Nurses provide essential patient care and support, while doctors diagnose and treat medical conditions using specialized knowledge. Discover the distinct roles and collaborative dynamics between nurses and doctors in this article.
Table of Comparison
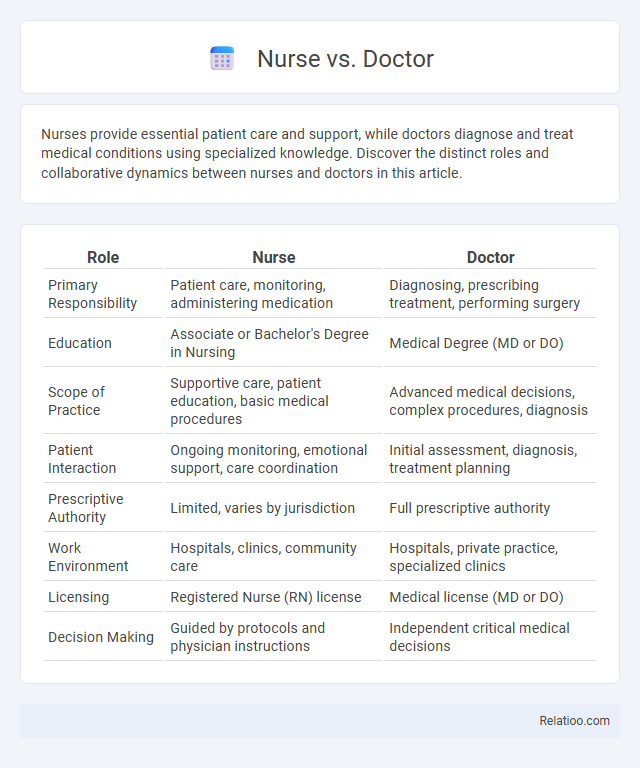
| Role | Nurse | Doctor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Patient care, monitoring, administering medication | Diagnosing, prescribing treatment, performing surgery |
| Education | Associate or Bachelor's Degree in Nursing | Medical Degree (MD or DO) |
| Scope of Practice | Supportive care, patient education, basic medical procedures | Advanced medical decisions, complex procedures, diagnosis |
| Patient Interaction | Ongoing monitoring, emotional support, care coordination | Initial assessment, diagnosis, treatment planning |
| Prescriptive Authority | Limited, varies by jurisdiction | Full prescriptive authority |
| Work Environment | Hospitals, clinics, community care | Hospitals, private practice, specialized clinics |
| Licensing | Registered Nurse (RN) license | Medical license (MD or DO) |
| Decision Making | Guided by protocols and physician instructions | Independent critical medical decisions |
Introduction: Understanding the Roles
Nurses provide essential patient care, focusing on daily needs and emotional support, while doctors diagnose illnesses and develop treatment plans. Patients receive medical attention and actively participate in their own health management. Understanding these distinct roles helps you navigate the healthcare system more effectively.
Education and Training Requirements
Nurses typically undergo diploma, associate, or bachelor's degree programs, followed by passing the NCLEX-RN exam for licensure, with some pursuing advanced practice degrees like a Nurse Practitioner (NP). Doctors complete an undergraduate degree, four years of medical school, and a residency program ranging from three to seven years depending on their specialty, requiring passing the USMLE exams for board certification. Patients receive healthcare services without formal medical education, relying on the expertise and training of nurses and doctors for diagnosis, treatment, and care management.
Scope of Practice
Nurses provide comprehensive patient care, including administering medications, monitoring vital signs, and educating patients within their licensed scope of practice. Doctors diagnose conditions, develop treatment plans, perform surgeries, and manage complex medical cases based on extensive medical training and certification. Your healthcare experience depends on the dynamic collaboration between these roles to ensure accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and continuous care.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Nurses provide direct patient care, administer medications, monitor vital signs, and assist with daily activities to ensure patient comfort and recovery. Doctors diagnose illnesses, develop treatment plans, perform procedures, and make critical medical decisions based on patient history and diagnostic tests. Patients actively participate in their care by communicating symptoms, following medical advice, and adhering to prescribed treatments for optimal health outcomes.
Patient Interaction and Care
Effective patient interaction and care depend on clear communication and empathy from nurses and doctors, who each play distinct roles in the healthcare process. Nurses provide continuous bedside care, monitor patient conditions, and offer emotional support, while doctors diagnose illnesses, develop treatment plans, and make critical medical decisions. Your experience improves when both professionals collaborate, ensuring comprehensive care tailored to your individual needs.
Work Settings and Environments
Nurses often work in dynamic hospital settings, including emergency rooms, intensive care units, and outpatient clinics, where direct patient care and monitoring are critical. Doctors typically operate in diverse environments such as private practices, specialized clinics, and hospital departments, focusing on diagnosis, treatment planning, and performing procedures. Your experience as a patient can vary significantly depending on whether care is provided in a fast-paced hospital ward, a personalized doctor's office, or a community health clinic.
Salary and Compensation
Nurses typically earn a median annual salary of around $75,000, while doctors' salaries vary widely but generally start at approximately $200,000 and can exceed $400,000 depending on specialization and experience. Patients do not receive direct compensation but benefit from the healthcare services provided by these professionals, which are often influenced by the economic dynamics of medical staff salaries. Your financial expectations in the healthcare field should consider the distinct compensation structures between nurses and doctors, shaped by education, responsibility, and demand.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Nurses have diverse career advancement options, including specialization in fields like nurse practitioner or nurse anesthetist, which offer higher autonomy and salary potential. Doctors follow a clear trajectory from residency to fellowship and board certification, enabling subspecialties with significant authority and compensation growth. Patients indirectly benefit from these advancements through access to highly skilled healthcare professionals and improved treatment outcomes.
Work-Life Balance and Job Satisfaction
Nurses often experience a demanding work-life balance due to irregular shifts and high patient loads, impacting job satisfaction differently than doctors who may face longer hours but typically have more control over their schedules. Doctors generally report higher job satisfaction linked to autonomy and financial rewards, though stress levels and on-call duties can challenge personal time. Patients benefit indirectly from the well-being of both nurses and doctors, as balanced healthcare providers tend to deliver improved care quality and patient outcomes, affecting your overall healthcare experience.
Choosing Between Nursing and Medicine
Choosing between nursing and medicine depends on preferred roles in patient care, with nurses focusing on holistic support and doctors concentrating on diagnosis and treatment plans. Nurses often engage more in direct patient interaction and ongoing care management, while doctors typically handle complex medical decisions and procedures. Career length, educational commitments, and work environment also influence the choice, as nursing requires less schooling and offers diverse practice settings compared to the longer training and higher specialization in medicine.
Infographic: Nurse vs Doctor
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com