Trust forms the foundation of healthy relationships by fostering mutual respect and emotional security, while dependency can lead to imbalance and decreased personal autonomy. Explore how balancing trust and dependency strengthens your connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
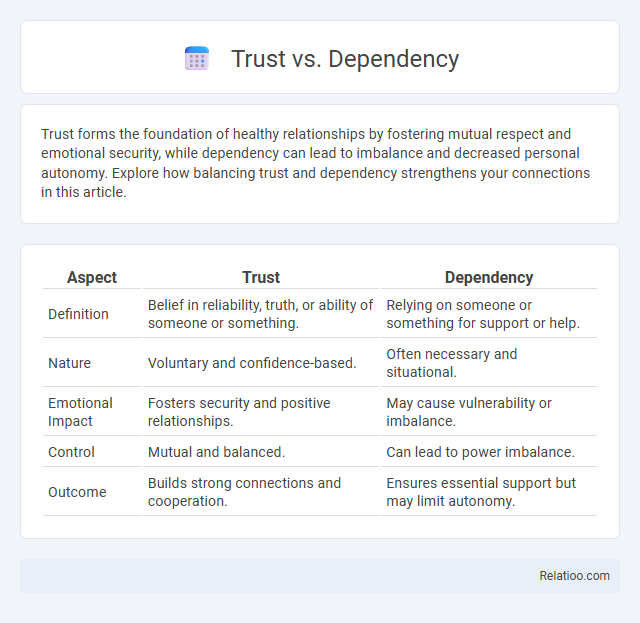
| Aspect | Trust | Dependency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in reliability, truth, or ability of someone or something. | Relying on someone or something for support or help. |
| Nature | Voluntary and confidence-based. | Often necessary and situational. |
| Emotional Impact | Fosters security and positive relationships. | May cause vulnerability or imbalance. |
| Control | Mutual and balanced. | Can lead to power imbalance. |
| Outcome | Builds strong connections and cooperation. | Ensures essential support but may limit autonomy. |
Understanding Trust: Foundations and Definitions
Trust is the foundational belief in the reliability, integrity, and competence of individuals or systems, shaping interpersonal and organizational relationships. Dependency occurs when one party relies excessively on another, often without reciprocal support, leading to potential vulnerability or imbalance. Interdependence represents a mutual reliance where all parties contribute and benefit, fostering collaboration and sustainable partnerships built upon balanced trust.
Defining Dependency: Nature and Types
Dependency refers to a state where one party relies heavily on another for support, resources, or decision-making, often resulting in an imbalance of power and control. Types of dependency include emotional dependency, financial dependency, and psychological dependency, each influencing relationships and interactions differently. Understanding the nature of your dependency helps identify areas where trust can be built or where interdependence can be cultivated for mutual benefit.
Key Differences Between Trust and Dependency
Trust involves confidence in someone's reliability and integrity, whereas dependency refers to relying on someone for support or assistance. Your ability to trust fosters mutual respect and openness, while dependency may create vulnerability or imbalance in relationships. Interdependence combines trust and dependency, emphasizing mutual reliance that strengthens collaboration and shared goals.
Psychological Roots of Trust and Dependency
Trust originates from early attachment experiences, where consistent caregiving fosters a secure base for emotional safety and confidence in relationships. Dependency arises when individuals rely excessively on others for validation and support, often linked to unmet emotional needs or insecure attachments. Interdependence reflects a balanced dynamic, where mutual trust allows for healthy reliance and collaboration without compromising autonomy.
Trust in Personal Relationships
Trust in personal relationships forms the foundation for emotional security, enabling open communication and vulnerability between partners. Unlike dependency, trust fosters mutual respect and autonomy without control or imbalance, promoting healthier connections. Building trust requires consistent honesty, reliability, and empathy, which strengthen relational resilience and intimacy over time.
Dependency in Personal Relationships
Dependency in personal relationships often involves relying heavily on another person for emotional support, decision-making, or daily needs, which can lead to an imbalance of power and loss of personal autonomy. Trust is a foundational element that supports healthy interdependence, where both partners maintain mutual respect and independence while being emotionally connected. Building awareness of unhealthy dependency patterns is crucial for fostering balanced relationships that encourage growth, self-reliance, and mutual support.
Healthy vs Unhealthy Dependency
Healthy dependency fosters mutual support and growth, enabling individuals to rely on each other without losing autonomy, while unhealthy dependency creates imbalance and stifles personal development. Trust forms the foundation for interdependence, where partnerships thrive on shared responsibilities and respect. You can cultivate strong relationships by recognizing the difference between supportive connections and toxic reliance that undermines well-being.
Building Trust Without Fostering Dependency
Building trust without fostering dependency requires establishing clear boundaries and promoting autonomy within relationships. You can encourage interdependence by fostering mutual respect and collaborative problem-solving, enabling each party to contribute equally. Trust grows strongest when individuals feel supported yet empowered to maintain their independence.
The Impact of Trust and Dependency on Communication
Trust significantly enhances communication by fostering openness and reducing misunderstandings, while dependency may hinder dialogue through power imbalances that restrict honest exchange. Interdependence promotes collaborative communication by balancing mutual reliance and autonomy, enabling effective sharing of information and joint problem-solving. Understanding the nuanced roles of trust and dependency helps optimize interaction dynamics for more productive and transparent communication processes.
Strategies for Balancing Trust and Dependency
Balancing trust and dependency requires establishing clear boundaries and promoting open communication to ensure mutual respect and accountability. Strategies include fostering transparency through consistent information sharing, setting realistic expectations, and encouraging reciprocal support to prevent over-reliance. Implementing feedback mechanisms and reinforcing autonomy cultivates interdependence, strengthening collaborative relationships while mitigating risks associated with blind trust or excessive dependency.
Infographic: Trust vs Dependency
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com