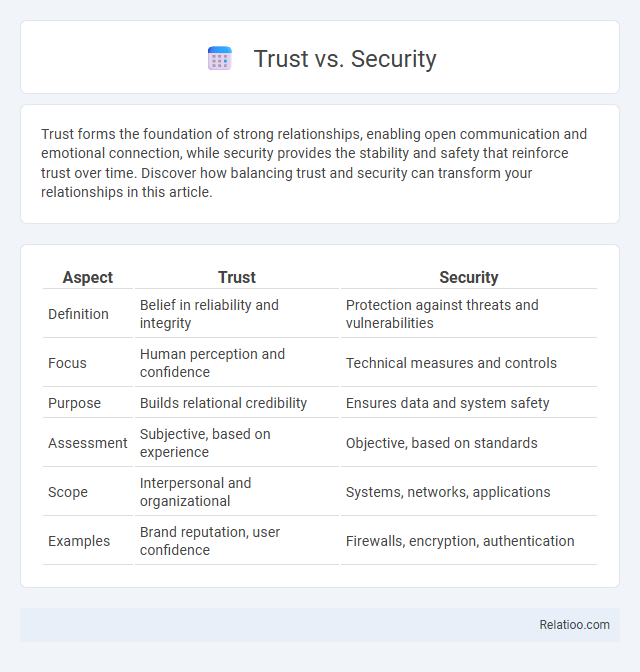
| Aspect | Trust | Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in reliability and integrity | Protection against threats and vulnerabilities |
| Focus | Human perception and confidence | Technical measures and controls |
| Purpose | Builds relational credibility | Ensures data and system safety |
| Assessment | Subjective, based on experience | Objective, based on standards |
| Scope | Interpersonal and organizational | Systems, networks, applications |
| Examples | Brand reputation, user confidence | Firewalls, encryption, authentication |
Understanding Trust and Security: Key Differences
Trust involves the belief in the reliability and integrity of a person, system, or organization, based on past interactions and reputation. Security refers to the measures and protocols implemented to protect assets, data, and systems from unauthorized access or harm. Understanding the key differences highlights that trust is subjective and relational, while security is objective and technical, providing a foundation for establishing and maintaining trust.
The Role of Trust in Digital Interactions
Trust in digital interactions forms the foundation for secure and safe online experiences, influencing how users share sensitive information and engage with platforms. Security measures like encryption and authentication protect your data, but without trust, users may hesitate to participate or transact. Building trust enhances user confidence, ensuring smoother digital collaboration and minimizing perceived risks.
Foundations of Security in Technology
Trust establishes the confidence users place in technology platforms and systems, forming the basis for secure interactions and transactions. Security encompasses the technical measures and protocols designed to protect data integrity, confidentiality, and availability from cyber threats. Safety refers to preventing harm to users and ensuring systems operate reliably; your understanding of these foundations is critical to building resilient technology solutions.
Trust vs Security: Why Both Matter
Trust and security are distinct yet interconnected concepts crucial for protecting your digital assets and relationships. Trust involves confidence in the reliability and integrity of systems or people, whereas security focuses on the technical measures and protocols safeguarding data from threats. Balancing trust with robust security measures ensures your digital interactions are both dependable and protected against breaches or vulnerabilities.
Building Trust in Online Systems
Building trust in online systems relies on robust security measures that protect your data from breaches and unauthorized access. Ensuring safety involves creating environments free from harm and fraud, reinforcing user confidence in digital interactions. Transparent policies and consistent security updates establish a reliable foundation, making users feel secure and fostering long-term trust.
Security Measures: Protecting Data and Privacy
Security measures encompass encryption, multi-factor authentication, and firewalls to protect data and privacy from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Implementing robust security protocols ensures confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information across digital platforms. Organizations adopt intrusion detection systems and regular security audits to mitigate risks and comply with data protection regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Trust Breaches: Causes and Consequences
Trust breaches often stem from data leaks, insider threats, and failure to meet privacy expectations, leading to significant reputational damage and loss of customer loyalty. Security vulnerabilities, such as inadequate encryption or outdated software, increase the risk of unauthorized access, impacting your organization's integrity and operational continuity. Understanding these causes is critical to preventing trust erosion and safeguarding your business against long-term negative consequences.
Enhancing Security to Foster Trust
Enhancing security measures such as multi-factor authentication, end-to-end encryption, and continuous monitoring significantly reduces vulnerabilities in digital systems, fostering user trust. Implementing robust security protocols not only prevents unauthorized access but also ensures data integrity and confidentiality, underpinning a reliable environment. This strategic focus on security elevates overall safety perceptions and solidifies long-term trust between organizations and their stakeholders.
Balancing Trust and Security in User Experience
Balancing trust and security in user experience requires implementing robust authentication methods while ensuring seamless interaction that does not frustrate users. Effective trust signals include transparent privacy policies, consistent security updates, and clear data handling practices that reassure users without compromising usability. Prioritizing a user-centric approach optimizes both protection against threats and confidence in the platform.
Future Trends: Evolving Concepts of Trust and Security
Future trends in trust, security, and safety emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain technologies to enhance transparency and accountability in digital ecosystems. Adaptive security models leveraging machine learning will predict and mitigate threats proactively, reshaping traditional frameworks of safety in cyber-physical environments. The evolution of trust will increasingly depend on decentralized identity systems and real-time risk assessment to support secure and resilient interactions across interconnected networks.
Infographic: Trust vs Security
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com