Detachment involves emotionally distancing oneself to avoid dependency, while nonattachment fosters a balanced connection without clinging or aversion. Explore the nuances and benefits of detachment versus nonattachment in this article.
Table of Comparison
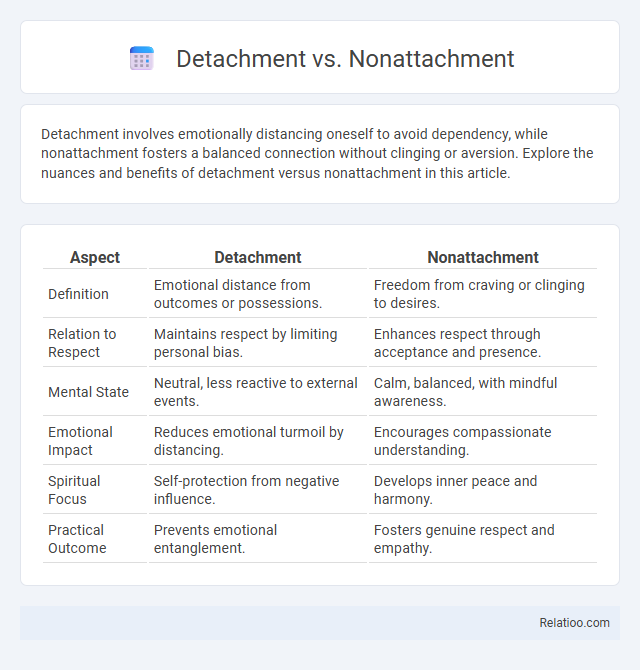
| Aspect | Detachment | Nonattachment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional distance from outcomes or possessions. | Freedom from craving or clinging to desires. |
| Relation to Respect | Maintains respect by limiting personal bias. | Enhances respect through acceptance and presence. |
| Mental State | Neutral, less reactive to external events. | Calm, balanced, with mindful awareness. |
| Emotional Impact | Reduces emotional turmoil by distancing. | Encourages compassionate understanding. |
| Spiritual Focus | Self-protection from negative influence. | Develops inner peace and harmony. |
| Practical Outcome | Prevents emotional entanglement. | Fosters genuine respect and empathy. |
Understanding Detachment and Nonattachment
Detachment involves maintaining emotional distance to avoid being overwhelmed by external circumstances, promoting objective thinking and mental clarity. Nonattachment emphasizes an internal state where one does not cling to desires, outcomes, or possessions, fostering acceptance and inner peace. Understanding detachment and nonattachment requires recognizing that detachment relates more to emotional regulation, while nonattachment centers on deeper spiritual freedom and letting go of ego-driven cravings.
Key Differences Between Detachment and Nonattachment
Detachment involves creating emotional distance to avoid being overwhelmed by situations, often leading to suppression of feelings, while nonattachment encourages embracing experiences without clinging or aversion, fostering inner peace and balance. Your practice of nonattachment allows you to remain present and engaged without dependence on outcomes, contrasting with detachment's tendency toward disconnection. Understanding these key differences helps cultivate emotional resilience and mindful awareness in daily life.
Historical Roots of Detachment and Nonattachment
Detachment and nonattachment both stem from ancient philosophical and spiritual traditions, with detachment rooted primarily in Stoicism, emphasizing emotional resilience by controlling desires and reactions. Nonattachment originates mainly from Eastern philosophies such as Buddhism and Hinduism, advocating freedom from attachment to transient worldly possessions and ego to achieve enlightenment. Understanding these historical roots can deepen your practice by clarifying how different cultures approach inner peace and freedom.
Psychological Impact of Detachment vs Nonattachment
Detachment involves emotionally distancing oneself from situations or people, often leading to numbness or avoidance, whereas nonattachment signifies a mindful state of acceptance without clinging, promoting emotional resilience and mental clarity. Psychological studies show nonattachment correlates with lower anxiety and depression by fostering present-moment awareness and reducing rumination. In contrast, detachment can result in interpersonal difficulties and emotional disengagement, highlighting the therapeutic benefits of cultivating nonattachment over detachment.
Misconceptions About Letting Go
Misconceptions about letting go often confuse detachment, nonattachment, and indifference, leading to misunderstandings about emotional health. Detachment involves maintaining emotional boundaries without becoming overwhelmed, while nonattachment cultivates a balanced relationship with desires and outcomes, promoting inner peace without ignoring responsibilities. Your practice of nonattachment is not about suppressing feelings but about freeing yourself from unhealthy clinging, fostering a more mindful and resilient approach to life's challenges.
Benefits of Practicing Nonattachment
Practicing nonattachment cultivates emotional resilience and reduces stress by encouraging acceptance of life's impermanence and uncontrollable outcomes. Unlike detachment, which may involve withdrawal or numbness, nonattachment fosters a balanced engagement with experiences, promoting inner peace and clarity. Embracing nonattachment enhances mental well-being and supports healthier relationships through greater empathy and reduced dependency.
Signs of Unhealthy Detachment
Unhealthy detachment often manifests as emotional numbness, avoidance of relationships, and difficulty processing feelings, leading to isolation and impaired social connections. Unlike healthy nonattachment, which promotes balanced emotional engagement without clinging, unhealthy detachment results in withdrawal and suppressed emotions. Recognizing these signs, such as persistent indifference and disconnection from personal experiences, is crucial for mental well-being and fostering genuine relationships.
How to Cultivate Nonattachment in Daily Life
Cultivating nonattachment in daily life involves practicing mindfulness to observe thoughts and emotions without clinging or aversion, fostering emotional balance and clarity. Engaging in regular meditation and reflecting on impermanence helps reduce the tendency toward excessive attachment to outcomes, possessions, or relationships. Adopting a flexible mindset that embraces change and accepts uncertainty supports the development of nonattachment, promoting inner peace and resilience.
Detachment vs Nonattachment in Relationships
Detachment in relationships often implies emotional withdrawal or indifference, creating distance that can hinder intimacy and connection. Nonattachment, however, encourages maintaining love and care without clinging or dependency, promoting healthy boundaries while allowing your emotions to flow freely. Understanding the difference between detachment and nonattachment helps you cultivate balanced relationships built on trust and freedom rather than control or avoidance.
Integrating Nonattachment for Personal Growth
Integrating nonattachment into personal growth cultivates emotional resilience by encouraging acceptance of change without clinging to outcomes, unlike detachment which may suggest emotional withdrawal. Nonattachment promotes mindful awareness and presence, allowing individuals to engage fully with experiences while maintaining inner freedom from dependency on external validations. This balanced approach fosters a grounded sense of self, enabling growth through clarity, reduced suffering, and enhanced well-being.
Infographic: Detachment vs Nonattachment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com