Prudence guides thoughtful decision-making by assessing risks and benefits, while temperance emphasizes self-control and moderation in actions. Discover how balancing prudence and temperance can strengthen your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
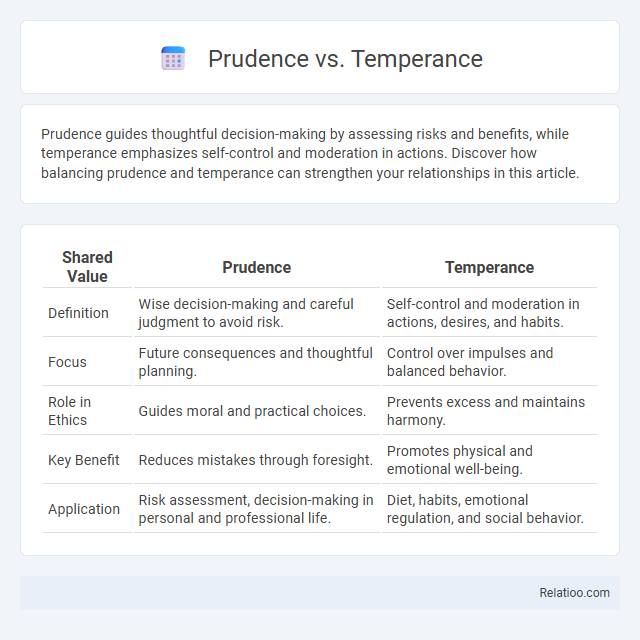
| Shared Value | Prudence | Temperance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Wise decision-making and careful judgment to avoid risk. | Self-control and moderation in actions, desires, and habits. |
| Focus | Future consequences and thoughtful planning. | Control over impulses and balanced behavior. |
| Role in Ethics | Guides moral and practical choices. | Prevents excess and maintains harmony. |
| Key Benefit | Reduces mistakes through foresight. | Promotes physical and emotional well-being. |
| Application | Risk assessment, decision-making in personal and professional life. | Diet, habits, emotional regulation, and social behavior. |
Understanding Prudence: Definition and Origins
Prudence is a cardinal virtue rooted in ancient philosophy, defined as the ability to govern and discipline oneself by the use of reason. Originating from the Latin term "prudentia," it emphasizes wise judgment, foresight, and careful decision-making to achieve moral and practical good. Unlike temperance, which focuses on self-restraint regarding desires, prudence encompasses broader strategic thinking and ethical discernment in actions.
Defining Temperance: Meaning and Historical Roots
Temperance, rooted in ancient Greek philosophy and Christian theology, refers to self-restraint and moderation in actions, desires, or consumption, aiming to maintain balance and avoid excess. Unlike prudence, which emphasizes wise decision-making and foresight, temperance centers on controlling impulses and maintaining discipline in your behavior. Historically, temperance was celebrated as one of the four cardinal virtues essential for moral character and social harmony.
Prudence in Everyday Decision-Making
Prudence guides Your everyday decision-making by promoting careful consideration of consequences before acting, helping to avoid impulsive choices. Temperance complements prudence by encouraging self-control, but prudence specifically emphasizes wise judgment and practical foresight. Together, these virtues enhance thoughtful planning and balanced actions in daily life.
The Role of Temperance in Self-Control
Temperance plays a crucial role in self-control by regulating desires and impulses, enabling you to maintain balance and moderation in behavior. Unlike prudence, which emphasizes wise decision-making and foresight, temperance specifically targets restraint in actions and consumption to foster discipline. This harmonious self-governance promotes long-term well-being and ethical conduct by curbing excess and encouraging thoughtful moderation.
Key Differences Between Prudence and Temperance
Prudence and temperance are distinct virtues with specific roles in ethical behavior; prudence involves wise decision-making and foresight to choose appropriate actions, while temperance centers on self-control and moderation in desires or pleasures. Prudence guides your judgment in complex situations, ensuring actions align with moral good, whereas temperance regulates impulses to maintain balance and avoid excess. Understanding these key differences helps you cultivate a balanced character by applying prudence in planning and temperance in restraint.
Similarities and Overlaps: Prudence vs Temperance
Prudence and temperance both serve as cardinal virtues that guide ethical behavior and self-regulation, with prudence emphasizing wise decision-making and foresight, while temperance focuses on moderation and self-control in desires and actions. These virtues overlap significantly in promoting balanced choices that prevent excess and recklessness, ensuring actions align with long-term well-being and moral integrity. Their intertwined roles reinforce disciplined judgment, where prudence assesses consequences and temperance restrains impulses, creating a harmonious approach to virtuous living.
Real-Life Examples of Prudence
Prudence involves making careful decisions based on foresight and practical reasoning, such as saving money for emergencies or researching career options before making a switch. Temperance centers on self-control and moderation, like maintaining a balanced diet or limiting screen time to improve overall health. Your ability to practice prudence in daily life ensures wise choices that protect your long-term well-being and financial stability.
Practical Applications of Temperance
Temperance, as a cardinal virtue, emphasizes self-control and moderation in your habits and desires, helping to maintain balance in daily decisions and actions. Practical applications of temperance include managing eating habits to promote health, regulating emotions to foster better relationships, and controlling impulses to enhance productivity. While prudence involves wise decision-making and foresight, and justice centers on fairness, temperance primarily guides you in practicing restraint and achieving personal well-being through measured choices.
The Importance of Balancing Prudence and Temperance
Balancing prudence and temperance is crucial for making wise decisions and maintaining self-control in daily life. Prudence guides your judgment by helping you evaluate risks and consequences, while temperance ensures moderation in actions and desires, preventing excess. By harmonizing both virtues, you achieve thoughtful restraint that supports long-term well-being and ethical behavior.
Cultivating Prudence and Temperance in Modern Life
Cultivating prudence in modern life involves making well-informed decisions by carefully evaluating risks and benefits, which enhances long-term personal and professional outcomes. Temperance, as a complementary virtue, emphasizes self-control and moderation in desires and behaviors, helping individuals maintain balance amidst consumerism and instant gratification. Together, prudence and temperance foster disciplined habits and mindful choices, promoting resilience and ethical living in a fast-paced, complex world.
Infographic: Prudence vs Temperance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com