Dignity in relationships emphasizes mutual respect and intrinsic worth, while rights focus on legally or socially recognized entitlements and protections. Explore how balancing dignity and rights fosters healthy, equitable relationships in this article.
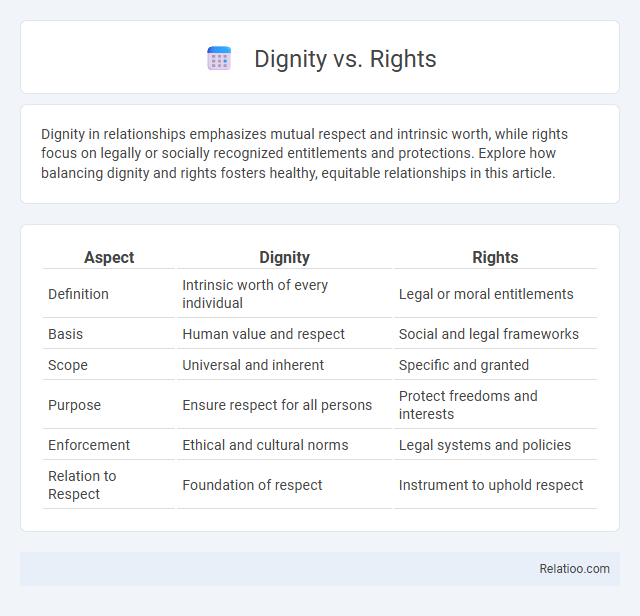
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dignity | Rights |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intrinsic worth of every individual | Legal or moral entitlements |
| Basis | Human value and respect | Social and legal frameworks |
| Scope | Universal and inherent | Specific and granted |
| Purpose | Ensure respect for all persons | Protect freedoms and interests |
| Enforcement | Ethical and cultural norms | Legal systems and policies |
| Relation to Respect | Foundation of respect | Instrument to uphold respect |
Understanding the Concept of Dignity
Dignity refers to the inherent worth and respect every individual deserves simply by being human, serving as the foundation for all human rights. Unlike rights, which are legal entitlements granted and protected by law, dignity is a universal, intrinsic value that underpins moral and ethical considerations in society. Understanding dignity involves recognizing its role as a guiding principle that shapes human interactions, social policies, and the protection of fundamental freedoms.
Defining Human Rights
Human rights are universal entitlements inherent to every individual, ensuring protection of fundamental freedoms and equality without discrimination. Dignity refers to the intrinsic worth of a person, forming the ethical foundation that human rights seek to uphold and protect. You must understand that while dignity underpins human rights, rights provide the legal framework to enforce and realize that dignity in society.
Historical Perspectives: Dignity and Rights
Historical perspectives reveal that dignity and rights emerged from distinct yet interconnected philosophical traditions; dignity, rooted in intrinsic human worth, was emphasized in ancient and religious texts, while rights developed through legal and political frameworks during Enlightenment thought. The concept of dignity often served as a moral foundation for the recognition of human rights, influencing key documents like the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948). Over time, dignity provided the ethical justification for rights, shaping the evolution of modern human rights law and international norms.
Key Differences Between Dignity and Rights
Dignity refers to the inherent worth and respect owed to every individual simply by being human, while rights are specific legal or moral entitlements granted to protect and promote that dignity. Your dignity is intrinsic and cannot be taken away, whereas rights can vary by culture, law, and context, often requiring enforcement through legal systems. Understanding this distinction is crucial for recognizing how dignity forms the foundational basis upon which rights are established and justified.
The Interdependence of Dignity and Rights
Dignity and rights are inherently interdependent, as dignity forms the moral foundation upon which human rights are established, ensuring every individual is treated with inherent worth and respect. Your recognition of human dignity reinforces the enforcement and protection of rights, creating a framework that upholds equality and justice in society. Violating someone's rights directly undermines their dignity, highlighting the essential connection that demands both concepts be safeguarded together for social harmony.
Dignity in International Law
Dignity in international law serves as the fundamental principle underpinning human rights, asserting the inherent worth of every individual regardless of nationality or status. Your dignity is recognized as the basis for universal protections against discrimination, torture, and inhumane treatment according to treaties like the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights. Unlike rights, which are specific entitlements, dignity represents the intrinsic value that mandates respect and protection under global legal frameworks.
Rights as Legal Protections
Rights serve as legal protections that safeguard your freedoms and entitlements within society, establishing clear boundaries enforced by law. While dignity represents the inherent worth and respect every individual deserves, rights translate this abstract value into concrete legal guarantees. Understanding the distinction clarifies how dignity underpins the moral foundation, whereas rights ensure accountability through formal legal frameworks.
Ethical Implications of Dignity vs Rights
Dignity emphasizes the intrinsic worth of individuals, serving as a foundational ethical principle that guides respectful treatment beyond legal mandates. Rights establish explicit legal protections and entitlements designed to safeguard individual freedoms, but they may not fully capture the moral depth conveyed by dignity. Ethical implications arise when rights are insufficient or violated, highlighting the necessity to uphold dignity as a universal standard that ensures humane and equitable treatment irrespective of legal recognition.
Real-World Examples: Dignity and Rights in Practice
Dignity and rights intersect in real-world scenarios where individuals' inherent worth guides legal protections, such as anti-discrimination laws that uphold both dignity and equal rights. Your ability to access healthcare exemplifies the practice of dignity through the right to health services, ensuring respect and fairness in treatment. In workplaces, balancing employee rights with policies promoting dignity creates environments that prevent abuses while fostering respect for personal integrity.
The Future of Dignity and Rights Discourse
The future of dignity and rights discourse hinges on integrating human dignity as a foundational principle that shapes the evolution of legal and ethical frameworks protecting individual freedoms. Your understanding of this integration emphasizes the need for policies that not only enforce rights but also uphold the inherent worth of every person in diverse cultural and social contexts. Advancements in international law and human rights mechanisms will increasingly reflect this synergy, promoting more inclusive, equitable societies worldwide.
Infographic: Dignity vs Rights
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com