Peacekeepers prioritize harmony and conflict resolution, fostering understanding and cooperation in relationships. Soldiers approach relationships with discipline and protection, emphasizing loyalty and strength. Discover more insights on the Peacekeeper vs Soldier dynamic in this article.
Table of Comparison
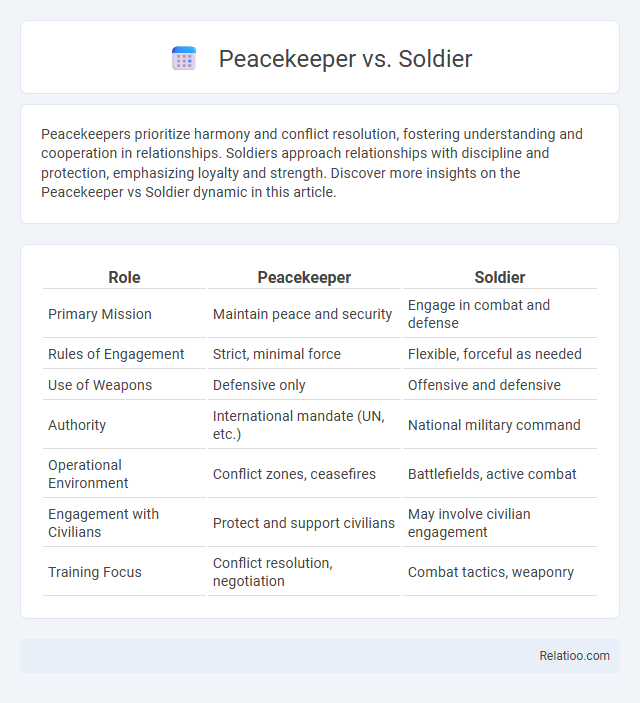
| Role | Peacekeeper | Soldier |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mission | Maintain peace and security | Engage in combat and defense |
| Rules of Engagement | Strict, minimal force | Flexible, forceful as needed |
| Use of Weapons | Defensive only | Offensive and defensive |
| Authority | International mandate (UN, etc.) | National military command |
| Operational Environment | Conflict zones, ceasefires | Battlefields, active combat |
| Engagement with Civilians | Protect and support civilians | May involve civilian engagement |
| Training Focus | Conflict resolution, negotiation | Combat tactics, weaponry |
Peacekeeper vs Soldier: Defining the Roles
The Peacekeeper operates primarily in maintaining order during civil unrest, often emphasizing non-lethal methods and negotiation tactics to de-escalate conflicts. Soldiers are trained for combat operations, focusing on offensive and defensive maneuvers in warfare, equipped to engage in armed conflict with lethal force. Understanding the distinct roles of Peacekeepers and Soldiers highlights their specialization: Peacekeepers prioritize conflict resolution and civilian protection, while Soldiers emphasize battlefield strategy and national defense.
Objectives and Mission Differences
Peacekeepers primarily focus on maintaining ceasefires and facilitating diplomatic negotiations to preserve peace in conflict zones, operating under mandates from international organizations like the United Nations. Soldiers are tasked with combat operations, defense missions, and achieving tactical objectives through military force to secure national interests and respond to threats. The contrasting missions highlight peacekeepers' emphasis on neutrality and conflict prevention, whereas soldiers prioritize direct combat engagement and defense strategies.
Training and Skill Set Comparison
Peacekeepers receive specialized training in conflict resolution, negotiation, and cultural sensitivity to maintain peace and protect civilians in volatile environments, emphasizing de-escalation tactics over combat. Soldiers undergo rigorous military training focused on combat readiness, tactical maneuvers, weapons proficiency, and strategic operations to engage effectively in warfare and defense missions. The Peacekeeper-Soldier hybrid role combines advanced peacekeeping skills with combat training, enabling personnel to both mediate conflicts and respond robustly to security threats, ensuring versatility in diverse mission scenarios.
Use of Force: Rules of Engagement
Peacekeeper Rules of Engagement (ROE) emphasize minimal use of force, strictly for self-defense or protection of civilians, adhering to international mandates. Soldier ROE allow for a broader range of force application, including offensive operations, often guided by military objectives within combat zones. Peacekeeper ROE prioritize restraint and de-escalation to maintain neutrality and support conflict resolution, ensuring force is a last resort under strict command oversight.
Uniforms and Identification
Peacekeepers typically wear distinct light blue helmets or berets and uniforms marked with United Nations insignia to clearly identify their neutral role in conflict zones. Soldiers, on the other hand, don national military camouflage tailored to different terrains and mission types, making them recognizable as combatants of their specific countries. Your ability to distinguish between these uniforms is crucial for understanding rules of engagement and ensuring compliance with international law during peacekeeping operations.
Operational Environments
The Peacekeeper is optimized for strategic deterrence in fixed-site operational environments, leveraging its mobile intercontinental ballistic missile capability. The Soldier thrives in dynamic, tactical combat zones requiring rapid maneuverability and adaptability across diverse terrains. Your mission effectiveness depends on selecting the Peacekeeper for long-range, high-stakes deterrence or the Soldier for ground-level, responsive engagements.
Interaction with Civilians
Peacekeepers prioritize nonviolent engagement and community-building, fostering trust and cooperation with civilians in conflict zones through dialogue and protection efforts. Soldiers conduct operations focused on security and tactical objectives, often resulting in a more authoritative and distant interaction with local populations. Peacekeepers operate under mandates emphasizing impartiality and human rights, enabling closer collaboration with civilians to support stability and humanitarian assistance.
International Law and Mandates
The Peacekeeper operates under strict international law mandates emphasizing neutrality, protection of civilians, and support for political processes, adhering to United Nations Security Council resolutions. Soldiers, often acting under national military command, may engage in combat operations with authority derived from state-specific rules of engagement and international humanitarian law. Your understanding of these roles highlights that Peacekeepers prioritize peaceful conflict resolution, while Soldiers focus on defense and enforcement actions within their legal mandates.
Psychological Challenges and Risks
Peacekeepers face unique psychological challenges including exposure to trauma, moral dilemmas, and the stress of maintaining neutrality in conflict zones, which can lead to anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder. Soldiers often confront intense combat-related stress, risking PTSD from direct engagement in hostile situations and life-threatening scenarios. Your mental resilience is crucial when operating in these roles, as both peacekeepers and soldiers must manage risks like emotional exhaustion, depression, and long-term psychological impact from continuous exposure to violence and instability.
Impact on Global Security
Peacekeepers play a critical role in maintaining global security by mitigating conflicts and providing stability in volatile regions, often working under United Nations mandates to enforce peace agreements and protect civilians. Soldiers, equipped for more robust combat operations, can decisively alter the balance of power during conflicts, influencing geopolitical dynamics and deterring aggression through military strength. Your understanding of these roles highlights how peacekeepers facilitate long-term security through diplomacy and protection, while soldiers ensure immediate defense and force projection in international security frameworks.
Infographic: Peacekeeper vs Soldier
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com