A Crisis Manager specializes in handling immediate threats and emergencies to minimize impact, while a Risk Manager focuses on identifying and mitigating potential risks before they escalate. Explore this article to understand the distinct roles and strategies of Crisis Managers versus Risk Managers.
Table of Comparison
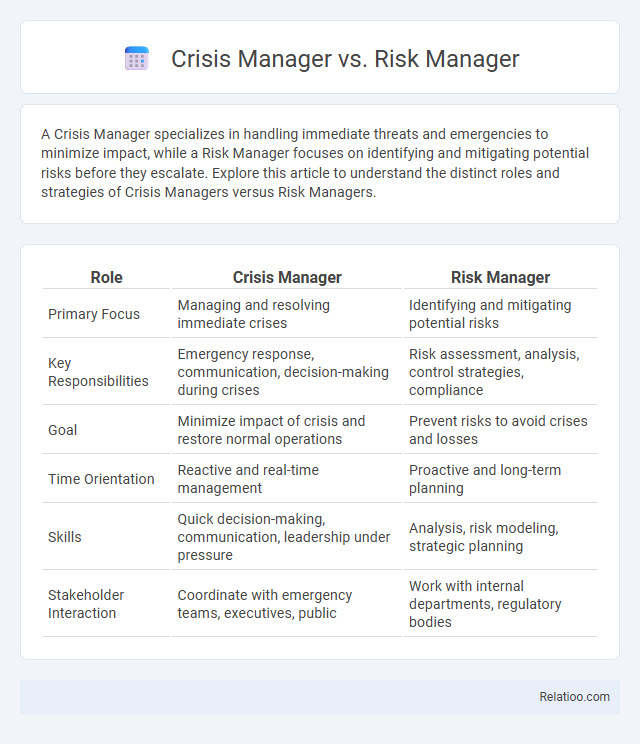
| Role | Crisis Manager | Risk Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Managing and resolving immediate crises | Identifying and mitigating potential risks |
| Key Responsibilities | Emergency response, communication, decision-making during crises | Risk assessment, analysis, control strategies, compliance |
| Goal | Minimize impact of crisis and restore normal operations | Prevent risks to avoid crises and losses |
| Time Orientation | Reactive and real-time management | Proactive and long-term planning |
| Skills | Quick decision-making, communication, leadership under pressure | Analysis, risk modeling, strategic planning |
| Stakeholder Interaction | Coordinate with emergency teams, executives, public | Work with internal departments, regulatory bodies |
Understanding Crisis Management and Risk Management
Crisis managers focus on responding to unexpected, high-impact events to minimize damage and restore operations, while risk managers proactively identify, assess, and mitigate potential threats to prevent crises. Understanding crisis management involves developing strategic response plans and communication protocols tailored to urgent situations, whereas risk management emphasizes continuous evaluation and control of vulnerabilities to reduce overall organizational risk. Your ability to integrate both functions ensures comprehensive protection by balancing preparedness with prevention.
Key Responsibilities of a Crisis Manager
A Crisis Manager plays a vital role in preparing organizations to handle unexpected emergencies by developing comprehensive response strategies and leading coordination efforts during incidents. Their key responsibilities include crisis communication, resource allocation, and swift decision-making to mitigate impact and ensure business continuity. Your ability to manage stakeholder expectations and conduct post-crisis evaluations distinguishes the Crisis Manager from a Risk Manager, whose focus lies primarily on identifying and reducing potential threats before they materialize.
Core Functions of a Risk Manager
Risk managers primarily focus on identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to an organization's assets, operations, and reputation through proactive analysis and strategic planning. Core functions include conducting risk assessments, implementing risk control measures, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements to minimize financial losses and legal liabilities. Your organization's resilience depends on effective risk management to prevent crises, while crisis managers address immediate response and recovery, and safety managers concentrate on workplace health and safety protocols.
Proactive vs. Reactive Approaches
Risk Managers adopt proactive approaches by identifying potential threats and implementing preventive measures to minimize vulnerabilities before incidents occur. Crisis Managers emphasize reactive strategies, focusing on effective response and recovery once a crisis has materialized, ensuring business continuity and stakeholder confidence. While Crisis Managers handle immediate disruption with tactical solutions, proactive Risk Managers work to mitigate risks through continuous assessment and strategic planning.
Essential Skills for Crisis Managers
Crisis Managers require rapid decision-making, effective communication under pressure, and strategic problem-solving to mitigate the impact of unforeseen events. Unlike Risk Managers who focus on identifying and assessing potential threats to prevent crises, Crisis Managers excel in real-time incident response and leadership during emergencies. Mastery of stress management, resource coordination, and stakeholder engagement are essential skills that distinguish Crisis Managers in high-stakes situations.
Key Competencies for Risk Managers
Risk Managers specialize in identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to an organization's assets and operations through proactive strategies and compliance with regulatory standards. Key competencies for Risk Managers include analytical skills, risk assessment methodologies, financial acumen, and a deep understanding of industry-specific regulations. You benefit from their expertise in developing risk mitigation frameworks that reduce vulnerabilities before crises occur, contrasting with Crisis Managers who focus primarily on response and recovery during emergencies.
Tools and Techniques Used
Crisis Managers rely on real-time communication platforms, incident management software, and scenario-based simulation tools to respond effectively to unfolding emergencies and ensure swift decision-making. Risk Managers utilize quantitative risk assessment models, predictive analytics, and compliance management systems to identify, evaluate, and mitigate potential hazards before they escalate. Both roles incorporate data visualization dashboards and stakeholder collaboration tools, but Crisis Managers emphasize rapid response technologies, while Risk Managers focus on preventive strategies supported by statistical and financial risk analysis techniques.
Collaborative Roles During Critical Events
Crisis Managers and Risk Managers play complementary roles during critical events, with Crisis Managers leading immediate response efforts while Risk Managers focus on identifying and mitigating potential threats before they escalate. Collaborative coordination ensures seamless communication, resource allocation, and decision-making to protect your organization's assets and reputation. Effective teamwork between these roles enhances resilience by integrating proactive risk assessment with real-time crisis management.
Impact on Organizational Resilience
Crisis managers focus on immediate incident response and recovery, ensuring your organization maintains continuity during disruptions. Risk managers proactively assess potential threats and implement strategies to minimize vulnerabilities, strengthening long-term organizational resilience. Combining these roles enhances your ability to anticipate, withstand, and quickly recover from crises, fostering a robust and adaptive organizational framework.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Organization
Choosing the right role between Crisis Manager and Risk Manager depends on your organization's specific needs in handling uncertainty and threats. A Risk Manager focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks before they materialize, while a Crisis Manager is responsible for managing and resolving emergency situations that impact the organization's operations and reputation. Your decision should consider whether your priority is proactive risk prevention or reactive crisis response to ensure optimal organizational resilience.
Infographic: Crisis Manager vs Risk Manager
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com