The refractory period is the recovery phase after orgasm during which it is physiologically difficult or impossible for an individual to achieve another climax, whereas multiple orgasms refer to the ability to experience successive orgasms without a significant refractory period. Explore this article to understand how these concepts impact sexual satisfaction and intimacy in relationships.
Table of Comparison
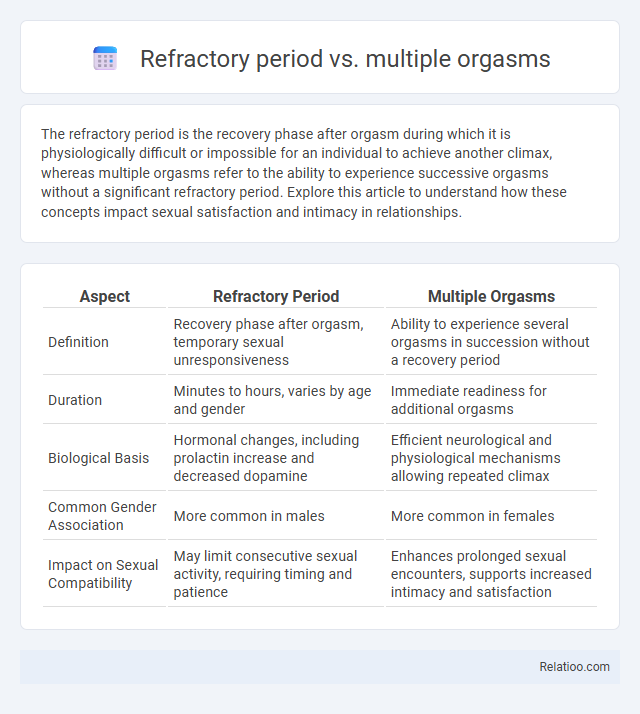
| Aspect | Refractory Period | Multiple Orgasms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recovery phase after orgasm, temporary sexual unresponsiveness | Ability to experience several orgasms in succession without a recovery period |
| Duration | Minutes to hours, varies by age and gender | Immediate readiness for additional orgasms |
| Biological Basis | Hormonal changes, including prolactin increase and decreased dopamine | Efficient neurological and physiological mechanisms allowing repeated climax |
| Common Gender Association | More common in males | More common in females |
| Impact on Sexual Compatibility | May limit consecutive sexual activity, requiring timing and patience | Enhances prolonged sexual encounters, supports increased intimacy and satisfaction |
Understanding the Refractory Period
The refractory period is the recovery phase following orgasm during which sexual arousal and erection are temporarily impossible, differing from the experience of multiple orgasms where some individuals can achieve successive climaxes without a significant rest interval. Understanding the refractory period helps you manage expectations about sexual performance and recovery time, as it varies based on age, health, and individual physiology. Recognizing the difference between refractory recovery and multiple orgasms can enhance sexual satisfaction and communication in intimate relationships.
What are Multiple Orgasms?
Multiple orgasms refer to the ability to experience several orgasms in succession with minimal or no refractory period, which is the recovery phase after orgasm when sexual arousal is temporarily reduced. Unlike the typical single orgasm followed by a refractory period, some individuals, particularly women, can achieve multiple orgasms through continued stimulation without losing sexual pleasure or function. Understanding your body's response to stimulation can help differentiate between experiencing a refractory period and achieving multiple orgasms.
Biological Mechanisms Behind Refractory Period
The refractory period is a biologically driven phase following orgasm during which the body, particularly in males, undergoes physiological changes such as decreased dopamine levels and increased prolactin secretion, resulting in temporary sexual unresponsiveness. In contrast, the ability to experience multiple orgasms, often observed in females, involves complex neurochemical interplay that bypasses or shortens this refractory phase by maintaining arousal and preventing typical hormonal shifts. Understanding these distinct biological mechanisms can help you better comprehend sexual function and enhance intimate experiences.
Factors Influencing the Refractory Period
The refractory period, the recovery phase after orgasm during which sexual arousal is temporarily impossible, varies significantly based on age, hormone levels, and overall health. Younger individuals often experience shorter refractory periods, enabling the possibility of multiple orgasms, while factors such as stress, fatigue, and medications can extend this recovery time. Understanding these factors helps explain individual differences in sexual response and the capacity for multiple orgasms versus a prolonged refractory phase.
How Multiple Orgasms Occur
Multiple orgasms occur when the body experiences successive climax responses without a prolonged refractory period, which is the recovery phase following ejaculation during which sexual arousal and orgasm are temporarily impossible. Unlike the typical refractory period seen in most men, some individuals have a shorter or nearly absent refractory period, allowing them to achieve multiple orgasms in a single sexual encounter. Your ability to experience multiple orgasms depends on factors like hormonal levels, pelvic muscle control, and neurological sensitivity.
Gender Differences in Refractory Periods
Gender differences in refractory periods are significant, with most men experiencing a refractory phase lasting minutes to hours before they can achieve another orgasm, while many women have shorter or even absent refractory periods, allowing for multiple orgasms in quick succession. You can enhance sexual satisfaction by understanding that female physiology often supports rapid recovery and repeated climax, contrasted with male biological constraints requiring recovery time. Research indicates hormonal and neurological variations contribute to these differences, influencing sexual response and recovery intervals across genders.
Techniques to Reduce Refractory Time
Techniques to reduce the refractory period include pelvic floor exercises, such as Kegels, which enhance blood flow and improve erectile function. Mental relaxation strategies and controlled breathing help manage arousal levels, potentially shortening recovery time between orgasms. Use of certain supplements like L-arginine and consistent cardiovascular exercise also contribute to faster physiological recovery, enabling multiple orgasms with minimal delay.
Health Benefits of Multiple Orgasms
Multiple orgasms provide significant health benefits, including enhanced cardiovascular health, improved mood through the release of endorphins, and reduced stress levels due to sustained hormonal balance. Unlike the refractory period experienced after a single orgasm, where physiological recovery limits sexual activity, multiple orgasms allow for repeated pleasurable experiences without the need for extended rest. This ability to maintain sexual activity fosters better circulation, strengthens pelvic floor muscles, and supports overall mental well-being.
Myths and Facts About Refractory Period and Orgasms
The refractory period is often misunderstood as a universal barrier preventing multiple orgasms, but this varies significantly across individuals and genders. While many men experience a refractory period during which orgasm is temporarily impossible, some women and a subset of men can achieve multiple orgasms with little to no refractory phase. Scientific studies clarify that myths around the refractory period stem from generalized assumptions, overlooking the complex hormonal, neurological, and physiological factors influencing orgasmic function and recovery time.
Enhancing Sexual Experience: Tips and Considerations
Understanding the refractory period and its impact on multiple orgasms is crucial for enhancing sexual experience, as the refractory period represents the recovery phase following orgasm during which achieving another erection or orgasm is physiologically challenging. Techniques such as pelvic floor exercises, mindfulness, and paced stimulation can help reduce refractory time, enabling multiple orgasms and prolonged pleasure. Considering factors like age, hormonal balance, and overall health also plays a significant role in optimizing sexual performance and satisfaction.
Infographic: Refractory period vs Multiple orgasms
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com