National sovereignty ensures that states retain ultimate authority over their own territory and policymaking, while global governance promotes coordinated international cooperation to address transnational challenges. Explore the balance between these concepts and their impact on global politics in this article.
Table of Comparison
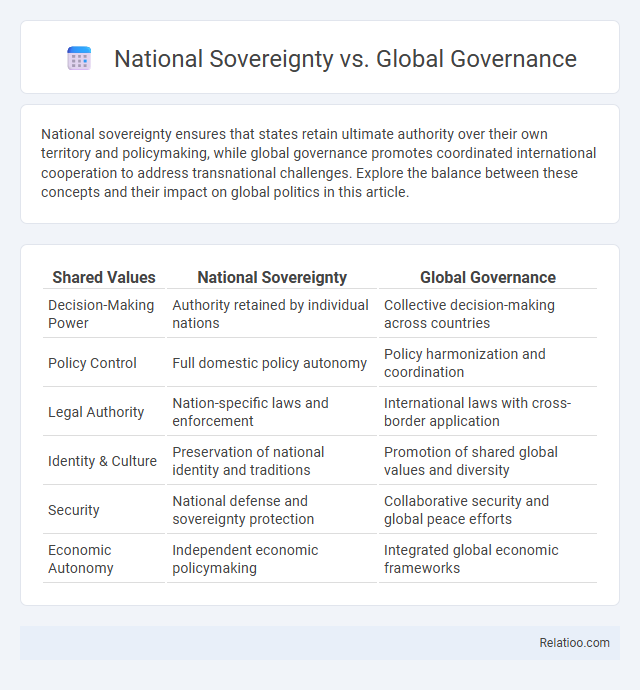
| Shared Values | National Sovereignty | Global Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making Power | Authority retained by individual nations | Collective decision-making across countries |
| Policy Control | Full domestic policy autonomy | Policy harmonization and coordination |
| Legal Authority | Nation-specific laws and enforcement | International laws with cross-border application |
| Identity & Culture | Preservation of national identity and traditions | Promotion of shared global values and diversity |
| Security | National defense and sovereignty protection | Collaborative security and global peace efforts |
| Economic Autonomy | Independent economic policymaking | Integrated global economic frameworks |
Defining National Sovereignty in the Modern Era
National sovereignty in the modern era emphasizes a nation's supreme authority to govern its territory and make decisions without external interference. Your understanding of sovereignty involves recognizing the balance between maintaining autonomous control over domestic affairs and engaging in global governance frameworks that address transnational issues. This dynamic interplay challenges traditional concepts of sovereignty while adapting to globalization's complexities.
The Rise and Role of Global Governance Institutions
The rise of global governance institutions such as the United Nations, World Trade Organization, and International Monetary Fund reflects increasing efforts to manage transnational challenges beyond the capacity of individual nation-states. These institutions facilitate cooperation on issues like climate change, international security, and economic regulation, often requiring states to cede aspects of national sovereignty to achieve collective goals. Balancing national sovereignty with the authority of supranational organizations remains a critical tension shaping contemporary international relations and global policymaking.
Historical Context: Sovereignty vs International Cooperation
National sovereignty has been a foundational principle since the Treaty of Westphalia in 1648, establishing states' exclusive authority within their borders. The evolution of global governance emerged post-World War II, emphasizing international cooperation to address transnational challenges such as security, trade, and human rights. Your understanding of the historical tension between preserving sovereign autonomy and engaging in multilateral institutions is key to navigating contemporary geopolitical dynamics.
Key Drivers of Tension between Nations and Global Bodies
National sovereignty centers on a country's autonomous control over its laws and policies, while global governance emphasizes international cooperation through bodies like the United Nations to address global challenges. Key drivers of tension include conflicting interests between preserving your nation's independence and adhering to international regulations on issues such as trade, security, and human rights. Divergent political agendas and economic disparities further complicate the balance between maintaining sovereignty and embracing global governance frameworks.
Sovereignty in the Age of Globalization
Sovereignty in the Age of Globalization faces unprecedented challenges as national borders become more porous to economic, technological, and political influences from global governance institutions. Your ability to maintain autonomous decision-making is often constrained by international agreements, trade pacts, and collective security frameworks that prioritize cooperative problem-solving over unilateral action. Balancing national sovereignty with the demands of global governance requires innovative frameworks that respect local authority while enabling effective participation in global networks.
Case Studies: National Sovereignty Challenged by Global Policies
National sovereignty faces significant challenges from global governance frameworks such as the Paris Agreement on climate change, where member states must comply with emission reduction targets that sometimes conflict with national economic priorities. The case of the European Union exemplifies tensions between national sovereignty and supranational regulations, as member countries cede some legislative authority to EU institutions to achieve regional integration. In trade disputes under the World Trade Organization, countries often confront limitations on their sovereign ability to impose tariffs or subsidies, highlighting the complex balance between maintaining sovereignty and adhering to global policy commitments.
Impacts of Supranational Organizations on Domestic Policy
Supranational organizations, such as the European Union and the United Nations, influence domestic policy by imposing regulations and standards that override national laws, thereby challenging traditional notions of national sovereignty. These bodies facilitate global governance by promoting policy coordination on issues like trade, climate change, and human rights, which can limit unilateral decision-making by individual states. The tension between maintaining national sovereignty and complying with supranational mandates shapes the evolving relationship between state authority and international cooperation.
Balancing National Interests with Global Responsibilities
Balancing national interests with global responsibilities requires integrating national sovereignty with global governance frameworks that promote cooperation on transnational issues like climate change, security, and trade. Effective global governance respects the autonomy of sovereign states while encouraging commitment to international agreements that address shared challenges. This balance ensures that national policies align with global goals without compromising a country's independent decision-making authority.
Future Trends: Evolving Dynamics of Sovereignty and Governance
National sovereignty and global governance are increasingly interconnected as emerging technologies, climate change, and transnational challenges reshape power structures and decision-making processes. Future trends indicate a shift toward hybrid models, where states maintain core sovereign functions while ceding selective authority to international institutions for coordinated global solutions. Digital sovereignty, cybersecurity, and supranational policymaking will dominate discussions, emphasizing adaptive governance frameworks that balance national interests with global cooperation.
Policy Solutions and Pathways to Harmonization
Policy solutions addressing the tension between national sovereignty and global governance emphasize multi-level cooperation respecting state autonomy while fostering collective action on transnational issues. Pathways to harmonization include establishing international legal frameworks with flexible implementation mechanisms, promoting regional integration initiatives, and enhancing diplomatic dialogues to reconcile domestic priorities with global commitments. Emphasizing subsidiarity and subsidiarity principles ensures decision-making occurs at the most effective level, balancing national interests with global responsibilities.
Infographic: National Sovereignty vs Global Governance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com