A sexologist holds a formal degree and specializes in researching human sexuality, while a sex counselor provides therapy to address sexual issues without requiring advanced scientific qualifications. Discover the key differences and benefits of consulting each expert in this article.
Table of Comparison
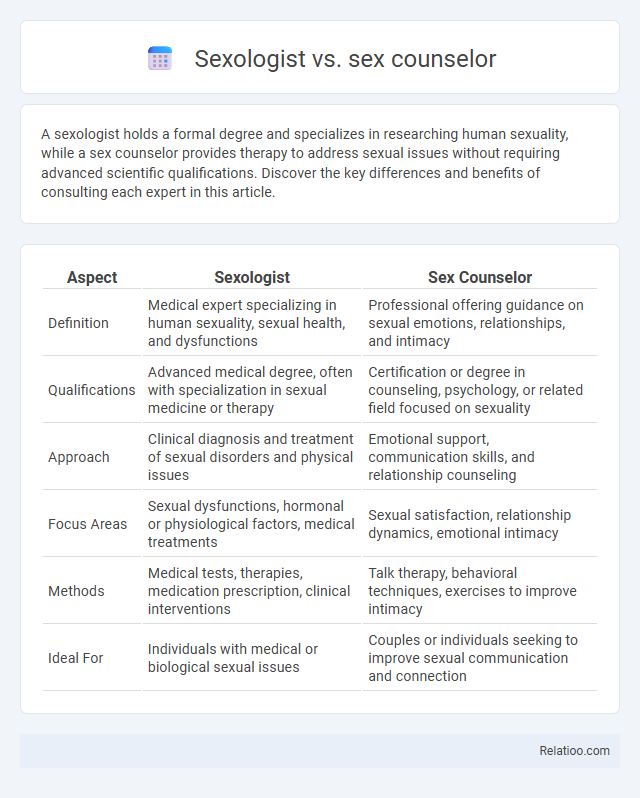
| Aspect | Sexologist | Sex Counselor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Medical expert specializing in human sexuality, sexual health, and dysfunctions | Professional offering guidance on sexual emotions, relationships, and intimacy |
| Qualifications | Advanced medical degree, often with specialization in sexual medicine or therapy | Certification or degree in counseling, psychology, or related field focused on sexuality |
| Approach | Clinical diagnosis and treatment of sexual disorders and physical issues | Emotional support, communication skills, and relationship counseling |
| Focus Areas | Sexual dysfunctions, hormonal or physiological factors, medical treatments | Sexual satisfaction, relationship dynamics, emotional intimacy |
| Methods | Medical tests, therapies, medication prescription, clinical interventions | Talk therapy, behavioral techniques, exercises to improve intimacy |
| Ideal For | Individuals with medical or biological sexual issues | Couples or individuals seeking to improve sexual communication and connection |
Understanding the Roles: Sexologist vs Sex Counselor
A sexologist is a trained expert specializing in the scientific study of human sexuality, often holding advanced degrees and conducting research, while a sex counselor provides practical guidance and support to clients facing sexual concerns or relationship issues through therapeutic techniques. Understanding the roles shows that sexologists focus more on education and research, whereas sex counselors emphasize personalized counseling and behavioral interventions. Your choice between a sexologist and a sex counselor depends on whether you seek in-depth scientific insight or targeted therapeutic support.
Educational Background and Credentials
Sexologists typically hold advanced degrees in human sexuality, psychology, or medical fields, often with extensive research experience and certification from recognized sexual health organizations. Sex counselors usually have graduate-level training in counseling or psychotherapy, supplemented by specialized certification in sexual health, allowing them to address emotional and relational aspects of sexuality. Understanding these educational backgrounds can help you choose the right professional based on your needs for clinical expertise or therapeutic support.
Scope of Practice: What Each Professional Offers
Sexologists conduct comprehensive research and provide expert guidance on human sexuality, often addressing biological, psychological, and social aspects of sexual behavior. Sex counselors focus on offering therapeutic support for relationship issues, sexual dysfunction, and emotional concerns related to intimacy through counseling sessions. Sex counselors primarily provide guidance and education on sexual health, promoting safe practices and communication but may have less clinical training than licensed therapists.
Common Issues Treated by Sexologists
Sexologists specialize in diagnosing and treating complex sexual health disorders such as erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, and sexual trauma, combining medical knowledge with psychological expertise. Sex counselors primarily address relationship issues, sexual communication, and intimacy concerns, helping couples improve their sexual connections. You may find that a sexologist is best suited for addressing significant physiological or psychological problems, while sex counselors focus on emotional and relational aspects of sexual well-being.
When to See a Sex Counselor
Seeing a sex counselor is recommended when experiencing difficulties with intimacy, sexual dysfunction, or relationship issues affecting sexual satisfaction. Sex counselors specialize in addressing emotional and psychological aspects of sexual health, offering therapeutic support for anxiety, trauma, or communication problems related to sex. For medical or physiological concerns, a sexologist may be more appropriate, while sex counselors focus on emotional and relational aspects.
Approaches and Therapeutic Techniques
Sexologists typically employ evidence-based medical and psychological approaches, integrating sexuality research and clinical assessment to address complex sexual health issues, often utilizing cognitive-behavioral therapy and psychophysiological interventions. Sex counselors focus on providing guidance through talk therapy, emphasizing communication skills, emotional support, and relationship dynamics, often incorporating humanistic and narrative therapy techniques. Sex counselors blend therapeutic listening with psychoeducation, aiming to improve clients' sexual well-being through relational and behavioral strategies tailored to individual or couple needs.
Consultation and Treatment Duration
Sexologists typically offer comprehensive consultations that delve into biological, psychological, and social aspects of sexual health, with treatment durations often extending over several months to address complex disorders. Sex counselors focus on shorter, solution-oriented sessions aimed at improving sexual communication and intimacy, usually lasting from a few weeks to a couple of months. Sex counselors, similar in scope, emphasize brief interventions and practical advice, often requiring fewer sessions compared to sexologists, with treatment duration tailored to specific client goals.
Privacy and Confidentiality Standards
Sexologists, sex counselors, and sex therapists adhere to strict privacy and confidentiality standards, ensuring client information remains protected under professional ethical codes like those from the American Association of Sexuality Educators, Counselors and Therapists (AASECT). Sexologists, with their scientific background in human sexuality, may have varied confidentiality obligations depending on their clinical or research role, while sex counselors and sex therapists typically follow counseling ethics emphasizing confidential sessions and informed consent. Maintaining privacy is crucial across these professions to foster trust and provide a safe environment for discussing sensitive sexual health and relationship issues.
Choosing the Right Professional for Your Needs
Choosing the right professional depends on your specific needs: a sexologist is a trained expert with extensive education in human sexuality, often holding advanced degrees and licenses, suitable for addressing complex sexual health issues and clinical concerns. A sex counselor provides guidance mainly through talk therapy and emotional support, ideal for individuals or couples dealing with relationship challenges or sexual dissatisfaction without medical or clinical interventions. Evaluating the scope of your issues and the credentials of each professional ensures you receive targeted, effective care tailored to your sexual well-being.
Myths and Misconceptions about Sexologists and Sex Counselors
Sexologists are often misunderstood as solely focusing on sexual performance, while sex counselors are mistakenly believed to only offer advice without addressing deeper psychological or relational issues. Your confusion between these professionals may stem from myths that sexologists are limited to medical diagnosis and treatment, whereas sex counselors provide comprehensive therapy for sexual health and emotional well-being. Understanding that sexologists study human sexuality scientifically and sex counselors offer therapeutic support debunks common misconceptions and clarifies their distinct but complementary roles.
Infographic: Sexologist vs sex counselor
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com