Prudence involves careful judgment and forethought in relationships, while practicality emphasizes realistic and efficient decision-making. Explore the balance between these qualities in relationships to enhance emotional intelligence and partnership success in this article.
Table of Comparison
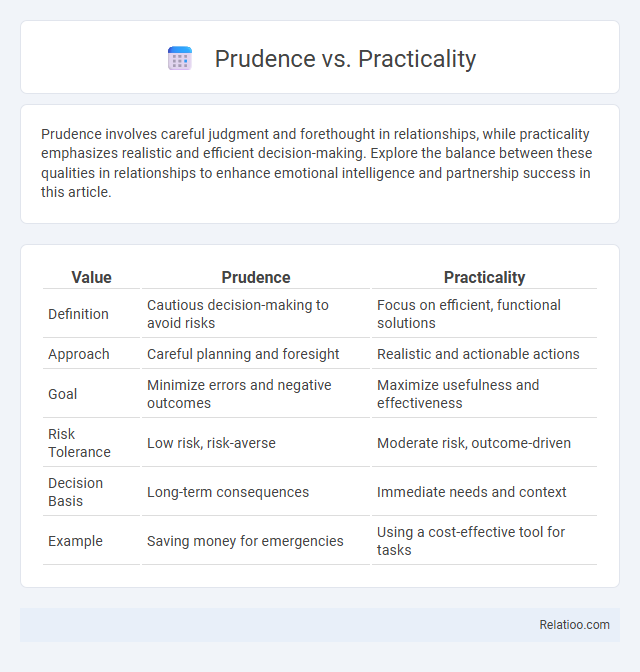
| Value | Prudence | Practicality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cautious decision-making to avoid risks | Focus on efficient, functional solutions |
| Approach | Careful planning and foresight | Realistic and actionable actions |
| Goal | Minimize errors and negative outcomes | Maximize usefulness and effectiveness |
| Risk Tolerance | Low risk, risk-averse | Moderate risk, outcome-driven |
| Decision Basis | Long-term consequences | Immediate needs and context |
| Example | Saving money for emergencies | Using a cost-effective tool for tasks |
Understanding Prudence: Definition and Core Principles
Prudence is the ability to govern and discipline oneself through the use of reason, emphasizing foresight, caution, and wise decision-making to avoid unnecessary risks. It involves evaluating potential consequences, prioritizing long-term benefits over short-term gains, and applying moral judgment to align actions with ethical standards. Core principles of prudence include temperance, discernment, and foresight, which collectively guide individuals to act responsibly and sustainably in both personal and professional contexts.
What is Practicality? A Comprehensive Overview
Practicality refers to the quality of being sensible, realistic, and focused on actual facts rather than theoretical ideas, emphasizing effective solutions and actions in everyday situations. It involves applying knowledge and experience to achieve achievable goals, optimizing resources, and managing risks with a pragmatic approach. Understanding practicality helps you make informed decisions that balance efficiency and functionality, ensuring outcomes that are both useful and sustainable.
Prudence vs Practicality: Key Differences
Prudence involves careful judgment and foresight, guiding your decisions with long-term wisdom and risk assessment, while practicality focuses on efficient, realistic solutions that work effectively in the present context. Understanding the key differences between prudence and practicality helps you balance thoughtful planning with immediate, actionable steps. Emphasizing prudence ensures sustainable outcomes, whereas practicality prioritizes functionality and ease of implementation.
Historical Perspectives on Prudence and Practicality
Historical perspectives on prudence emphasize its role as a cardinal virtue rooted in ancient philosophy, guiding rational judgment and moral discernment in decision-making. Practicality, evolving from utilitarian principles and Enlightenment thought, prioritizes efficiency and results-driven approaches in solving everyday problems. Your understanding of these concepts deepens when recognizing how historical contexts framed prudence as ethical wisdom, while practicality emerged as a pragmatic tool for achieving tangible outcomes.
Benefits of Embracing Prudence in Decision-Making
Embracing prudence in decision-making enhances your ability to weigh potential risks and rewards carefully, leading to more thoughtful and informed choices that reduce errors and costly mistakes. Prudence fosters long-term vision by encouraging caution and foresight, which helps in navigating uncertainty and avoiding impulsive actions. Prioritizing prudence improves strategic planning, resulting in better resource management and increased likelihood of achieving sustainable success.
The Role of Practicality in Everyday Life
Practicality plays a crucial role in everyday life by guiding decision-making through realistic and efficient solutions tailored to immediate needs and resources. Unlike prudence, which emphasizes caution and foresight to avoid risks, practicality focuses on actionable steps that yield tangible results in daily activities. Balancing practicality with prudence allows individuals to navigate challenges effectively while minimizing unnecessary risks.
Challenges of Balancing Prudence and Practicality
Balancing prudence and practicality presents challenges such as mitigating risks without compromising efficiency and making decisions that are cautious yet feasible in fast-paced environments. The tension between these principles often requires evaluating potential long-term consequences alongside immediate benefits, which can complicate strategic planning. Effective decision-making hinges on striking an equilibrium where prudent risk assessment aligns with practical implementation to optimize outcomes.
Prudence and Practicality in Professional Settings
Prudence in professional settings involves careful judgment and foresight to avoid risks and make ethical decisions that protect long-term interests, while practicality emphasizes efficient, realistic solutions that address immediate challenges effectively. Balancing prudence and practicality helps you navigate complex workplace scenarios by considering both strategic consequences and operational feasibility. Prioritizing these qualities leads to sound decision-making that ensures sustainable success and adaptability in dynamic environments.
Case Studies: When Prudence or Practicality Prevails
Case studies reveal that prudence prevails in financial risk management by prioritizing long-term stability over short-term gains, as seen in conservative investment strategies during market volatility. Practicality dominates in emergency response scenarios where swift, effective decision-making ensures immediate safety and resource optimization, exemplified by disaster relief operations. Balancing prudence and practicality is critical in corporate governance, where cautious regulatory compliance coexists with pragmatic business growth initiatives to enhance sustainable performance.
Choosing Between Prudence and Practicality: Best Practices
Choosing between prudence and practicality involves balancing cautious decision-making with efficient, outcome-focused actions. Best practices recommend assessing risks objectively, prioritizing long-term benefits over immediate gains while adapting strategies to real-world constraints. Emphasizing scenario analysis and stakeholder impact ensures that decisions reflect both prudent judgment and practical feasibility.
Infographic: Prudence vs Practicality
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com