Goodwill represents the intangible value of a brand or company beyond its physical assets, while recognition measures the awareness and acknowledgment of that brand by consumers. Explore this article to understand how goodwill and recognition impact relationship-building in business.
Table of Comparison
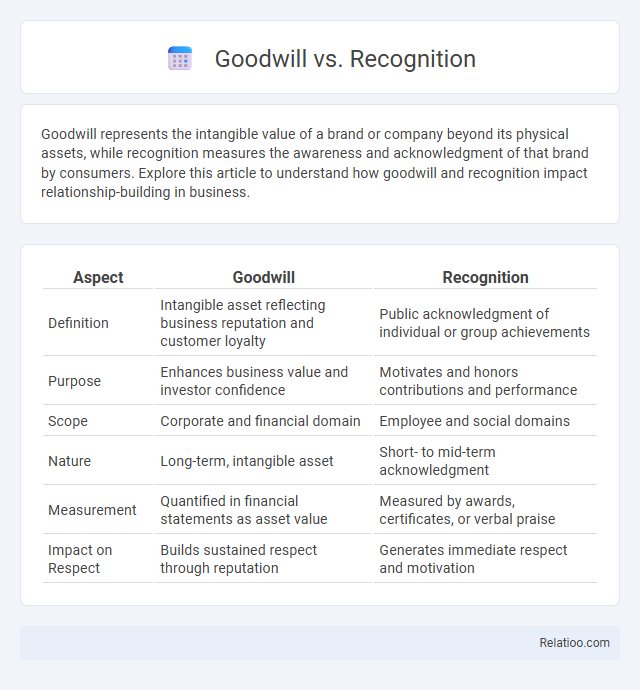
| Aspect | Goodwill | Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intangible asset reflecting business reputation and customer loyalty | Public acknowledgment of individual or group achievements |
| Purpose | Enhances business value and investor confidence | Motivates and honors contributions and performance |
| Scope | Corporate and financial domain | Employee and social domains |
| Nature | Long-term, intangible asset | Short- to mid-term acknowledgment |
| Measurement | Quantified in financial statements as asset value | Measured by awards, certificates, or verbal praise |
| Impact on Respect | Builds sustained respect through reputation | Generates immediate respect and motivation |
Understanding Goodwill: Definition and Importance
Goodwill represents the intangible asset arising when a company acquires another for more than the fair value of its net identifiable assets, reflecting brand reputation, customer loyalty, and intellectual property. Recognition of goodwill on financial statements is crucial for accurate company valuation and informs stakeholders about potential future earnings beyond tangible assets. Your understanding of goodwill helps in assessing business acquisitions and investment decisions, highlighting its significant role in financial analysis and strategic planning.
What is Recognition in Business Context?
Recognition in a business context refers to the formal acknowledgment or appreciation of an employee's achievements, contributions, or performance, which boosts motivation and morale. It differs from goodwill, which is an intangible asset representing a company's reputation and customer loyalty acquired through positive business relations. While goodwill reflects external brand value, recognition focuses internally on rewarding individuals or teams to enhance productivity and engagement.
Key Differences Between Goodwill and Recognition
Goodwill represents the intangible asset arising from a company's reputation and customer relationships, while recognition refers to the acknowledgment of achievements or contributions by individuals or organizations. The key difference lies in goodwill's financial and accounting implications as an asset on the balance sheet, contrasting with recognition's role in motivation and morale without direct monetary valuation. Goodwill impacts company valuation during acquisitions, whereas recognition enhances employee engagement and organizational culture.
How Goodwill Impacts Business Value
Goodwill significantly impacts business value by representing intangible assets such as brand reputation, customer loyalty, and intellectual property that exceed the fair market value of a company's net identifiable assets. Recognition of goodwill in financial statements enhances investor confidence by reflecting the company's potential for sustained earnings and competitive advantage. Proper valuation of goodwill ensures accurate business valuation during mergers and acquisitions, influencing pricing, negotiation, and future growth opportunities.
Types of Recognition in Organizations
Organizations use various types of recognition to enhance employee engagement and goodwill, including formal recognition, informal recognition, peer-to-peer recognition, and performance-based rewards. Formal recognition often involves structured programs such as employee of the month awards or service milestone celebrations, which contribute to building goodwill by acknowledging consistent contributions. Informal and peer-to-peer recognition foster a supportive work culture by encouraging spontaneous appreciation and collaboration, further strengthening organizational goodwill and motivation.
Goodwill in Accounting: Measurement and Reporting
Goodwill in accounting represents the intangible value arising from business acquisitions, reflecting factors such as brand reputation, customer loyalty, and intellectual property exceeding the fair market value of identifiable net assets. Measurement of goodwill involves calculating the excess of purchase consideration over the net identifiable assets acquired, requiring thorough due diligence and fair value assessments at the acquisition date. Reporting goodwill mandates annual impairment testing under standards like IFRS and GAAP, ensuring accurate reflection of its recoverable amount and preventing overstatement of company assets on financial statements.
The Role of Employee Recognition in Workplace Culture
Employee recognition plays a pivotal role in enhancing workplace culture by fostering goodwill among team members, which boosts morale and productivity. Unlike goodwill as an intangible asset on a company's balance sheet, employee recognition directly influences interpersonal relationships and creates a positive environment where employees feel valued and motivated. Your organization benefits from implementing consistent recognition programs that strengthen goodwill by acknowledging individual contributions and promoting a culture of appreciation.
Goodwill vs Recognition: Real-World Examples
Goodwill often represents the intangible value a company gains from brand reputation, customer loyalty, and employee satisfaction, while recognition typically refers to the acknowledgment or appreciation of specific achievements or contributions. For example, when a business acquires another, the premium paid over the fair value of net assets is recorded as goodwill, reflecting expected future benefits; in contrast, an employee receiving an award for exceptional service illustrates recognition in action. Your understanding of these concepts can clarify financial statements and enhance motivation within organizational cultures.
Best Practices for Enhancing Goodwill and Recognition
Enhancing goodwill and recognition in your organization involves consistently delivering exceptional value and fostering genuine relationships with stakeholders. Best practices include personalized appreciation, transparent communication, and aligning recognition programs with your company values to create meaningful and lasting positive impressions. Your efforts should focus on building trust and emotional connections that differentiate your brand and reinforce goodwill effectively.
Strategic Benefits of Goodwill and Recognition for Long-Term Success
Goodwill enhances your brand reputation by fostering trust and loyalty, leading to sustained customer relationships and increased market value. Recognition motivates employees and stakeholders, boosting productivity and engagement that drive innovation and competitive advantage. Combining goodwill and recognition strategically supports long-term success through strengthened brand identity and a committed workforce.
Infographic: Goodwill vs Recognition
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com