Nonviolence fosters understanding and lasting peace by addressing conflicts through dialogue and empathy, whereas violence often escalates tensions and causes harm. Discover comprehensive insights on cultivating nonviolent relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
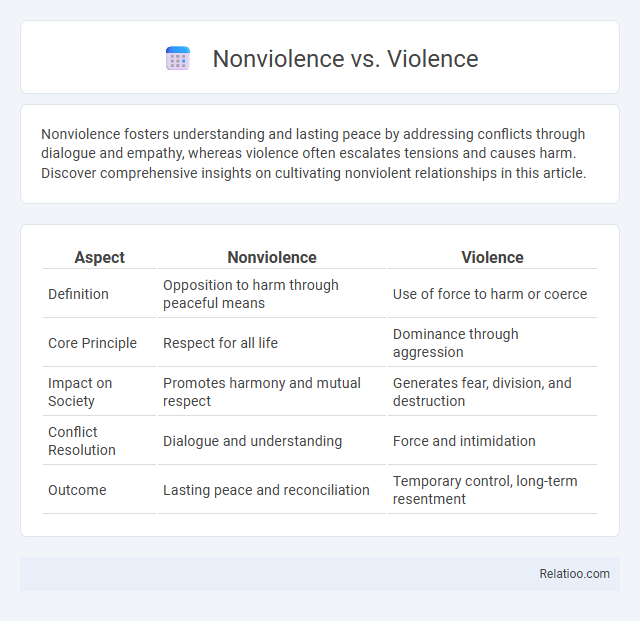
| Aspect | Nonviolence | Violence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Opposition to harm through peaceful means | Use of force to harm or coerce |
| Core Principle | Respect for all life | Dominance through aggression |
| Impact on Society | Promotes harmony and mutual respect | Generates fear, division, and destruction |
| Conflict Resolution | Dialogue and understanding | Force and intimidation |
| Outcome | Lasting peace and reconciliation | Temporary control, long-term resentment |
Understanding Nonviolence: Principles and Philosophy
Understanding nonviolence involves embracing principles rooted in respect, empathy, and active resistance without harm. It emphasizes the power of peaceful actions to achieve social change by appealing to moral conscience and fostering dialogue instead of conflict. Your commitment to nonviolence encourages transformative justice and sustainable peace through compassion and intentional restraint.
Defining Violence: Forms and Motivations
Violence manifests in physical, psychological, and structural forms, each driven by motivations such as power, control, or defense. Nonviolence rejects these harmful tactics, emphasizing peaceful resistance and compassion as tools for social change. Your understanding of violence's complexities can empower more effective advocacy for lasting peace.
Historical Perspectives on Nonviolence and Violence
Historical perspectives on nonviolence and violence reveal profound impacts on social and political movements worldwide. Nonviolence, notably championed by leaders like Mahatma Gandhi and Martin Luther King Jr., has demonstrated enduring success in achieving civil rights and independence through peaceful resistance. Conversely, violent uprisings, while sometimes accelerating political change, often result in prolonged conflict and societal disruption, underscoring the complex dynamics between these opposing strategies in shaping history.
Comparative Success of Nonviolent vs Violent Movements
Nonviolent movements have demonstrated a higher success rate, with a study by Erica Chenoweth showing that 53% of violent campaigns achieve their objectives compared to 26% for violent ones. Nonviolent resistance tends to attract broader participation, including diverse social groups, which enhances legitimacy and pressure on opponents. Furthermore, nonviolent movements often result in more stable and democratic post-conflict outcomes, reducing the likelihood of renewed violence.
Psychological Roots of Violent and Nonviolent Actions
The psychological roots of violent actions often stem from unresolved anger, fear, and a need for control, whereas nonviolent behaviors are typically grounded in empathy, self-regulation, and moral conviction. Your ability to choose nonviolence relies on cultivating emotional intelligence and recognizing the deeper motivations behind aggression. Understanding these contrasting psychological drivers helps in fostering peaceful conflict resolution and reducing the inclination toward violent responses.
The Role of Leadership in Shaping Protest Strategies
Leadership plays a crucial role in shaping protest strategies by determining whether movements adopt nonviolence or violence as their approach. Effective leaders prioritize nonviolent methods to maintain moral high ground, attract broader support, and achieve sustainable social change. Your understanding of leadership dynamics can influence how protests are organized, ensuring that strategic decisions align with long-term goals for justice and peace.
Societal Impacts: Nonviolence vs Violence Outcomes
Societal impacts of nonviolence include the promotion of social cohesion, sustainable conflict resolution, and long-term peace, while violence often leads to widespread destruction, social fragmentation, and perpetuated cycles of retaliation. Your commitment to nonviolent methods encourages dialogue, strengthens community resilience, and fosters environments where justice can be achieved without further harm. Data shows that societies embracing nonviolence experience lower rates of crime and greater political stability compared to those entrenched in violent conflict.
Media Representation of Nonviolent and Violent Acts
Media representation of nonviolent and violent acts shapes public perception by emphasizing different narratives and emotional responses. Violent acts often receive sensational coverage that highlights conflict and chaos, while nonviolent actions are portrayed through themes of resilience and moral strength, influencing societal attitudes toward each approach. Studies show that biased media framing can either legitimize aggression or inspire peaceful protest, affecting policy and social movements.
Ethical Considerations: Justifying Means and Ends
Nonviolence prioritizes ethical integrity by rejecting harm and emphasizing peaceful resistance as a means to achieve justice, aligning with moral principles that avoid suffering. Violence often raises complex ethical dilemmas, as it can produce immediate results but at the cost of human rights violations and long-term societal harm. Ethical considerations in justifying means and ends demand evaluating whether the pursuit of goals legitimizes the use of force or whether nonviolent methods better uphold human dignity and sustainable peace.
Pathways Forward: Building a Culture of Nonviolence
Building a culture of nonviolence requires embracing education, empathy, and conflict resolution strategies that prioritize understanding and mutual respect. Community programs promoting dialogue and restorative justice serve as effective pathways to reduce violence and foster social cohesion. Investing in equitable policies and empowering marginalized groups strengthens the foundation for sustainable peace and nonviolent coexistence.
Infographic: Nonviolence vs Violence
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com