IUDs and implants are highly effective, long-lasting contraceptive methods with success rates exceeding 99%, differing mainly in insertion technique and hormone release duration. Discover detailed comparisons of IUD vs implant effectiveness, side effects, and suitability in this article.
Table of Comparison
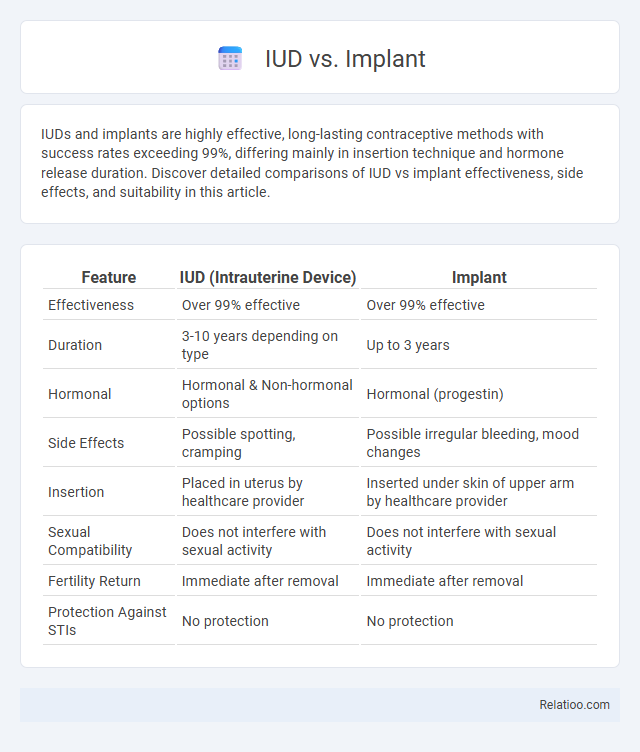
| Feature | IUD (Intrauterine Device) | Implant |
|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness | Over 99% effective | Over 99% effective |
| Duration | 3-10 years depending on type | Up to 3 years |
| Hormonal | Hormonal & Non-hormonal options | Hormonal (progestin) |
| Side Effects | Possible spotting, cramping | Possible irregular bleeding, mood changes |
| Insertion | Placed in uterus by healthcare provider | Inserted under skin of upper arm by healthcare provider |
| Sexual Compatibility | Does not interfere with sexual activity | Does not interfere with sexual activity |
| Fertility Return | Immediate after removal | Immediate after removal |
| Protection Against STIs | No protection | No protection |
Introduction to IUDs and Implants
IUDs and implants are highly effective, long-term birth control methods designed to provide reliable contraception without daily attention. IUDs, small T-shaped devices inserted into the uterus, prevent pregnancy by releasing hormones or using copper to create an inhospitable environment for sperm. Implants, slim rods placed under the skin of your arm, steadily release hormones to inhibit ovulation, offering convenience and extended protection lasting several years.
How IUDs Work
IUDs (intrauterine devices) are small T-shaped devices inserted into the uterus that prevent pregnancy by releasing copper or hormones to create an inhospitable environment for sperm and fertilized eggs. Unlike implants, which release hormones into the bloodstream via a small rod inserted under the skin, IUDs primarily function within the uterus to disrupt sperm motility and egg implantation. Birth control methods vary widely, but IUDs offer long-term, reversible contraception with efficacy rates above 99%, making them a highly effective choice compared to daily pills or other hormonal methods.
How Implants Work
Implants are small, flexible rods inserted under the skin of the upper arm that release a steady dose of progestin to prevent pregnancy by thickening cervical mucus and suppressing ovulation. Compared to intrauterine devices (IUDs), which primarily prevent fertilization by creating a hostile uterine environment, implants offer up to three years of continuous contraception with over 99% effectiveness. Birth control methods vary in hormone type and delivery, but implants provide a low-maintenance, reversible option without daily adherence requirements.
Effectiveness Comparison
IUDs, implants, and birth control pills each offer varying levels of effectiveness, with IUDs and implants being over 99% effective in preventing pregnancy due to their long-acting reversible nature. Birth control pills require daily compliance and have a typical use effectiveness rate of around 91%, making them less reliable if doses are missed. Your choice should consider how consistent you can be with the method to maximize pregnancy prevention.
Benefits of IUDs
IUDs offer long-lasting, highly effective birth control with failure rates below 1%, providing peace of mind for up to 10 years depending on the type. Their hormone-free options reduce side effects commonly associated with implants and oral contraception, making them suitable for those sensitive to hormones. You benefit from discreet, low-maintenance contraception that requires minimal user intervention, unlike daily pills or periodic implant replacements.
Benefits of Implants
Implants offer long-lasting, reversible contraception that can protect against pregnancy for up to 3-5 years with a single small device inserted under the skin. Your hormone levels remain steady, reducing the risk of side effects like mood swings or irregular bleeding often seen with other birth control methods. Compared to IUDs and pills, implants provide discreet, low-maintenance birth control without the need for daily attention or invasive procedures.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) may cause side effects including cramping, irregular bleeding, and a small risk of uterine perforation during insertion. Implants commonly lead to irregular menstrual bleeding, headaches, and potential weight gain, with rare cases of infection at the insertion site. Oral birth control pills carry risks such as blood clots, hypertension, and hormonal side effects like nausea or breast tenderness, especially in smokers and women over 35 years old.
Suitability: Who Should Consider Each?
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) suit individuals seeking long-term, reversible contraception with minimal maintenance, especially those comfortable with a medical insertion procedure and needing protection for 3 to 10 years. Implants offer a highly effective option for people preferring a discreet, hormone-based method lasting up to 3 years, ideal for those with contraindications to estrogen or who want fertility quickly restored after removal. Birth control pills fit individuals willing to manage daily dosing schedules and benefit from hormone regulation but require consistent adherence for optimal efficacy and suit those without risk factors for blood clots or hormone-sensitive conditions.
Cost and Accessibility
IUDs generally cost between $500 and $1,000 upfront, including insertion, but they last 5 to 10 years, making them cost-effective over time. Implants cost around $400 to $800 with insertion fees, providing contraception for up to 3 years, yet accessibility can be limited by provider availability and location. Birth control pills cost approximately $20 to $50 per month without insurance, offering easier accessibility but higher cumulative expense, especially where healthcare coverage is limited.
Making the Right Choice
Choosing between an IUD, implant, and other birth control methods depends on factors such as duration of effectiveness, side effects, and personal health conditions. IUDs offer long-term protection ranging from 3 to 12 years with minimal maintenance, while implants provide up to 3 years of hormonal contraception and are easily reversible. Evaluating lifestyle preferences, potential hormonal impacts, and consultation with a healthcare provider ensures selecting the most suitable contraceptive option.
Infographic: IUD vs Implant
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com