Balancing privacy and secrecy is crucial in relationships, as privacy fosters trust and respect, while secrecy often leads to mistrust and conflict. Discover how to navigate these boundaries effectively in this article.
Table of Comparison
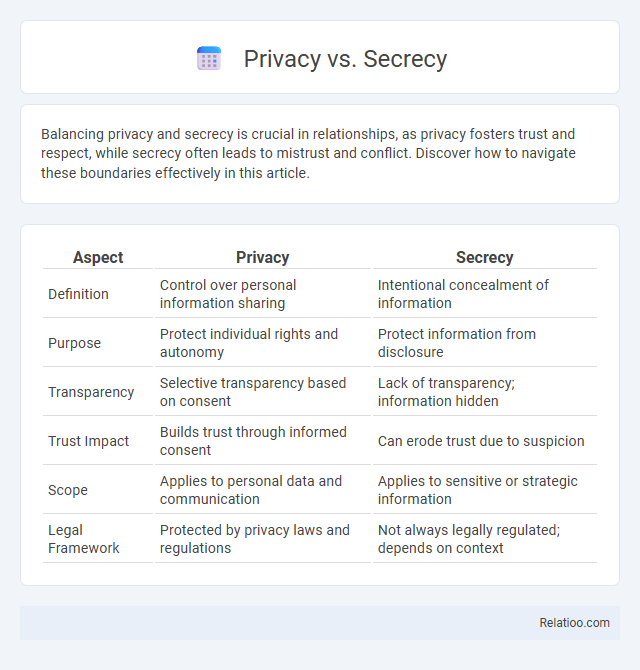
| Aspect | Privacy | Secrecy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Control over personal information sharing | Intentional concealment of information |
| Purpose | Protect individual rights and autonomy | Protect information from disclosure |
| Transparency | Selective transparency based on consent | Lack of transparency; information hidden |
| Trust Impact | Builds trust through informed consent | Can erode trust due to suspicion |
| Scope | Applies to personal data and communication | Applies to sensitive or strategic information |
| Legal Framework | Protected by privacy laws and regulations | Not always legally regulated; depends on context |
Understanding Privacy: Definition and Importance
Privacy involves controlling access to your personal information, ensuring that sensitive data is shared only with authorized individuals. It is essential for protecting your identity, maintaining autonomy, and fostering trust in digital and real-world interactions. Understanding privacy empowers you to safeguard your data against misuse and unauthorized surveillance.
What is Secrecy? Key Characteristics
Secrecy involves deliberately withholding information from others to protect sensitive data, maintain confidentiality, or secure competitive advantages. Key characteristics of secrecy include controlled access, intentional concealment, and the selective sharing of information only with trusted individuals or groups. Unlike privacy, which centers on individual control over personal information, secrecy emphasizes strategic restriction and protection of information from unauthorized disclosure.
Privacy vs Secrecy: Core Differences Explained
Privacy involves controlling access to your personal information, ensuring it is only shared with authorized individuals, while secrecy entails deliberately hiding information to prevent others from knowing it. Privacy respects your right to confidentiality and personal boundaries, whereas secrecy often implies concealment to avoid detection or judgment. Understanding this core difference helps you manage information disclosure with greater awareness and intentionality.
Historical Perspectives on Privacy and Secrecy
Historical perspectives on privacy and secrecy reveal distinct yet overlapping roles in society, with privacy emerging as a fundamental human right protecting individual autonomy, while secrecy traditionally supported power structures and strategic advantages. Secrecy, often linked to political and military contexts, allowed states and organizations to withhold information for security or competitive purposes, contrasting with privacy's emphasis on personal boundaries and protection from surveillance. Over centuries, evolving legal frameworks and cultural attitudes have increasingly distinguished privacy as a safeguard against unwarranted intrusion, whereas secrecy remains a tool wielded selectively in governance and diplomacy.
Personal Privacy in the Digital Age
Personal privacy in the digital age emphasizes controlling your own information rather than hiding it completely, distinguishing it from secrecy which involves deliberately concealing data. Digital privacy tools like encryption and secure authentication help protect your sensitive data from unauthorized access while allowing selective sharing. Understanding the balance between privacy and secrecy is crucial for safeguarding your digital identity and maintaining trust online.
The Role of Secrecy in Governments and Organizations
Secrecy in governments and organizations serves as a critical mechanism to protect sensitive information related to national security, strategic operations, and confidential business practices. Unlike privacy, which centers on individual data protection, secrecy involves deliberately withholding information to maintain power, control, or competitive advantage. Effective secrecy management balances transparency demands with the necessity to safeguard classified data critical for strategic decision-making and diplomatic relations.
Ethical Implications: When Privacy Becomes Secrecy
Privacy ensures your personal information is protected while maintaining transparency and accountability, whereas secrecy often involves concealing information to avoid scrutiny or ethical responsibility. Ethical implications arise when privacy shifts into secrecy, potentially fostering mistrust, abuse of power, or harm to others. Balancing privacy with openness is crucial to uphold ethical standards and protect individual rights without enabling unethical concealment.
Legal Frameworks: Rights to Privacy vs Secrets
Legal frameworks distinguish rights to privacy as protected personal information, ensuring individuals control data about themselves under laws like GDPR and HIPAA. Secrecy involves withholding information deliberately, often protected by trade secret laws or national security regulations that balance confidentiality with public interest. Privacy rights emphasize transparency and consent, whereas secrecy prioritizes safeguarding sensitive knowledge, resulting in distinct but overlapping legal protections.
Real-World Examples: Privacy Breaches and Secret Leaks
Privacy involves protecting personal data from unauthorized access, as seen in the Facebook-Cambridge Analytica scandal where user data was exploited without consent. Secrecy entails deliberately withholding information, exemplified by government black budgets that remain undisclosed for national security reasons. Secret leaks occur when confidential information, such as the Snowden revelations on NSA surveillance, is exposed to the public, highlighting conflicts between state secrecy and citizen privacy.
Striking a Balance: Navigating Privacy and Secrecy
Striking a balance between privacy and secrecy is essential for protecting personal and organizational information without fostering distrust or isolation. Privacy involves controlling access to your personal data to maintain autonomy, while secrecy often implies withholding information to protect sensitive or strategic interests. By understanding the distinctions and applying appropriate boundaries, you can ensure transparency where needed and confidentiality where necessary, fostering trust and security simultaneously.
Infographic: Privacy vs Secrecy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com