Spontaneous arousal occurs naturally without external stimuli, while responsive arousal is triggered by a partner's actions or environment. Explore the differences and impact on intimacy in this article.
Table of Comparison
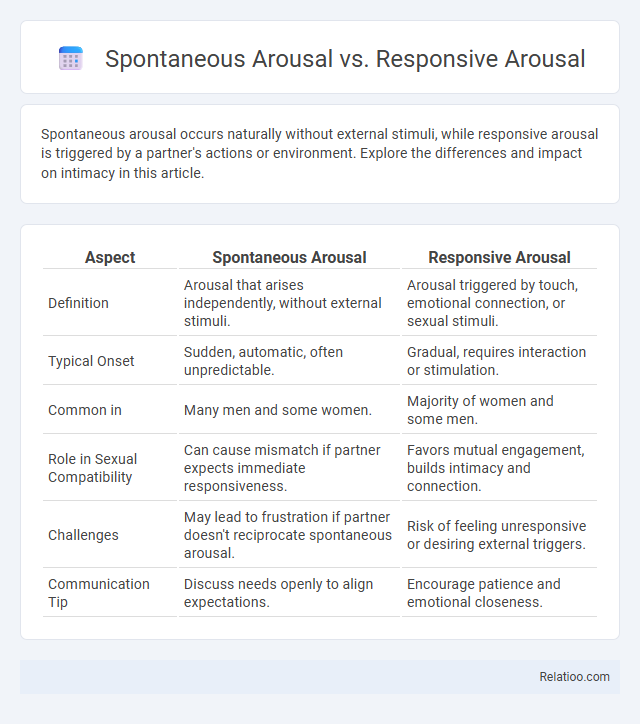
| Aspect | Spontaneous Arousal | Responsive Arousal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Arousal that arises independently, without external stimuli. | Arousal triggered by touch, emotional connection, or sexual stimuli. |
| Typical Onset | Sudden, automatic, often unpredictable. | Gradual, requires interaction or stimulation. |
| Common in | Many men and some women. | Majority of women and some men. |
| Role in Sexual Compatibility | Can cause mismatch if partner expects immediate responsiveness. | Favors mutual engagement, builds intimacy and connection. |
| Challenges | May lead to frustration if partner doesn't reciprocate spontaneous arousal. | Risk of feeling unresponsive or desiring external triggers. |
| Communication Tip | Discuss needs openly to align expectations. | Encourage patience and emotional closeness. |
Understanding Sexual Arousal: An Overview
Understanding sexual arousal involves differentiating spontaneous arousal, which occurs without direct external stimuli, from responsive arousal triggered by specific sexual cues or interactions. Spontaneous arousal often arises from internal factors such as hormonal fluctuations or thoughts, while responsive arousal depends on situational or sensory input. Recognizing these distinctions aids in comprehending various sexual experiences and addressing related challenges in sexual health.
Defining Spontaneous Arousal
Spontaneous arousal refers to the natural, involuntary increase in sexual excitement that occurs without any direct external stimuli or conscious focus, distinguishing it from responsive arousal, which depends on deliberate physical or psychological triggers. This type of arousal is commonly observed during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep or unexpected moments, highlighting its intrinsic physiological basis. Understanding spontaneous arousal is crucial for differentiating normal sexual function from conditions related to arousal disorders.
What Is Responsive Arousal?
Responsive arousal refers to sexual arousal triggered by external stimuli such as touch, visual cues, or emotional connection, rather than occurring spontaneously. It contrasts with spontaneous arousal, which happens without any apparent external cause. This type of arousal is often influenced by psychological and environmental factors, making it an important aspect of sexual response and intimacy.
Key Differences Between Spontaneous and Responsive Arousal
Spontaneous arousal occurs without external stimuli, driven by internal physiological or psychological factors, whereas responsive arousal is triggered directly by sensory input or environmental cues. Key differences include the origin of the arousal--internal versus external--and the predictability, with spontaneous arousal being less predictable compared to the typically situational responsive arousal. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for studies in sexual health and human behavior, as they affect responses and experiences in different contexts.
Biological Factors Influencing Arousal Types
Biological factors influencing spontaneous arousal involve intrinsic neural mechanisms, such as hormone fluctuations and neurotransmitter activity independent of external stimuli, often regulated by the limbic system and hypothalamus. Responsive arousal, triggered by sensory input or environmental cues, depends on the interaction between sensory pathways and brain regions like the amygdala and prefrontal cortex, modulating physiological responses. General arousal levels are governed by the autonomic nervous system and neurochemical modulators including dopamine, serotonin, and oxytocin, which collectively regulate alertness, emotional states, and sexual responsiveness.
Psychological Aspects of Sexual Arousal
Spontaneous arousal occurs without external stimuli and is often linked to intrinsic psychological factors such as mood, hormonal fluctuations, or subconscious thoughts, reflecting the brain's internal regulation of sexual desire. Responsive arousal is triggered by external stimuli and depends heavily on cognitive appraisal, context, and emotional state, highlighting the interplay between perception and psychological receptivity. Understanding arousal as a complex psychological process reveals how both automatic neural mechanisms and conscious cognitive evaluations shape sexual experience and desire.
Gender Differences in Arousal Patterns
Spontaneous arousal occurs without an explicit external stimulus, often differing by gender, with men typically experiencing more frequent spontaneous arousal due to physiological factors. Responsive arousal, triggered by specific stimuli, tends to be more prominent in women, reflecting the complex interaction of psychological and contextual influences. Understanding your unique arousal patterns, whether spontaneous or responsive, can enhance awareness of gender-specific tendencies and improve sexual health communication.
Common Misconceptions About Arousal Types
Spontaneous arousal occurs without external stimuli, while responsive arousal is triggered by specific sensory or emotional cues, and general arousal refers to overall physiological excitation. A common misconception is that spontaneous arousal implies a lack of desire, when in reality, it can indicate underlying biological or psychological factors independent of sexual interest. Understanding these differences can help you better recognize how your body responds to various stimuli and manage expectations around sexual arousal.
Navigating Arousal Differences in Relationships
Understanding the distinctions between spontaneous arousal, which occurs without external stimuli, and responsive arousal, triggered by specific cues or interactions, helps you navigate intimacy dynamics effectively in relationships. Recognizing that arousal varies individually allows partners to foster deeper communication and mutual satisfaction. Emphasizing empathy and open dialogue around these arousal differences supports emotional connection and enhances relationship harmony.
Enhancing Intimacy: Embracing Diverse Arousal Styles
Understanding Spontaneous Arousal, which occurs unexpectedly, versus Responsive Arousal, triggered by external stimuli, helps you recognize different pathways to intimacy. Embracing these diverse arousal styles fosters deeper connection and communication between partners. Enhancing intimacy involves honoring both patterns to create a more fulfilling and empathetic relationship experience.
Infographic: Spontaneous Arousal vs Responsive Arousal
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com