Sovereignty emphasizes a nation's complete control over its internal affairs without external interference, while intervention challenges this principle by justifying involvement for humanitarian or security reasons. Explore the complexities and debates surrounding Sovereignty vs Intervention in this article.
Table of Comparison
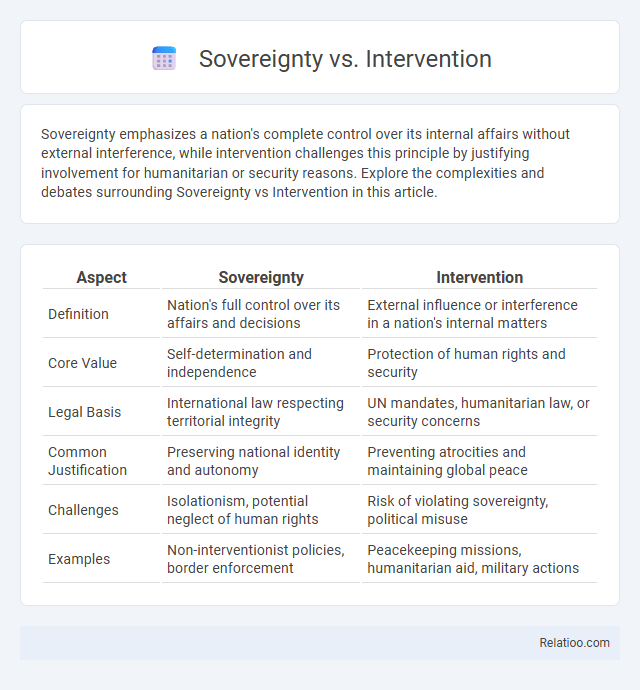
| Aspect | Sovereignty | Intervention |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Nation's full control over its affairs and decisions | External influence or interference in a nation's internal matters |
| Core Value | Self-determination and independence | Protection of human rights and security |
| Legal Basis | International law respecting territorial integrity | UN mandates, humanitarian law, or security concerns |
| Common Justification | Preserving national identity and autonomy | Preventing atrocities and maintaining global peace |
| Challenges | Isolationism, potential neglect of human rights | Risk of violating sovereignty, political misuse |
| Examples | Non-interventionist policies, border enforcement | Peacekeeping missions, humanitarian aid, military actions |
Understanding the Concept of Sovereignty
Sovereignty refers to the absolute authority of a state to govern itself without external interference, highlighting the fundamental principle of territorial integrity and political independence. Understanding sovereignty involves recognizing its role in international law, where states have the power to make decisions about their internal affairs while respecting the rights of other nations. Your grasp of sovereignty is crucial when examining the tension between non-intervention and humanitarian or strategic intervention in global politics.
Historical Perspectives on Sovereignty
Historical perspectives on sovereignty reveal its evolution from absolute state control to more nuanced interpretations balancing intervention and self-governance. The Westphalian system established sovereignty as the inviolable authority of states, yet colonial and modern interventions challenged this principle by prioritizing humanitarian or strategic interests. Understanding these shifts helps you grasp how sovereignty remains a contested concept shaped by legal, political, and ethical considerations over time.
Defining Intervention in International Relations
Intervention in international relations refers to the deliberate act by one state or group of states to influence the internal affairs of another sovereign state, often to address issues such as human rights violations, conflict, or threats to international peace. This concept challenges the traditional notion of absolute sovereignty, which holds that states have exclusive authority within their territorial boundaries without external interference. The debate centers on balancing respect for state sovereignty with the international community's responsibility to prevent harm and uphold global norms.
Legal Frameworks Governing Sovereignty
Legal frameworks governing sovereignty establish the principles that define a state's authority over its territory and the limits on external intervention. International law, including the United Nations Charter and customary international law, balances state sovereignty with the legal grounds for intervention, such as in cases of human rights violations or threats to peace. Your understanding of these frameworks is crucial for navigating disputes where sovereignty and intervention interests conflict, emphasizing the importance of respecting territorial integrity while recognizing humanitarian needs.
Justifications for Humanitarian Intervention
Humanitarian intervention is justified primarily on the grounds of preventing gross human rights violations such as genocide, ethnic cleansing, and crimes against humanity, overriding traditional notions of state sovereignty that prioritize non-interference. The Responsibility to Protect (R2P) doctrine further legitimizes intervention when a state fails to protect its population or actively perpetrates abuses, emphasizing the international community's duty to act. Balancing sovereignty and intervention requires adherence to international law, ensuring interventions are multilateral, proportionate, and aimed at restoring peace and safeguarding human dignity.
Case Studies: Notable Interventions in History
Notable interventions in history highlight the delicate balance between state sovereignty and international responsibility, as seen in NATO's 1999 intervention in Kosovo to stop ethnic cleansing and the UN's sanction-driven involvement in Iraq post-1990 invasion of Kuwait. The Rwandan Genocide of 1994 underscores the consequences of delayed or absent intervention under the guise of respecting state sovereignty. Understanding these case studies informs Your perspective on how sovereignty can be challenged or preserved in response to humanitarian crises and global security threats.
Sovereignty and the Role of the United Nations
Sovereignty remains a fundamental principle of international law, asserting a state's exclusive authority over its territory and domestic affairs. The United Nations plays a crucial role in balancing state sovereignty with the need for intervention, particularly through mechanisms like the Responsibility to Protect (R2P) doctrine aimed at preventing humanitarian crises. UN Security Council resolutions exemplify how sovereignty can be respectfully overridden to maintain international peace and security while upholding the legitimacy of state governance.
Ethical Dilemmas in Sovereignty vs. Intervention
Ethical dilemmas in sovereignty versus intervention center on balancing a nation's right to self-governance with the international community's responsibility to prevent human rights abuses. Your decisions must weigh respect for national sovereignty against the moral imperative to intervene in cases of genocide, war crimes, or severe humanitarian crises. Navigating these conflicts requires careful consideration of the legitimacy, timing, and consequences of intervention to uphold global justice without undermining state autonomy.
Balancing National Interests and Global Responsibility
Balancing national sovereignty and international intervention requires prioritizing state autonomy while acknowledging global responsibilities through multilateral frameworks and international law. Effective governance hinges on safeguarding territorial integrity alongside cooperative measures to address transnational challenges such as security threats, human rights, and environmental sustainability. This equilibrium supports national interests without undermining the collective goals of peace, stability, and shared prosperity.
Future Trends: Evolving Norms in Sovereignty and Intervention
Future trends in sovereignty and intervention emphasize the rising importance of digital sovereignty as states seek control over cyber domains amid growing cyber threats. Evolving norms increasingly recognize the legitimacy of humanitarian intervention while stressing respect for state sovereignty to prevent abuse and unilateral actions. Multilateral frameworks and international law are progressively shaping balanced approaches that uphold sovereignty but allow intervention under defined humanitarian conditions.
Infographic: Sovereignty vs Intervention
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com