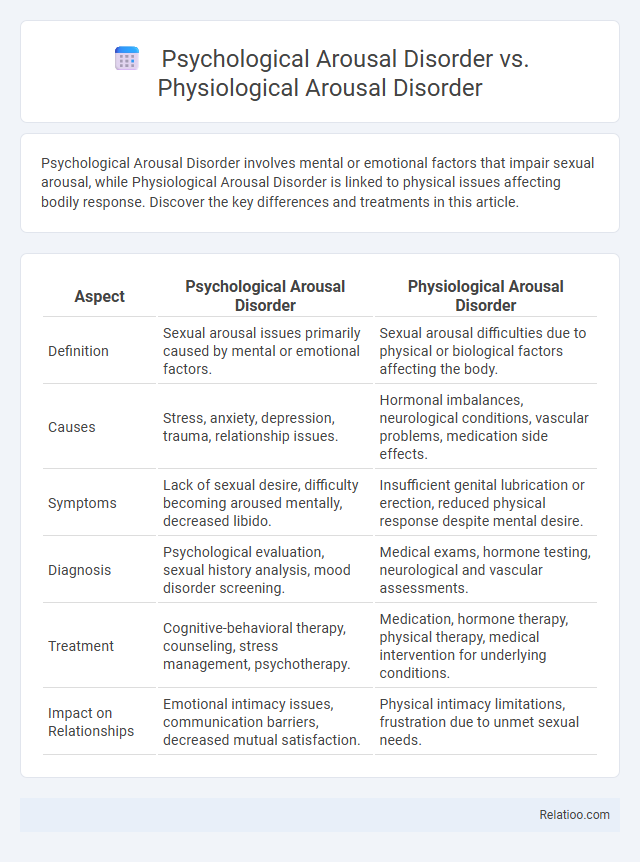
Psychological Arousal Disorder involves mental or emotional factors that impair sexual arousal, while Physiological Arousal Disorder is linked to physical issues affecting bodily response. Discover the key differences and treatments in this article.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Psychological Arousal Disorder | Physiological Arousal Disorder |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sexual arousal issues primarily caused by mental or emotional factors. | Sexual arousal difficulties due to physical or biological factors affecting the body. |
| Causes | Stress, anxiety, depression, trauma, relationship issues. | Hormonal imbalances, neurological conditions, vascular problems, medication side effects. |
| Symptoms | Lack of sexual desire, difficulty becoming aroused mentally, decreased libido. | Insufficient genital lubrication or erection, reduced physical response despite mental desire. |
| Diagnosis | Psychological evaluation, sexual history analysis, mood disorder screening. | Medical exams, hormone testing, neurological and vascular assessments. |
| Treatment | Cognitive-behavioral therapy, counseling, stress management, psychotherapy. | Medication, hormone therapy, physical therapy, medical intervention for underlying conditions. |
| Impact on Relationships | Emotional intimacy issues, communication barriers, decreased mutual satisfaction. | Physical intimacy limitations, frustration due to unmet sexual needs. |
Understanding Arousal Disorders: An Overview
Arousal disorders encompass psychological arousal disorder, physiological arousal disorder, and general arousal disorder, each affecting your body's response mechanisms differently. Psychological arousal disorder involves disruptions in emotional or mental stimuli processing, leading to anxiety or hypervigilance, while physiological arousal disorder pertains to irregularities in autonomic nervous system functions, impacting heart rate, respiration, and muscle tension. Understanding these distinctions helps in identifying appropriate therapeutic interventions tailored to your specific arousal dysfunction.
Defining Psychological Arousal Disorder
Psychological Arousal Disorder involves disruptions in mental or emotional excitement, often linked to anxiety, stress, or trauma impacting your cognitive and emotional responses. Physiological Arousal Disorder, in contrast, pertains to physical manifestations such as heart rate, blood pressure, or hormonal imbalances that affect bodily functions independently of psychological factors. Arousal disorder broadly refers to any dysfunction in the activation process, but Psychological Arousal Disorder specifically centers on the interplay between mind and emotion.
Characteristics of Physiological Arousal Disorder
Physiological Arousal Disorder is characterized by abnormal autonomic nervous system responses, leading to symptoms such as tachycardia, hyperventilation, and muscle tension without psychological triggers. Unlike Psychological Arousal Disorder, which stems from cognitive or emotional factors like anxiety or trauma, Physiological Arousal Disorder involves direct physical dysfunctions affecting heart rate, respiration, and hormonal release. Understanding these distinctions helps you identify symptoms rooted in bodily processes rather than psychological causes.
Key Differences Between Psychological and Physiological Arousal Disorders
Psychological arousal disorders primarily involve emotional or cognitive triggers leading to heightened arousal states, such as anxiety or panic disorders, whereas physiological arousal disorders stem from bodily dysfunctions affecting the autonomic nervous system, like hyperthyroidism or cardiovascular conditions. Key differences include the origin of symptoms--psychological arousal disorders originate in brain processes affecting mood and perception, while physiological counterparts are linked to measurable physical abnormalities or imbalances. Diagnosis relies on distinguishing mental health evaluations from clinical tests assessing physical health markers to tailor appropriate treatments.
Causes and Risk Factors
Psychological Arousal Disorder often stems from stress, anxiety, or trauma, affecting your mental state and emotional response. Physiological Arousal Disorder originates from medical conditions such as hormonal imbalances, neurological issues, or cardiovascular diseases that disrupt normal bodily functions. General Arousal Disorder involves a combination of psychological and physiological causes, with risk factors including chronic illness, mental health disorders, and lifestyle factors like poor sleep and substance use.
Symptoms and Diagnostic Criteria
Psychological Arousal Disorder is characterized by symptoms such as anxiety, panic attacks, and heightened emotional responses, often diagnosed through clinical interviews and standardized psychological assessments identifying cognitive and emotional triggers. Physiological Arousal Disorder presents with physical symptoms including increased heart rate, sweating, and muscle tension, diagnosed using autonomic function tests and exclusion of psychological causes. Arousal Disorder encompasses both psychological and physiological symptoms, requiring comprehensive evaluation through combined mental health assessments and medical examinations to differentiate the primary source of arousal dysregulation.
Impact on Mental and Physical Health
Psychological Arousal Disorder primarily impacts mental health by causing anxiety, stress, and emotional dysregulation, often leading to impaired cognitive function and mood disturbances. Physiological Arousal Disorder predominantly affects physical health through symptoms such as increased heart rate, muscle tension, and hormonal imbalances that can contribute to chronic fatigue and cardiovascular issues. Arousal disorder as a general category encompasses both mental and physical health impairments, with interconnected psychological and physiological symptoms that exacerbate overall well-being and quality of life.
Treatment Approaches and Therapies
Psychological Arousal Disorder often requires cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) targeting anxiety and emotional regulation, while Physiological Arousal Disorder benefits from medical treatments such as pharmacotherapy or hormone therapy to address underlying biological factors. Arousal disorders encompassing both psychological and physiological components may necessitate an integrative approach combining psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications for effective management. Tailoring treatment plans based on the specific arousal disorder subtype enhances therapeutic outcomes and symptom relief.
Coping Strategies and Lifestyle Modifications
Psychological arousal disorder requires coping strategies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindfulness meditation, and stress management techniques to regulate emotional triggers. Physiological arousal disorder benefits from lifestyle modifications like regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and adequate sleep to stabilize autonomic nervous system responses. Arousal disorder, encompassing both psychological and physiological aspects, often demands an integrated approach combining therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes to optimize overall functioning.
Seeking Professional Help and Support
Seeking professional help for Psychological Arousal Disorder involves therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and counseling to address emotional and mental triggers impacting arousal. For Physiological Arousal Disorder, medical evaluations and treatments such as hormone therapy or medication adjustments target underlying physical causes. Understanding your specific type of arousal disorder ensures tailored support, improving treatment effectiveness and overall well-being.
Infographic: Psychological Arousal Disorder vs Physiological Arousal Disorder
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com