Trust fosters strong, secure relationships by promoting openness and reliability, while mistrust breeds doubt and uncertainty, leading to increased alienation and emotional distance. Explore the dynamics of trust, mistrust, and alienation in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
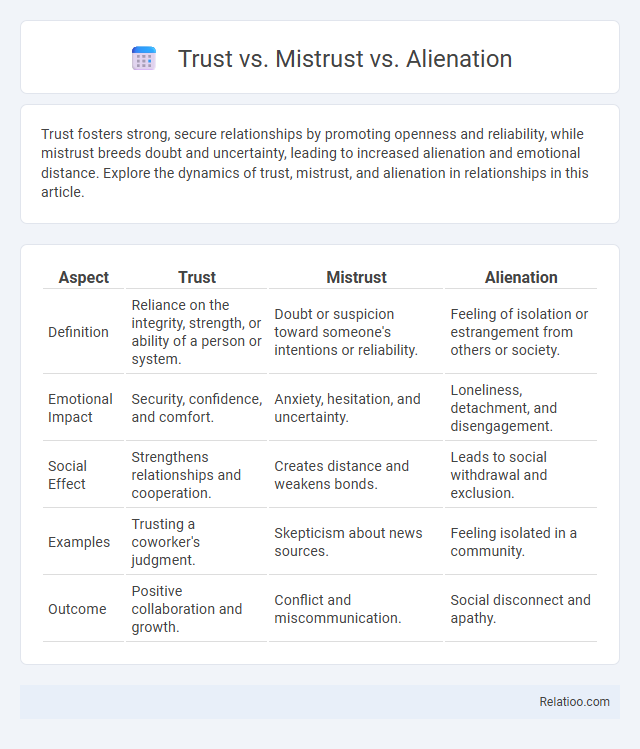
| Aspect | Trust | Mistrust | Alienation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reliance on the integrity, strength, or ability of a person or system. | Doubt or suspicion toward someone's intentions or reliability. | Feeling of isolation or estrangement from others or society. |
| Emotional Impact | Security, confidence, and comfort. | Anxiety, hesitation, and uncertainty. | Loneliness, detachment, and disengagement. |
| Social Effect | Strengthens relationships and cooperation. | Creates distance and weakens bonds. | Leads to social withdrawal and exclusion. |
| Examples | Trusting a coworker's judgment. | Skepticism about news sources. | Feeling isolated in a community. |
| Outcome | Positive collaboration and growth. | Conflict and miscommunication. | Social disconnect and apathy. |
Understanding Trust: Definition and Importance
Trust is the firm belief in the reliability, truth, and integrity of a person or system, serving as the foundation for secure relationships and effective communication. Understanding trust involves recognizing its role in fostering emotional safety, cooperation, and social cohesion, which are vital for personal and professional success. Mistrust and alienation arise when trust is broken, leading to social disconnection and emotional isolation, highlighting the importance of maintaining trustworthy interactions.
The Roots and Causes of Mistrust
Mistrust often originates from early experiences where inconsistent caregiving disrupted the development of secure attachment during infancy, leading to deep-seated feelings of alienation. Factors such as neglect, emotional unavailability, or trauma undermine trust-building, resulting in defensive behaviors and social withdrawal to protect against perceived threats. The roots of mistrust lie in unmet needs and broken relational bonds, which shape an individual's worldview as inherently unsafe or unreliable.
Alienation: Meaning and Psychological Impact
Alienation refers to a state of estrangement where individuals feel disconnected from themselves, others, or their environment, often resulting in feelings of isolation, powerlessness, and meaninglessness. Psychologically, alienation can lead to increased vulnerability to anxiety, depression, and a diminished sense of identity, impairing social relationships and personal well-being. Understanding alienation is crucial for addressing mental health issues and fostering a sense of belonging and purpose in therapeutic and social contexts.
Trust vs Mistrust: Key Differences
Trust vs Mistrust centers on the foundational emotional bond developed in infancy, where caregivers' responsiveness fosters a secure attachment and sense of safety. Alienation involves feelings of isolation and estrangement often emerging later in life, reflecting a breakdown in social connections rather than early relational trust. The key difference lies in Trust vs Mistrust establishing the baseline for healthy relational development, while Alienation represents the disruption or absence of that fundamental trust in social contexts.
Signs and Consequences of Alienation
Signs of alienation include feelings of isolation, emotional detachment, and a sense of powerlessness within social or personal relationships. Consequences of alienation often lead to decreased mental well-being, impaired trust-building, and increased vulnerability to loneliness and depression. Understanding these effects helps you recognize the importance of fostering genuine connections to combat alienation.
The Role of Early Relationships in Trust Development
Early relationships play a critical role in shaping trust development, where consistent and responsive caregiving fosters a secure attachment foundation. Experiences marked by reliability and emotional warmth encourage a sense of trust, while neglect or inconsistency often leads to mistrust and feelings of alienation. The quality of these formative interactions influences an individual's ability to form healthy connections and navigate social environments effectively.
Societal Influences on Trust, Mistrust, and Alienation
Societal influences profoundly shape your experiences of trust, mistrust, and alienation through family dynamics, cultural norms, and social institutions. Trust develops when consistent support and reliable social structures affirm your sense of security, while mistrust arises from unpredictable or hostile environments that undermine confidence in others. Alienation emerges when societal exclusion or systemic inequalities disconnect individuals from communities, fostering feelings of isolation and eroding social cohesion.
Overcoming Mistrust: Effective Strategies
Overcoming mistrust requires consistent communication, transparency, and empathetic engagement to rebuild relationships and foster trust. Strategies such as active listening, validating feelings, and demonstrating reliability help counter feelings of alienation and promote connection. Establishing clear boundaries and encouraging vulnerability create a safe environment that supports the transition from mistrust to trust and reduces social alienation.
Rebuilding Trust After Alienation
Rebuilding trust after alienation requires consistent communication, empathy, and transparency to restore damaged relationships effectively. Establishing clear boundaries and demonstrating reliability over time helps overcome feelings of mistrust rooted in past alienation. Therapeutic interventions and supportive environments play a crucial role in facilitating emotional healing and reconnecting individuals.
Cultivating Authentic Connections in a Fragmented World
Trust builds the foundation for authentic connections, allowing you to foster meaningful relationships even in a fragmented world. Mistrust and alienation disrupt this foundation, creating barriers that isolate individuals and hinder emotional bonding. Cultivating genuine interactions requires overcoming these challenges by embracing vulnerability and empathy to bridge divides and restore a sense of community.
Infographic: Trust vs Mistrust vs Alienation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com