A financier primarily provides funding through various financial instruments, while a venture capitalist invests equity in high-growth startups, often offering strategic support. Explore this article to understand the key differences and roles in startup financing.
Table of Comparison
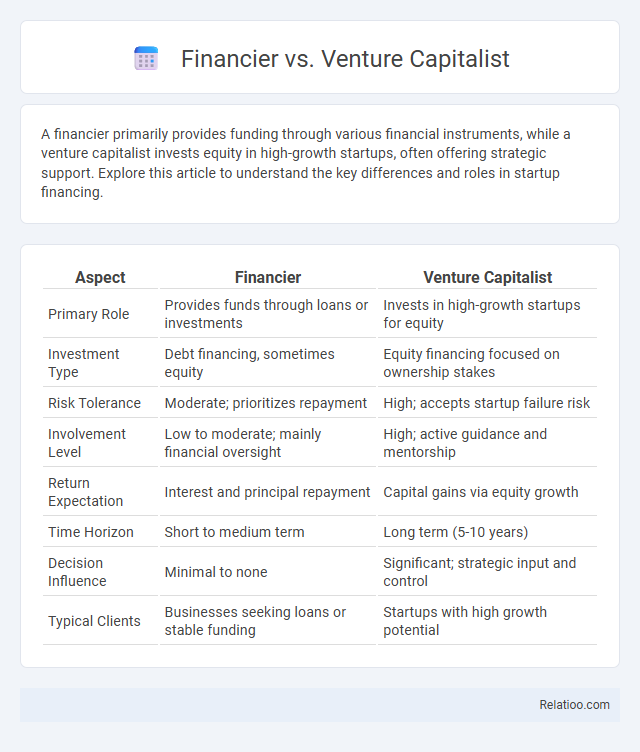
| Aspect | Financier | Venture Capitalist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Provides funds through loans or investments | Invests in high-growth startups for equity |
| Investment Type | Debt financing, sometimes equity | Equity financing focused on ownership stakes |
| Risk Tolerance | Moderate; prioritizes repayment | High; accepts startup failure risk |
| Involvement Level | Low to moderate; mainly financial oversight | High; active guidance and mentorship |
| Return Expectation | Interest and principal repayment | Capital gains via equity growth |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term | Long term (5-10 years) |
| Decision Influence | Minimal to none | Significant; strategic input and control |
| Typical Clients | Businesses seeking loans or stable funding | Startups with high growth potential |
Introduction to Financier and Venture Capitalist
A financier is an individual or firm specializing in managing large-scale investments, funding projects, and providing capital for various financial ventures across industries. Venture capitalists specifically invest in early-stage startups and high-growth companies, offering equity financing and strategic guidance in exchange for ownership stakes. While financiers encompass a broad range of financial activities, venture capitalists concentrate on funding innovative companies with high growth potential.
Defining a Financier
A financier is a broad term encompassing individuals or institutions that provide funding or capital for various financial activities, including investments, loans, and asset management. Unlike venture capitalists who specifically invest in early-stage startups with high growth potential, financiers operate across diverse sectors and asset classes, including real estate, mergers and acquisitions, and corporate finance. Understanding a financier involves recognizing their role in orchestrating complex financial transactions, managing risk, and allocating capital to optimize returns across multiple industries.
Understanding Venture Capitalists
Venture capitalists specialize in funding early-stage, high-growth startups by providing capital in exchange for equity ownership, aiming for substantial returns through business scaling and exits like IPOs or acquisitions. Unlike traditional financiers who may offer loans or debt financing with fixed repayments, venture capitalists actively engage in business strategy and mentoring to enhance your company's value. Recognizing the unique role of venture capitalists is crucial for entrepreneurs seeking not just funding but strategic partnerships that drive innovation and long-term growth.
Key Differences Between Financiers and Venture Capitalists
Financiers primarily focus on providing a broad range of funding options including loans, bonds, and equity investments across various industries, whereas venture capitalists specialize in investing in early-stage, high-growth startups with significant equity stakes and active involvement in company strategy. Financiers often pursue more diversified and lower-risk portfolios with returns tied to interest or asset performance, while venture capitalists accept higher risks with the potential for substantial capital gains through company exit events like IPOs or acquisitions. The key difference lies in the investment approach: financiers are lenders or investors with diverse capital deployment methods, whereas venture capitalists act as strategic partners driving innovation by funding startup ventures.
Roles and Responsibilities
Financiers manage the allocation of capital across various asset classes, focusing on risk assessment, portfolio management, and funding strategies to maximize returns. Venture capitalists specialize in identifying, funding, and mentoring high-growth startups, emphasizing due diligence, equity negotiation, and strategic scaling. Investment bankers facilitate large-scale financial transactions, including mergers, acquisitions, and public offerings, by providing advisory services and structuring deals to optimize client value.
Sources of Funding and Capital
Financiers typically provide funding through private, debt-based, or equity investments sourced from personal or institutional capital, whereas venture capitalists primarily manage pooled funds from limited partners, investing in high-growth startups with equity stakes. Unlike financiers, angel investors often use their own money, focusing on early-stage companies, while venture capitalists rely on structured funds to scale ventures. Your choice between these funding sources depends on the capital amount, investment terms, and your business's growth stage.
Risk Appetite and Investment Strategies
Financiers typically exhibit a moderate risk appetite, focusing on stable returns through traditional investment strategies such as loans or bonds, while venture capitalists pursue high-risk, high-reward opportunities by investing in early-stage startups with innovative potential. Your choice between these investors depends on your business stage and growth objectives, as financiers prioritize capital preservation, whereas venture capitalists support aggressive scaling and market disruption. Understanding these differences in risk tolerance and investment approaches enables better alignment with your financing needs and long-term goals.
Impact on Startups and Businesses
Venture capitalists drive startup growth by providing substantial funding, strategic guidance, and industry connections, accelerating innovation and market entry. Financiers, including banks and private lenders, offer loans or credit with fixed terms, supporting businesses with capital needs but less involvement in strategic decisions. The key difference lies in venture capitalists' active role in scaling startups versus financiers' primarily financial support without direct influence on business operations.
Pros and Cons for Entrepreneurs
Financiers typically provide debt financing, offering entrepreneurs the advantage of retaining full ownership but imposing repayment obligations with interest that can strain cash flow. Venture capitalists bring substantial funding and industry expertise, accelerating growth, yet demand equity stakes and significant control, potentially diluting founders' influence. Entrepreneurs must weigh financiers' predictable repayment against venture capitalists' strategic support and ownership dilution to align funding choices with business goals.
Choosing Between a Financier and a Venture Capitalist
Choosing between a financier and a venture capitalist depends on your business stage and funding needs; financiers typically offer loans or credit with fixed repayment terms, providing stable capital without equity dilution. Venture capitalists invest in early-stage or high-growth companies in exchange for equity, offering not only funding but strategic guidance and networking opportunities. Your decision should align with your business goals, risk tolerance, and willingness to share ownership.
Infographic: Financier vs Venture Capitalist
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com