Sexual orientation refers to an individual's enduring emotional, romantic, or sexual attraction to others, whereas sexual preference implies a choice or desire that may be flexible. Explore this article to understand the distinctions and implications for relationships.
Table of Comparison
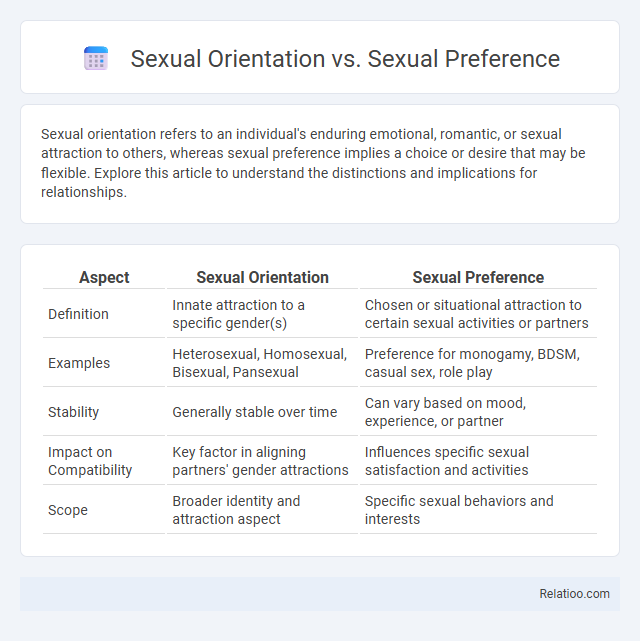
| Aspect | Sexual Orientation | Sexual Preference |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Innate attraction to a specific gender(s) | Chosen or situational attraction to certain sexual activities or partners |
| Examples | Heterosexual, Homosexual, Bisexual, Pansexual | Preference for monogamy, BDSM, casual sex, role play |
| Stability | Generally stable over time | Can vary based on mood, experience, or partner |
| Impact on Compatibility | Key factor in aligning partners' gender attractions | Influences specific sexual satisfaction and activities |
| Scope | Broader identity and attraction aspect | Specific sexual behaviors and interests |
Introduction to Sexual Orientation and Sexual Preference
Sexual orientation refers to an inherent pattern of emotional, romantic, or sexual attraction towards others, including identities such as heterosexual, homosexual, bisexual, and more. Sexual preference, often used interchangeably but inaccurately, implies a conscious choice or inclination, which differs from the innate nature of sexual orientation. Understanding these distinctions is essential for effective sex education, empowering you with accurate knowledge to respect diverse identities and enhance personal and societal well-being.
Defining Sexual Orientation
Sexual orientation refers to an individual's enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attraction to men, women, both, neither, or people of various genders. It is distinct from sexual preference, which implies a choice or voluntary aspect, whereas sexual orientation is an innate aspect of identity. Comprehensive sex education includes accurate definitions of sexual orientation to promote understanding and acceptance while dispelling myths.
Understanding Sexual Preference
Understanding sexual preference involves recognizing an individual's enduring pattern of romantic or sexual attraction toward certain genders or types of people, which differs from sexual orientation as a broader, innate identity. Your awareness of sexual preference helps in fostering respect for diverse expressions of attraction and promotes more inclusive sexual education that addresses personal experiences and needs. Comprehensive sex education that includes discussions on sexual preference equips individuals with knowledge to make informed decisions and enhances empathy towards others' identities.
Key Differences Between Sexual Orientation and Sexual Preference
Sexual orientation refers to an inherent, enduring pattern of romantic or sexual attraction to others, while sexual preference implies a choice or inclination that can change over time. Your sexual orientation is an intrinsic part of your identity, encompassing categories like heterosexual, homosexual, bisexual, or asexual. Sex education provides accurate information that helps distinguish these concepts, fostering understanding and acceptance of diverse sexual identities.
Biological and Psychological Perspectives
Sexual orientation refers to an inherent pattern of emotional, romantic, or sexual attraction toward others, shaped by a complex interplay of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors influencing brain development and psychological identity. Sexual preference implies a conscious choice in sexual behavior or partners, which contrasts with orientation as a core aspect of identity emerging from biological and psychological determinants beyond volition. Comprehensive sex education integrates these perspectives by addressing the scientific basis of orientation and preference, promoting understanding of human sexuality's diversity and supporting Your psychological well-being through informed knowledge.
Social and Cultural Influences
Sexual orientation, distinct from sexual preference, refers to an inherent pattern of emotional, romantic, or sexual attraction shaped by biological, psychological, and social factors, whereas sexual preference often implies a conscious choice influenced by personal desires or experiences. Social and cultural influences play a critical role in shaping attitudes towards sexual orientation and preference by dictating norms, stigmas, and acceptance levels within communities, which can affect individuals' self-identification and expression. Comprehensive sex education that incorporates diverse sexual orientations and challenges cultural stereotypes fosters greater understanding, reduces discrimination, and promotes healthier social environments.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Sexual orientation is an inherent aspect of a person's identity, describing enduring patterns of emotional, romantic, or sexual attraction, while sexual preference incorrectly implies voluntary choice, leading to misconceptions about changeability. Sex education often faces myths that it promotes promiscuity or inappropriate content, despite evidence showing comprehensive programs improve understanding and reduce risky behaviors. Dispelling confusion between orientation, preference, and factual sex education is essential to fostering acceptance, accurate knowledge, and informed discussions about human sexuality.
Importance of Using Inclusive Language
Inclusive language in sexual orientation, sexual preference, and sex education fosters respect and understanding by recognizing diverse identities and experiences. It reduces stigma and discrimination, creating safe, supportive environments for learning and personal growth. Emphasizing inclusive terminology ensures accurate representation and validation of all individuals' rights and feelings.
The Impact on Mental Health and Well-Being
Sexual orientation and sexual preference are distinct concepts where orientation refers to an inherent attraction pattern, while preference implies a conscious choice; misunderstandings between these terms can contribute to stigma and negatively affect mental health. Comprehensive sex education that accurately addresses sexual orientation and preference promotes acceptance, reduces anxiety, and improves overall well-being by fostering a supportive environment. Research consistently shows that inclusive education decreases rates of depression, suicide, and discrimination among LGBTQ+ individuals, highlighting its importance in mental health frameworks.
Conclusion: Respecting Individual Identities
Respecting individual identities requires recognizing that sexual orientation is an innate aspect of who a person is, while sexual preference may reflect personal choices within that orientation. Comprehensive sex education fosters understanding and acceptance by providing accurate information that debunks myths and promotes empathy. Your commitment to respecting these distinctions supports a more inclusive and affirming environment for everyone.
Infographic: Sexual Orientation vs Sexual Preference
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com