Peacekeepers maintain harmony by avoiding conflict, while peacemakers actively resolve disputes and promote understanding. Discover the key differences and how each role impacts relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
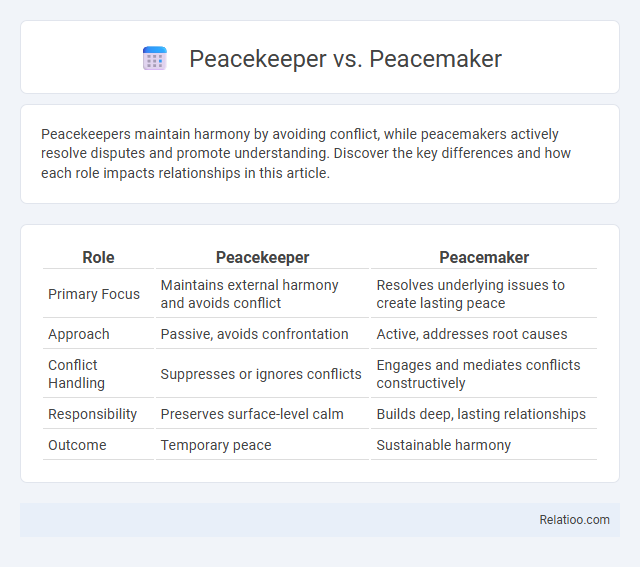
| Role | Peacekeeper | Peacemaker |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Maintains external harmony and avoids conflict | Resolves underlying issues to create lasting peace |
| Approach | Passive, avoids confrontation | Active, addresses root causes |
| Conflict Handling | Suppresses or ignores conflicts | Engages and mediates conflicts constructively |
| Responsibility | Preserves surface-level calm | Builds deep, lasting relationships |
| Outcome | Temporary peace | Sustainable harmony |
Introduction: Defining Peacekeeper and Peacemaker
A peacekeeper operates primarily to maintain order and enforce ceasefires during conflicts using military or law enforcement authority. A peacemaker seeks to resolve disputes through dialogue, negotiation, and diplomacy, aiming for a lasting and voluntary agreement. Both roles contribute to conflict resolution but differ fundamentally in methods and objectives.
Historical Contexts of Peacekeeping and Peacemaking
Peacekeeping historically involves deploying neutral forces to maintain ceasefires and stability, exemplified by United Nations missions such as in Cyprus since 1964. Peacemaking refers to diplomatic efforts and negotiations to resolve conflicts, highlighted by the Camp David Accords of 1978 between Egypt and Israel. Peacekeepers primarily enforce peace agreements on the ground, while peacemakers actively engage in dialogue and conflict resolution to prevent escalation.
Core Characteristics: Peacekeeper vs Peacemaker
Peacekeepers prioritize maintaining harmony by avoiding conflict and ensuring stability, while Peacemakers actively seek to resolve disputes through dialogue and understanding. Your choice between these roles influences how you address tensions--Peacekeepers prefer to keep peace by minimizing disruptions, whereas Peacemakers engage in transformative conflict resolution. Both focus on peace, but Peacekeepers emphasize order, and Peacemakers emphasize reconciliation.
Roles and Responsibilities in Conflict Resolution
Peacekeepers maintain ceasefires and create stable environments by monitoring and enforcing peace agreements, often under UN mandates. Peacemakers actively negotiate between conflicting parties to reach diplomatic solutions and promote reconciliation through dialogue and mediation. Peacebuilders focus on restoring social trust and fostering long-term development to ensure sustainable peace by addressing root causes of conflict.
Approaches to Maintaining and Building Peace
Peacekeeper efforts prioritize maintaining peace by enforcing ceasefires and monitoring conflict zones, relying on impartial military or police forces to prevent violence. Peacemakers focus on resolving underlying conflicts through dialogue, negotiation, and addressing root causes to achieve long-term peace agreements. Your choice between these approaches depends on whether you need immediate stability through enforcement or sustainable harmony through mediation and reconciliation.
Peacekeeper Methods: Containment and Control
Peacekeeper methods primarily involve containment and control tactics designed to maintain order and prevent escalation of conflicts without direct confrontation. These strategies emphasize monitoring, regulating movement, and restricting hostile actions to stabilize volatile situations. Your understanding of peacekeeping highlights how these techniques support conflict management by limiting violence while fostering conditions for dialogue and resolution.
Peacemaker Strategies: Dialogue and Reconciliation
Peacemaker strategies emphasize dialogue and reconciliation to resolve conflicts by fostering mutual understanding and trust among disputing parties. These approaches involve active listening, empathy, and collaborative problem-solving to address underlying issues and promote sustainable peace. Effective peacemaking prioritizes communication channels and restorative justice mechanisms to rebuild relationships and prevent future tensions.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Case studies highlight the distinct roles of Peacekeepers, Peacemakers, and Peacebuilders in conflict resolution across various regions. In the UN peacekeeping mission in Cyprus, Peacekeepers maintained ceasefires and protected civilians, while Peacemakers in Northern Ireland facilitated critical negotiations leading to the Good Friday Agreement. Your understanding of these roles can enhance strategic approaches to conflict management by recognizing the importance of both intervention and long-term peacebuilding efforts.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Role
Peacekeepers excel at maintaining order and enforcing rules, leveraging authority to prevent conflict escalation, but they may struggle with flexibility and addressing underlying issues. Peacemakers specialize in mediation and dialogue, fostering understanding and reconciliation, yet they might face challenges in controlling immediate tensions or enforcing agreements. Peacekeepers combine elements of both roles by balancing authority with negotiation skills, although this dual role can create tension between enforcement and empathy, potentially diluting effectiveness in either domain.
Choosing the Right Approach for Sustainable Peace
Choosing the right approach for sustainable peace requires understanding the distinct roles of Peacekeeper, Peacemaker, and Peacebuilder. A Peacekeeper maintains order and prevents violence through monitoring and enforcement, while a Peacemaker actively negotiates and mediates to resolve underlying conflicts. Your decision should prioritize long-term stability by combining immediate security with dialogue and reconciliation efforts.
Infographic: Peacekeeper vs Peacemaker
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com