Abstinence involves complete avoidance of certain behaviors or desires, while delayed gratification emphasizes resisting immediate impulses to achieve long-term rewards. Explore the key differences and benefits of abstinence versus delayed gratification in this article.
Table of Comparison
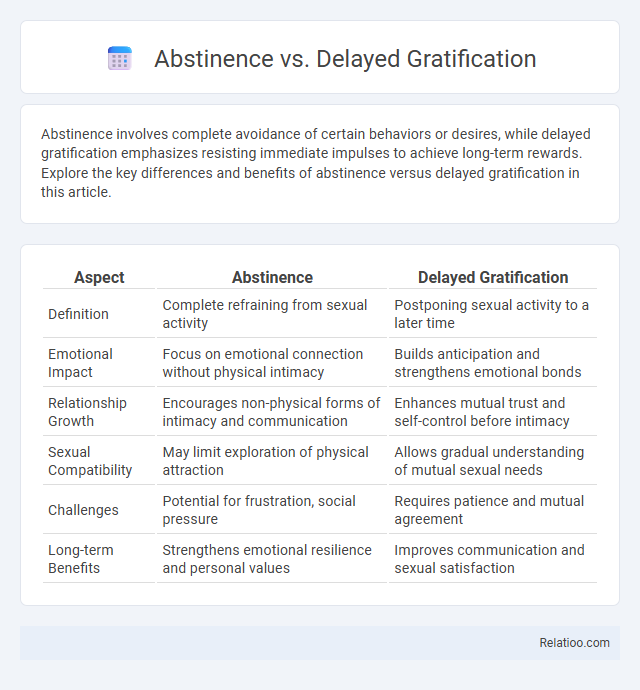
| Aspect | Abstinence | Delayed Gratification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete refraining from sexual activity | Postponing sexual activity to a later time |
| Emotional Impact | Focus on emotional connection without physical intimacy | Builds anticipation and strengthens emotional bonds |
| Relationship Growth | Encourages non-physical forms of intimacy and communication | Enhances mutual trust and self-control before intimacy |
| Sexual Compatibility | May limit exploration of physical attraction | Allows gradual understanding of mutual sexual needs |
| Challenges | Potential for frustration, social pressure | Requires patience and mutual agreement |
| Long-term Benefits | Strengthens emotional resilience and personal values | Improves communication and sexual satisfaction |
Defining Abstinence and Delayed Gratification
Abstinence refers to the deliberate decision to completely avoid engaging in certain behaviors or consumption, such as alcohol, drugs, or sexual activity, often for health, moral, or personal reasons. Delayed gratification involves the ability to resist immediate temptations or rewards in favor of long-term benefits, enhancing self-control and goal achievement. Your understanding of these concepts can improve decision-making by distinguishing complete avoidance from strategic patience to attain greater rewards.
Historical Perspectives on Self-Control
Historical perspectives on self-control reveal distinct approaches in abstinence, delayed gratification, and restraint. Abstinence traditionally emphasizes complete avoidance of specific behaviors or substances, often rooted in religious or cultural practices, while delayed gratification involves postponing immediate pleasures to achieve longer-term rewards, as illustrated by the famous marshmallow test in psychology. These concepts collectively highlight evolving understandings of self-discipline, motivation, and human behavior across different societies and time periods.
Psychological Foundations of Abstinence
Psychological foundations of abstinence emphasize self-control mechanisms rooted in cognitive-behavioral theories, highlighting the role of impulse regulation and long-term goal orientation. Unlike delayed gratification, which involves postponing immediate rewards for future benefits, abstinence requires complete avoidance of specific stimuli, reinforcing identity-based motivation and habit formation. Neuroscientific research links abstinence to enhanced prefrontal cortex activity, crucial for executive functions and inhibitory control.
The Science Behind Delayed Gratification
Delayed gratification involves the ability to resist immediate rewards in favor of larger, long-term benefits, supported by research linking stronger prefrontal cortex activity to improved self-control and decision-making. Abstinence, often used in contexts such as addiction or diet, requires completely refraining from specific behaviors or substances, whereas delayed gratification emphasizes regulating impulses without total avoidance. Understanding the neuroscience behind delayed gratification can help you develop better habits by strengthening your brain's executive functions to prioritize future rewards over instant satisfaction.
Benefits of Practicing Abstinence
Practicing abstinence offers significant benefits such as enhanced emotional well-being, reduced risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and prevention of unintended pregnancies. By choosing abstinence, individuals often experience greater self-control and improved decision-making skills, which contribute to healthier relationships. Studies indicate that abstinence can promote long-term physical and mental health by fostering personal responsibility and reinforcing positive life choices.
Advantages of Delayed Gratification
Delayed gratification offers significant advantages by enhancing self-control and improving long-term decision-making, allowing You to prioritize future rewards over immediate pleasure. This practice strengthens emotional resilience and promotes greater success in personal and financial goals by preventing impulsive actions driven by short-term temptations. Unlike strict abstinence, delayed gratification provides flexibility, making it a sustainable approach for managing desires while still achieving meaningful outcomes.
Common Challenges and Misconceptions
Common challenges in abstinence, delayed gratification, and temptation resistance include managing emotional stress, maintaining motivation, and overcoming social pressures that often lead to relapse or inconsistency. Misconceptions arise when you believe that abstinence is the only effective method, ignoring the value of delayed gratification as a sustainable strategy for long-term self-control and personal growth. Understanding the nuanced differences helps in choosing the right approach tailored to your goals and psychological resilience.
Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
Abstinence is commonly observed in addiction recovery programs where individuals completely avoid substances like alcohol or drugs to maintain sobriety, demonstrating strict behavioral control. Delayed gratification is exemplified by students who forego immediate leisure to study for exams, leading to improved academic performance and long-term career success. Case studies from behavioral psychology reveal that while abstinence enforces total avoidance, delayed gratification fosters self-control and resilience, both crucial for sustainable habit formation and goal achievement.
Practical Strategies for Success
Practical strategies for success in abstinence and delayed gratification involve setting clear goals, developing strong self-discipline, and using mindfulness techniques to manage impulses effectively. You can enhance your commitment by creating supportive environments, tracking progress consistently, and rewarding small achievements to build sustainable habits. Understanding the difference between immediate urge control in abstinence and long-term reward postponement in delayed gratification empowers you to choose the best approach for your personal growth.
Choosing the Right Approach for Personal Growth
Choosing the right approach between abstinence, delayed gratification, and moderation depends on your personal goals and circumstances. Abstinence offers complete avoidance of certain behaviors for clear boundaries, while delayed gratification builds self-control by postponing rewards, fostering long-term success. Understanding your motivations and lifestyle helps tailor the strategy that best supports your personal growth and overall well-being.
Infographic: Abstinence vs Delayed Gratification
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com