Trust builds strong and lasting relationships by fostering open communication and emotional safety, while suspicion undermines connections through doubt and insecurity. Explore this article to understand how balancing trust and suspicion shapes healthier bonds.
Table of Comparison
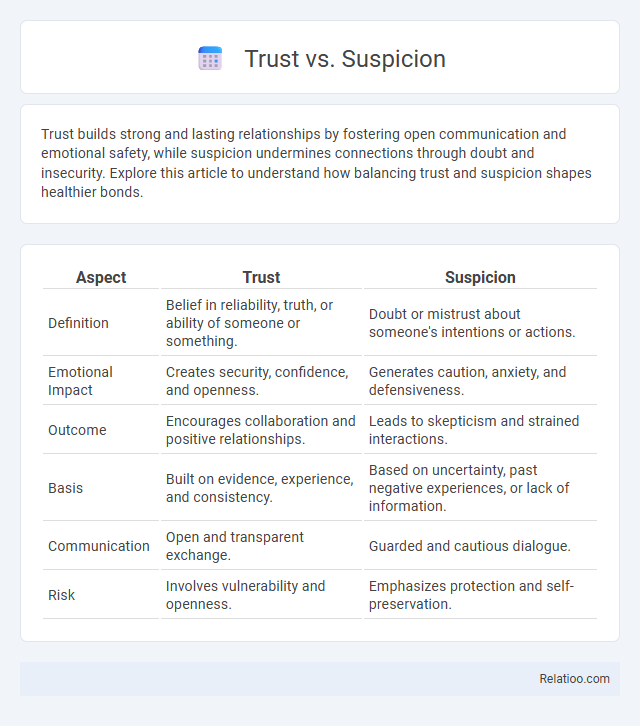
| Aspect | Trust | Suspicion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in reliability, truth, or ability of someone or something. | Doubt or mistrust about someone's intentions or actions. |
| Emotional Impact | Creates security, confidence, and openness. | Generates caution, anxiety, and defensiveness. |
| Outcome | Encourages collaboration and positive relationships. | Leads to skepticism and strained interactions. |
| Basis | Built on evidence, experience, and consistency. | Based on uncertainty, past negative experiences, or lack of information. |
| Communication | Open and transparent exchange. | Guarded and cautious dialogue. |
| Risk | Involves vulnerability and openness. | Emphasizes protection and self-preservation. |
Understanding Trust: Foundations and Importance
Understanding trust involves recognizing its foundation in reliability, honesty, and consistent behavior, which fosters strong interpersonal and organizational relationships. Trust enhances cooperation, reduces uncertainty, and builds a sense of safety, making it a critical element for successful communication and collaboration. Suspicion, by contrast, arises from doubt and perceived risk, undermining trust and impeding effective connection and decision-making.
The Roots of Suspicion: Why We Doubt
Suspicion originates from innate survival instincts that compel individuals to question unfamiliar motives and potential threats, especially in unpredictable environments. Cognitive biases such as confirmation bias and past negative experiences amplify distrust by shaping perceptions toward anticipating deceit or harm. Neuroscientific studies reveal that the amygdala activates during suspicious thought processes, highlighting the emotional basis of doubt and vigilance in social interactions.
Psychological Impact of Trust and Suspicion
Trust fosters psychological well-being by promoting feelings of safety, openness, and emotional connection, which support mental resilience and stress reduction. Suspicion triggers heightened vigilance and anxiety, impairing cognitive function and increasing emotional distress through distrust and uncertainty. Understanding how your interactions influence trust or suspicion can help you cultivate healthier relationships and enhance emotional stability.
Trust vs Suspicion in Relationships
Trust in relationships fosters emotional security by creating a foundation of reliability and honesty, enabling deeper intimacy and effective communication. Suspicion, on the other hand, undermines connection, leading to doubt, defensiveness, and emotional distance. Establishing clear boundaries and open dialogue is essential for building trust and minimizing suspicion between partners.
Building Trust: Strategies and Challenges
Building trust requires consistent transparency, reliable communication, and demonstrated competence, which reduce suspicion and foster positive relationships. Challenges include overcoming past breaches, managing differing expectations, and addressing unconscious biases that fuel distrust. Implementing clear policies, encouraging open dialogue, and practicing empathy serve as effective strategies to transform suspicion into mutual trust.
Recognizing Harmful Suspicion Patterns
Recognizing harmful suspicion patterns involves identifying persistent doubts without evidence that damage relationships and trust. Your ability to differentiate between healthy skepticism and destructive suspicion protects emotional well-being and promotes clearer communication. Focusing on transparency and open dialogue disrupts cycles of mistrust and fosters stronger connections.
The Role of Communication in Trust Development
Effective communication plays a crucial role in developing trust by fostering transparency, clarity, and consistent messaging that helps to reduce suspicion. Clear, open exchanges of information allow Your concerns to be addressed promptly, which diminishes doubts and builds confidence in relationships. Establishing trust requires ongoing dialogue that ensures mutual understanding and reliability between parties.
Social and Cultural Influences on Trust
Social and cultural influences significantly shape your perception of trust, guiding how you interpret others' actions and intentions within various contexts. Collective norms and shared values embedded in cultures foster communal trust, while divergent cultural backgrounds may heighten suspicion due to differing communication styles and social expectations. Understanding these influences can help navigate complex social interactions by recognizing the underlying cultural factors that impact trust and suspicion dynamics.
Consequences of Chronic Suspicion
Chronic suspicion can severely damage your relationships by fostering distrust and emotional distance, leading to isolation and increased stress. Constantly doubting others' intentions may impair your ability to collaborate effectively, resulting in missed opportunities and weakened social support networks. Over time, this pervasive distrust can contribute to mental health issues such as anxiety and paranoia, diminishing overall well-being.
Balancing Trust and Caution: Best Practices
Balancing trust and caution requires evaluating the credibility of information sources while remaining vigilant to potential risks. You should establish clear boundaries and verify facts before fully relying on others, fostering relationships grounded in transparency and accountability. Implementing consistent communication and regularly reassessing your trust levels helps maintain a healthy equilibrium between confidence and skepticism.
Infographic: Trust vs Suspicion
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com