The Shot and Pill are two popular hormonal birth control methods with distinct usage schedules and hormone delivery systems-- the Shot is administered every three months via injection, while the Pill requires daily oral intake. Explore this article to understand their effectiveness, benefits, side effects, and determine which option suits your lifestyle best.
Table of Comparison
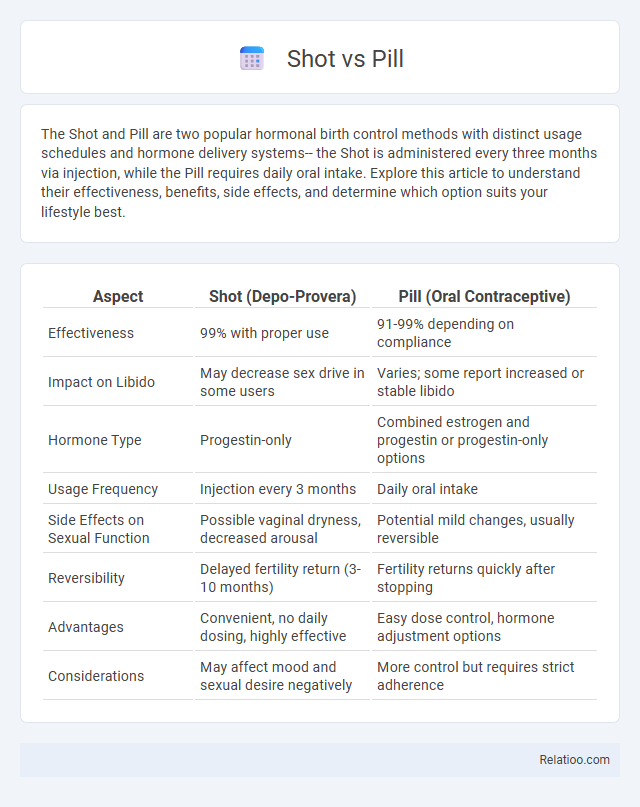
| Aspect | Shot (Depo-Provera) | Pill (Oral Contraceptive) |
|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness | 99% with proper use | 91-99% depending on compliance |
| Impact on Libido | May decrease sex drive in some users | Varies; some report increased or stable libido |
| Hormone Type | Progestin-only | Combined estrogen and progestin or progestin-only options |
| Usage Frequency | Injection every 3 months | Daily oral intake |
| Side Effects on Sexual Function | Possible vaginal dryness, decreased arousal | Potential mild changes, usually reversible |
| Reversibility | Delayed fertility return (3-10 months) | Fertility returns quickly after stopping |
| Advantages | Convenient, no daily dosing, highly effective | Easy dose control, hormone adjustment options |
| Considerations | May affect mood and sexual desire negatively | More control but requires strict adherence |
Introduction: Shot vs Pill – What’s the Difference?
The birth control shot and pill differ primarily in administration and hormonal dosage frequency, with the shot providing a three-month hormone release and the pill requiring daily intake. The shot often contains progestin only, while many pills combine estrogen and progestin, influencing side effects and effectiveness. Your choice between the shot and pill depends on lifestyle, medical history, and convenience preferences.
How Shots Work in the Body
Shots, such as the Depo-Provera injection, deliver a synthetic form of the hormone progestin directly into muscle tissue, providing contraception by thickening cervical mucus to prevent sperm from reaching the egg and suppressing ovulation. The injected hormone remains active for about 12 weeks, ensuring continuous hormone levels in the bloodstream to maintain effectiveness. This method effectively reduces the risk of pregnancy by altering the hormonal cycle without requiring daily administration, unlike birth control pills.
How Pills Are Absorbed and Used
Oral contraceptive pills are absorbed primarily through the gastrointestinal tract after ingestion, where active hormones such as estrogen and progestin enter the bloodstream. These hormones regulate the menstrual cycle by preventing ovulation, thickening cervical mucus, and thinning the uterine lining to reduce the likelihood of pregnancy. The effectiveness of birth control pills depends on consistent daily intake to maintain stable hormone levels for optimal contraceptive action.
Effectiveness: Shot vs Pill
The birth control shot, like Depo-Provera, offers effectiveness rates of about 94% with typical use, reducing the chance of pregnancy significantly through a quarterly injection. Oral contraceptive pills, taken daily, have a typical use effectiveness of around 91%, with missed doses increasing the risk of unintended pregnancy. Your choice between the shot and pill should consider adherence preferences and lifestyle to ensure optimal contraceptive protection.
Speed of Action: Which Works Faster?
The birth control pill begins to prevent pregnancy within 7 days if started during the first five days of the menstrual cycle, while the contraceptive shot (Depo-Provera) may take up to 48 hours to become effective after administration. Emergency contraception methods work faster, with pills like Plan B reducing pregnancy risk within 72 hours after unprotected sex, but the contraceptive shot is designed for ongoing prevention rather than immediate action. Speed of action depends on the method, with pills offering quicker protection onset compared to the injectable shot, which requires a brief waiting period.
Side Effects Comparison: Shot vs Pill
The birth control shot, typically administered every three months, may cause side effects like weight gain, irregular menstrual bleeding, and mood changes, whereas the pill often leads to nausea, breast tenderness, and spotting. Your hormonal birth control choice influences how your body responds, with the shot delivering a steady hormone dose and the pill requiring daily intake, impacting side effect patterns. Understanding these differences helps you select the method aligning best with your health needs and lifestyle.
Convenience and Ease of Use
The birth control shot offers convenience with just one injection every three months, eliminating daily routine concerns. Birth control pills require consistent daily intake at the same time for maximum effectiveness, which demands more discipline and attention. You can choose the method that best fits your lifestyle based on ease of use, with the shot being less frequent but requiring clinic visits, while pills provide more control but need daily commitment.
Cost Differences: Shot vs Pill
The cost difference between the birth control shot and pill can vary significantly depending on insurance coverage and local healthcare providers. The birth control shot typically incurs a higher upfront cost per dose, around $50 to $150 every three months, while birth control pills usually cost $20 to $50 per month but require monthly refills. You should consider long-term expenses and convenience to determine which option is more cost-effective for your specific needs.
Patient Preferences and Lifestyle Considerations
Patient preferences and lifestyle considerations play a critical role in choosing between the birth control shot, pill, and other methods. Women who prefer a low-maintenance option might favor the birth control shot, which requires an injection every three months, while those seeking daily control often choose the pill due to its ease of discontinuation and predictable scheduling. Lifestyle factors such as the ability to adhere to daily routines, concerns about side effects, and convenience during travel also influence the decision-making process in selecting the most suitable contraception method.
Choosing the Right Option: Shot or Pill?
Choosing the right birth control option depends on lifestyle, convenience, and health factors. The birth control shot, administered every three months, offers a low-maintenance, discreet solution without daily attention, ideal for those with busy schedules or difficulty remembering pills. In contrast, birth control pills require daily intake and provide more flexibility in controlling menstrual cycles and managing hormonal side effects.
Infographic: Shot vs Pill
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com