Frequency mismatch in relationships often leads to misunderstandings and emotional disconnect, while frequency match fosters stronger communication and deeper intimacy. Discover how aligning your emotional and communication frequencies can transform your connection in this article.
Table of Comparison
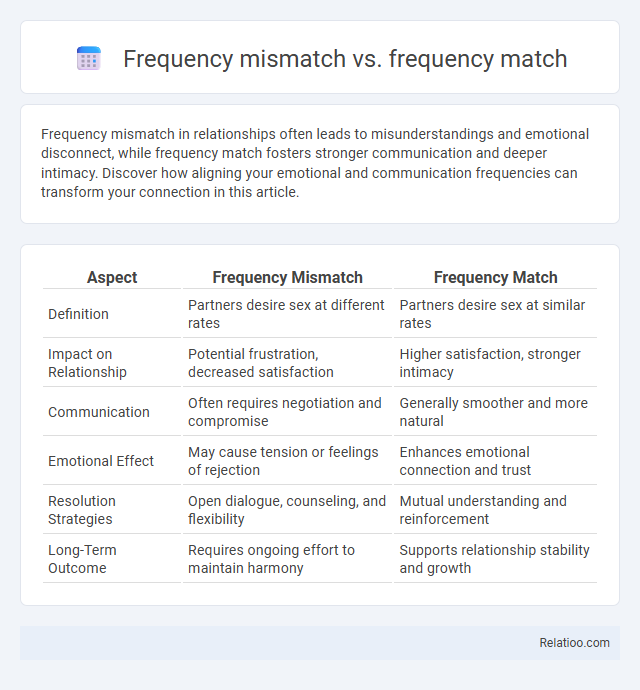
| Aspect | Frequency Mismatch | Frequency Match |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Partners desire sex at different rates | Partners desire sex at similar rates |
| Impact on Relationship | Potential frustration, decreased satisfaction | Higher satisfaction, stronger intimacy |
| Communication | Often requires negotiation and compromise | Generally smoother and more natural |
| Emotional Effect | May cause tension or feelings of rejection | Enhances emotional connection and trust |
| Resolution Strategies | Open dialogue, counseling, and flexibility | Mutual understanding and reinforcement |
| Long-Term Outcome | Requires ongoing effort to maintain harmony | Supports relationship stability and growth |
Understanding Frequency Match and Mismatch
Frequency match occurs when your communication style aligns with the other person's energy and tone, fostering clear understanding and rapport. Frequency mismatch happens when the styles diverge, leading to misunderstandings and frustration. Understanding these patterns enables you to adjust your approach, enhancing effective interaction through dual desire, where both parties seek connection despite differences.
The Science Behind Frequency Alignment
Frequency mismatch occurs when entities operate on divergent vibrational levels, leading to inefficiencies and discord within systems. Frequency match involves synchronizing these vibrational states to enhance coherence and optimize energy flow, thereby facilitating stronger connections and improved functionality. Dual desire reflects the simultaneous intention to both resonate at a specific frequency and adapt to varying frequencies, promoting dynamic alignment and resilience in complex environments.
Causes of Frequency Mismatch
Frequency mismatch occurs when your desired wavelength or signal frequency differs from the operational frequency of a system or medium, causing inefficiencies and signal loss. Causes of frequency mismatch include improper tuning, hardware limitations, and environmental factors that shift or distort the intended frequency, leading to diminished performance. Frequency match and dual desire concepts emphasize alignment of frequencies for optimal transmission and reception, minimizing the issues caused by mismatches.
Impact of Frequency Match on System Performance
Frequency match in electronic systems ensures that signal sources operate at the same frequency, significantly improving synchronization and reducing phase noise, which enhances overall system stability. Frequency mismatch causes signal distortion and inefficiencies, leading to degraded performance and increased error rates. Dual desire scenarios, where two competing frequency preferences exist, highlight the importance of achieving optimal frequency match to maximize throughput and minimize interference in communication systems.
Common Scenarios of Frequency Mismatch
Frequency mismatch often arises in relationships when one partner seeks connection or communication more frequently than the other, leading to feelings of frustration or neglect. In common scenarios, this disparity can cause misunderstandings, emotional distance, and unbalanced efforts to nurture the relationship. Your ability to identify whether you're experiencing a frequency mismatch, a frequency match, or dual desire helps address these dynamics and fosters healthier, more satisfying interactions.
Diagnosing Frequency Matching Issues
Diagnosing frequency matching issues involves understanding the distinctions between frequency mismatch, frequency match, and dual desire in telecommunication systems. Frequency mismatch occurs when the transmitted and received frequencies are not aligned, leading to signal degradation, whereas frequency match ensures synchronization and optimal signal integrity. Your ability to identify dual desire, where both ends attempt frequency control simultaneously, is crucial for resolving interference and maintaining efficient communication channels.
Solutions for Resolving Frequency Mismatch
Frequency mismatch in relationships occurs when partners have differing levels of emotional, physical, or communicative needs, often leading to frustration or disconnect. Frequency match signifies aligned desires and communication styles, fostering stronger intimacy and mutual satisfaction. Solutions for resolving frequency mismatch include open communication to understand each partner's needs, scheduling regular quality time to bridge gaps, and seeking therapy or counseling to develop effective compromise strategies.
Frequency Match in Communication Systems
Frequency match in communication systems ensures that the transmitter and receiver operate on the same carrier frequency, minimizing signal loss and enhancing data integrity. A frequency mismatch causes issues such as signal fading, interference, and increased bit error rates by disrupting synchronization. Your communication system's performance drastically improves with precise frequency match, enabling clearer signal reception and more efficient bandwidth utilization compared to dual desire approaches that attempt to balance multiple frequency requirements.
Frequency Alignment in Power Systems
Frequency alignment in power systems ensures system stability by matching generation and load frequencies to avoid disturbances. Frequency mismatch causes power imbalances leading to oscillations and potential blackouts, while frequency match maintains synchronous operation and optimal performance. The concept of dual desire integrates both consumer and generator frequency preferences, promoting coordinated frequency control for enhanced grid reliability and resilience.
Future Trends in Frequency Matching Technologies
Frequency mismatch challenges in wireless communication are being addressed by advanced adaptive algorithms that optimize signal alignment, enhancing data transmission efficiency. Frequency match technologies are evolving with machine learning integration to dynamically synchronize frequencies in real-time, reducing latency and interference in IoT and 5G networks. Dual desire approaches, combining frequency matching and mismatch correction, are expected to drive future trends by enabling seamless spectrum utilization and improving network robustness in increasingly complex radio environments.
Infographic: Frequency mismatch vs Frequency match
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com