Female Sexual Arousal Disorder (FSAD) involves a persistent inability to attain or maintain sexual excitement, often linked to psychological or physiological factors, while Male Sexual Arousal Disorder primarily includes erectile dysfunction caused by vascular, neurological, or hormonal issues. Understanding the distinct causes, symptoms, and treatments of FSAD versus Male Sexual Arousal Disorder can improve relationship satisfaction and sexual health; discover detailed insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
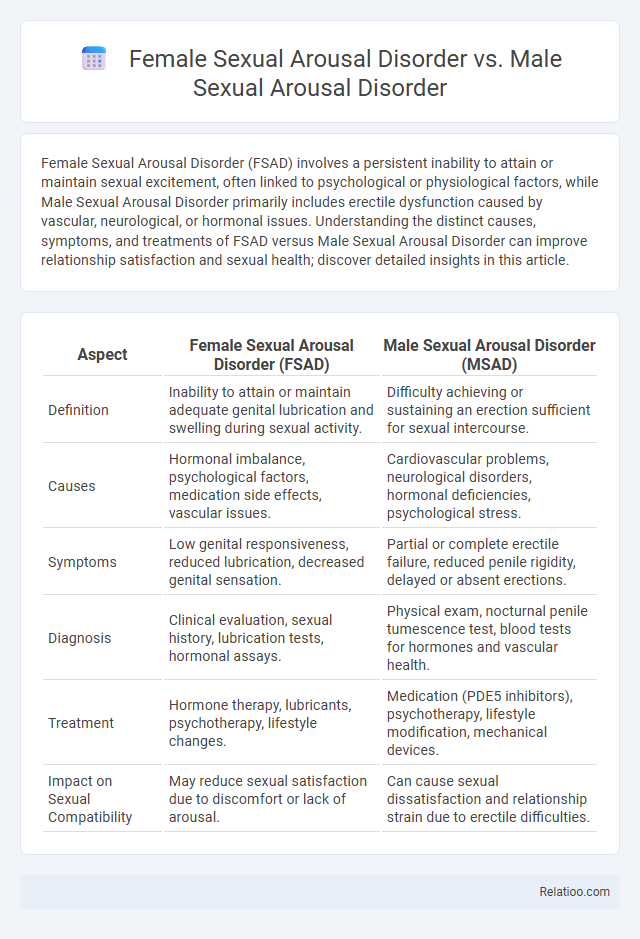
| Aspect | Female Sexual Arousal Disorder (FSAD) | Male Sexual Arousal Disorder (MSAD) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inability to attain or maintain adequate genital lubrication and swelling during sexual activity. | Difficulty achieving or sustaining an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. |
| Causes | Hormonal imbalance, psychological factors, medication side effects, vascular issues. | Cardiovascular problems, neurological disorders, hormonal deficiencies, psychological stress. |
| Symptoms | Low genital responsiveness, reduced lubrication, decreased genital sensation. | Partial or complete erectile failure, reduced penile rigidity, delayed or absent erections. |
| Diagnosis | Clinical evaluation, sexual history, lubrication tests, hormonal assays. | Physical exam, nocturnal penile tumescence test, blood tests for hormones and vascular health. |
| Treatment | Hormone therapy, lubricants, psychotherapy, lifestyle changes. | Medication (PDE5 inhibitors), psychotherapy, lifestyle modification, mechanical devices. |
| Impact on Sexual Compatibility | May reduce sexual satisfaction due to discomfort or lack of arousal. | Can cause sexual dissatisfaction and relationship strain due to erectile difficulties. |
Understanding Sexual Arousal Disorders
Sexual arousal disorders involve the persistent inability to attain or maintain adequate sexual excitement, affecting both females and males but manifesting differently due to physiological and psychological factors. Female Sexual Arousal Disorder (FSAD) typically presents as a lack of genital lubrication or swelling despite sexual stimulation, while Male Sexual Arousal Disorder often relates to erectile dysfunction and difficulties in achieving or sustaining an erection. Understanding sexual arousal disorders requires analyzing symptoms, hormonal influences, vascular health, and psychological components to tailor effective treatment strategies for each gender-specific condition.
Defining Female Sexual Arousal Disorder (FSAD)
Female Sexual Arousal Disorder (FSAD) is characterized by an inability to attain or maintain sufficient sexual excitement, often linked to decreased vaginal lubrication and genital sensation, affecting a woman's sexual response cycle. In contrast, Male Sexual Arousal Disorder primarily involves erectile dysfunction or difficulties in achieving penile rigidity. Understanding the distinct physiological and psychological factors underpinning these arousal disorders empowers you to seek targeted treatments and improve sexual health outcomes.
Defining Male Sexual Arousal Disorder (MSAD)
Male Sexual Arousal Disorder (MSAD) is defined as the persistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance, affecting physiological, psychological, and neurovascular functions. Distinct from Female Sexual Arousal Disorder, which primarily involves difficulties in genital lubrication and swelling, MSAD focuses on erectile dysfunction related to vascular insufficiency, hormonal imbalances, or neural impairment. Arousal disorders encompass broader dysfunctions in sexual response cycles, but MSAD specifically targets erectile capacity and penile hemodynamics in males.
Key Symptoms in Women vs. Men
Female Sexual Arousal Disorder typically presents with a persistent inability to attain or maintain adequate vaginal lubrication and swelling during sexual activity, while Male Sexual Arousal Disorder is characterized by difficulty achieving or sustaining an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. Both disorders involve a notable reduction in sexual excitement and physiological responses, but symptoms in women often include a lack of genital sensations and overall sexual pleasure, whereas men primarily experience erectile dysfunction. Understanding Your specific symptoms can guide targeted treatment approaches for these arousal disorders.
Biological Causes: Female vs. Male
Female Sexual Arousal Disorder often stems from hormonal imbalances, such as low estrogen or testosterone levels, and vascular issues affecting genital blood flow. In contrast, Male Sexual Arousal Disorder is frequently linked to erectile dysfunction caused by circulatory problems, nerve damage, or low testosterone. Understanding these biological causes can help tailor effective treatments for Your specific arousal disorder type.
Psychological Factors Influencing Arousal
Psychological factors such as anxiety, depression, and stress play a significant role in Female Sexual Arousal Disorder (FSAD), often leading to decreased vaginal lubrication and reduced genital sensation. In Male Sexual Arousal Disorder (MSAD), psychological influences like performance anxiety and relationship conflicts can impair erectile function, impeding the ability to achieve or maintain an erection. Arousal disorder broadly encompasses these psychological factors, highlighting the interplay between mental health conditions and neurobiological responses critical for sexual arousal in both sexes.
Diagnostic Criteria and Assessment
Female Sexual Arousal Disorder (FSAD) is characterized by an inability to attain or maintain adequate sexual excitement, primarily involving insufficient genital lubrication and swelling, whereas Male Sexual Arousal Disorder (MSAD) pertains to the persistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection adequate for sexual performance. Diagnostic criteria for FSAD in the DSM-5 emphasize symptoms lasting at least six months with significant distress, assessed through clinical interviews, self-reports, and sometimes physiological measures like vaginal photoplethysmography. In contrast, MSAD diagnosis relies on patient history, physical examination, and assessments such as nocturnal penile tumescence testing to distinguish between psychological and organic causes, while the broader term Arousal Disorder encompasses these gender-specific diagnoses under the umbrella of sexual function impairments.
Treatment Options for FSAD
Female Sexual Arousal Disorder (FSAD) treatment options include hormonal therapy such as estrogen or testosterone, topical lubricants, and counseling to address psychological factors. In contrast, Male Sexual Arousal Disorder often involves phosphodiesterase inhibitors like sildenafil or tadalafil, penile injections, and lifestyle changes. Arousal disorders in general require tailored approaches based on gender-specific physiological and psychological factors to optimize therapeutic outcomes.
Treatment Approaches for MSAD
Treatment approaches for Male Sexual Arousal Disorder (MSAD) often involve a combination of pharmacotherapy, psychological counseling, and lifestyle modifications focused on improving blood flow and addressing underlying medical conditions. In contrast, Female Sexual Arousal Disorder (FSAD) treatments may emphasize hormonal therapies, lubrication aids, and cognitive-behavioral therapy to enhance sexual responsiveness. General arousal disorders require individualized evaluation, but MSAD particularly benefits from phosphodiesterase inhibitors like sildenafil, vacuum erection devices, and targeted psychotherapy to restore sexual function effectively.
Overcoming Stigma: Gender Differences in Seeking Help
Female Sexual Arousal Disorder (FSAD) and Male Sexual Arousal Disorder (MSAD) present unique challenges influenced by societal norms and gender roles that affect willingness to seek help. Research indicates women with FSAD often face greater stigma due to cultural expectations surrounding female sexuality, leading to underreporting and delayed treatment. Men with MSAD may experience stigma related to perceived loss of masculinity, but are more likely to seek medical advice, highlighting the importance of tailored interventions to overcome gender-specific barriers.
Infographic: Female Sexual Arousal Disorder vs Male Sexual Arousal Disorder
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com