Pharmacists specialize in medication management and patient counseling, while physicians diagnose conditions and prescribe treatments. Explore this article to understand how collaboration between pharmacists and physicians improves patient care outcomes.
Table of Comparison
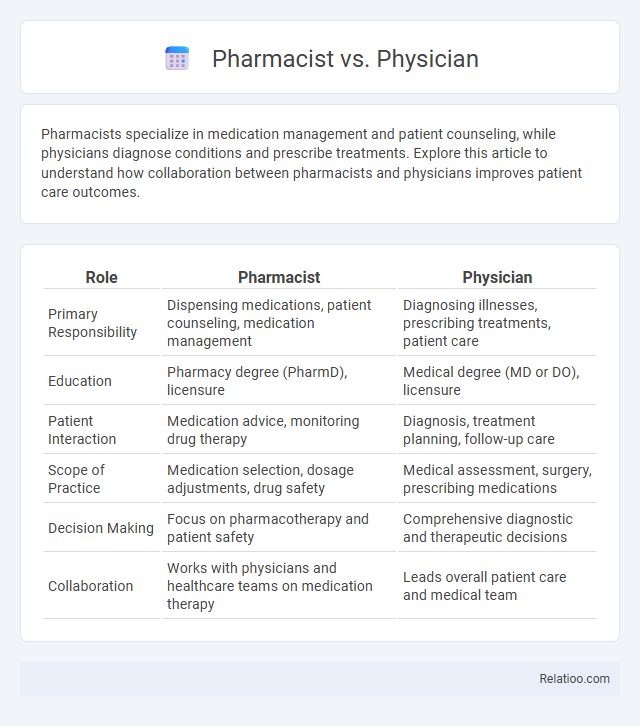
| Role | Pharmacist | Physician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Dispensing medications, patient counseling, medication management | Diagnosing illnesses, prescribing treatments, patient care |
| Education | Pharmacy degree (PharmD), licensure | Medical degree (MD or DO), licensure |
| Patient Interaction | Medication advice, monitoring drug therapy | Diagnosis, treatment planning, follow-up care |
| Scope of Practice | Medication selection, dosage adjustments, drug safety | Medical assessment, surgery, prescribing medications |
| Decision Making | Focus on pharmacotherapy and patient safety | Comprehensive diagnostic and therapeutic decisions |
| Collaboration | Works with physicians and healthcare teams on medication therapy | Leads overall patient care and medical team |
Introduction: Pharmacist vs Physician
Pharmacists specialize in medication management, ensuring the safe and effective use of drugs, while physicians diagnose illnesses and develop treatment plans. Your healthcare relies on the collaboration between pharmacists and physicians to optimize therapy outcomes and reduce medication errors. Understanding the distinct yet complementary roles of pharmacists and physicians enhances patient care quality and safety.
Roles and Responsibilities
Pharmacists are responsible for dispensing medications, ensuring drug safety, and counseling patients on proper medication use, while physicians diagnose illnesses, develop treatment plans, and prescribe appropriate therapies. Patients play an active role by communicating symptoms accurately, following treatment regimens, and providing feedback on medication efficacy and side effects. Collaboration among pharmacists, physicians, and patients enhances healthcare outcomes through coordinated medication management and informed decision-making.
Education and Training Pathways
Pharmacists complete a Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) program, typically requiring four years of professional study after undergraduate prerequisites, followed by licensure exams. Physicians undergo extensive training including a four-year medical degree (MD or DO), passing the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE), and several years of residency depending on specialty. Patients engage primarily in health education through interactions with healthcare providers but do not follow formal medical or pharmaceutical training pathways.
Areas of Expertise
Pharmacists specialize in medication management, drug interactions, and patient counseling to ensure safe and effective pharmaceutical care. Physicians focus on diagnosing illnesses, developing treatment plans, and providing comprehensive medical care across various specialties. Patients contribute personal health experiences and adherence information, playing a vital role in successful treatment outcomes.
Scope of Practice
Pharmacists specialize in medication management, including dispensing prescriptions, counseling on drug interactions, and monitoring therapeutic outcomes within regulatory guidelines. Physicians diagnose medical conditions, develop comprehensive treatment plans, and perform procedures, holding a broader authority in patient care decisions. Patients engage actively by providing health history, adhering to prescribed treatments, and communicating symptoms, playing a crucial role in achieving optimal health outcomes.
Patient Interaction and Care
Pharmacists ensure optimal medication therapy by counseling patients on drug usage, side effects, and adherence, enhancing safety and treatment outcomes. Physicians diagnose illnesses and develop comprehensive care plans while maintaining patient trust through effective communication and empathy. Patients actively participate in their health management by sharing symptoms, asking questions, and following professional advice, creating a collaborative healthcare environment.
Work Environments
Pharmacists typically work in retail pharmacies, hospitals, or clinical settings where they manage medication dispensing, provide patient counseling, and collaborate with healthcare teams. Physicians operate primarily in hospitals, private practices, clinics, or specialized medical centers, focusing on diagnosing, treating, and managing patient health conditions. Patients interact with a variety of healthcare environments, including outpatient clinics, emergency rooms, and pharmacies, where they receive medical care, prescriptions, and health advice tailored to their needs.
Collaboration in Healthcare Teams
Effective collaboration between pharmacists, physicians, and patients enhances healthcare outcomes by combining the clinical expertise of physicians with the medication management skills of pharmacists and the lived experiences of patients. Your active participation ensures clear communication, adherence to treatment plans, and timely adjustments to therapies, fostering a patient-centered approach. This interdisciplinary teamwork reduces medication errors, optimizes therapeutic efficacy, and improves overall patient safety.
Career Opportunities and Advancement
Pharmacists have diverse career opportunities in clinical pharmacy, research, and pharmaceutical industry roles, with advancement through specialization and management positions. Physicians offer extensive career paths in various medical specialties, surgery, and healthcare administration, often progressing to senior consultant or hospital leadership roles. Patients engage with both professions primarily as healthcare recipients but can influence career trends through patient advocacy and feedback shaping healthcare delivery.
Choosing Between Pharmacist and Physician
Choosing between a pharmacist and a physician depends on your healthcare needs and the level of medical intervention required. Pharmacists specialize in medication management, offering expert advice on drug interactions, side effects, and over-the-counter treatments, making them ideal for managing minor ailments and medication-related queries. Physicians provide comprehensive medical diagnoses, treatment plans, and long-term care for complex health conditions, so your choice should align with whether you require medication guidance or in-depth medical evaluation.
Infographic: Pharmacist vs Physician
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com