Submissiveness involves yielding to another's authority voluntarily, reflecting an internal acceptance, while obedience is the act of following commands or rules, often motivated by external pressure. Explore the nuances between submissiveness and obedience in relationships to understand their impact on dynamics in this article.
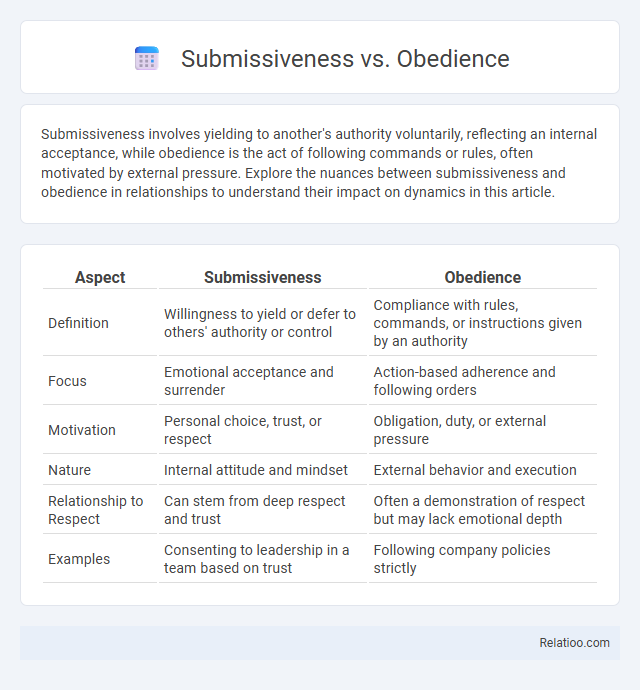
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Submissiveness | Obedience |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Willingness to yield or defer to others' authority or control | Compliance with rules, commands, or instructions given by an authority |
| Focus | Emotional acceptance and surrender | Action-based adherence and following orders |
| Motivation | Personal choice, trust, or respect | Obligation, duty, or external pressure |
| Nature | Internal attitude and mindset | External behavior and execution |
| Relationship to Respect | Can stem from deep respect and trust | Often a demonstration of respect but may lack emotional depth |
| Examples | Consenting to leadership in a team based on trust | Following company policies strictly |
Understanding Submissiveness: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding submissiveness involves recognizing it as a voluntary and psychological state where an individual willingly yields control, contrasting with obedience, which requires following explicit orders or rules. Submissiveness is deeply tied to consent and emotional connection, reflecting personal choice rather than mere compliance. Your insight into these distinctions enhances interpersonal dynamics and fosters respectful, meaningful relationships.
Defining Obedience in Personal and Social Contexts
Obedience in personal and social contexts refers to the act of following directives or rules set by an authority figure, reflecting compliance rather than voluntary submission. Social obedience often involves adhering to societal norms or legal requirements, whereas personal obedience may emerge within family dynamics or close relationships. Distinguishing obedience from submissiveness highlights compliance driven by external control, contrasting with submissiveness, which implies yielding or acceptance often based on internal disposition.
Key Differences Between Submissiveness and Obedience
Submissiveness involves a voluntary yielding to another's authority or influence, often reflecting personal acceptance and internal agreement. Obedience, however, is the act of following explicit commands or rules imposed by an external authority, regardless of personal feelings. The key difference lies in submissiveness being a choice rooted in consent, whereas obedience typically requires compliance without necessarily involving consent or personal agreement.
Psychological Foundations of Submissiveness
Submissiveness in psychology is characterized by a voluntary yielding to authority or influence, often rooted in a desire for social harmony or fear of conflict, whereas obedience typically involves compliance with explicit commands from a recognized authority figure. The psychological foundations of submissiveness include attachment styles, low self-esteem, and social conditioning, which collectively influence how you respond to power dynamics in relationships. Understanding these factors can help you navigate the complex interplay between personal autonomy and external control, distinguishing genuine submission from mere obedience.
The Role of Authority in Fostering Obedience
Authority significantly influences obedience by establishing clear power dynamics that compel individuals to comply with directives, often without question. Psychological studies, such as Milgram's experiments, demonstrate that perceived legitimate authority intensifies willingness to obey even against personal moral judgments. Authority figures utilize social cues, legitimacy, and structured hierarchies to reinforce obedience, distinguishing it from submissiveness which may arise more from personal disposition than external commands.
Cultural Influences Shaping Submissive and Obedient Behaviors
Cultural influences significantly shape the distinctions between submissiveness and obedience, affecting how individuals respond to authority and social expectations. In collectivist societies, submissiveness often reflects a deep respect for hierarchy and harmony, while obedience may be viewed as adherence to explicit rules or commands. Understanding these nuances can help you navigate social dynamics and recognize the cultural context behind submissive and obedient behaviors.
Submissiveness vs Obedience in Relationships
Submissiveness in relationships involves yielding to a partner's influence with a focus on emotional connection and trust, while obedience emphasizes compliance with specific rules or commands often without questioning. Submissive behavior reflects voluntary surrender for harmony and mutual respect, whereas obedience may imply hierarchical control and authority. Understanding the balance between submissiveness and obedience is crucial for healthy dynamics, fostering partnership rather than dominance.
Impacts on Mental Health: Submissiveness and Obedience
Submissiveness involves willingly yielding control and often relates to personal boundaries, whereas obedience compels compliance typically driven by external authority, both impacting mental health differently. Chronic submissiveness can lead to diminished self-esteem and increased anxiety due to suppressed autonomy, while enforced obedience risks psychological distress stemming from reduced personal agency. Understanding these distinctions helps mental health professionals tailor interventions addressing the balance between autonomy and compliance for improved psychological well-being.
Healthy Boundaries: Balancing Assertiveness and Compliance
Balancing submissiveness, obedience, and assertiveness requires recognizing your personal boundaries while respecting others' expectations, ensuring interactions remain healthy and consensual. Establishing clear communication allows you to comply when appropriate without sacrificing your autonomy or well-being. Understanding these distinctions helps maintain mutual respect, fostering relationships built on trust rather than control or coercion.
Empowering Change: Moving Beyond Blind Obedience and Submissiveness
Empowering change requires distinguishing between submissiveness, obedience, and true empowerment by fostering critical thinking and personal agency. Unlike blind obedience or passive submissiveness, your ability to question directives and assert boundaries leads to genuine growth and transformation. Embracing informed choices empowers you to break free from unquestioned compliance and advance toward meaningful change.
Infographic: Submissiveness vs Obedience
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com