Equanimity in relationships involves maintaining calm and balanced emotions during conflicts, fostering understanding and resilience. Indifference, however, reflects emotional detachment that can create distance and hinder connection; discover more insights on balancing these states in this article.
Table of Comparison
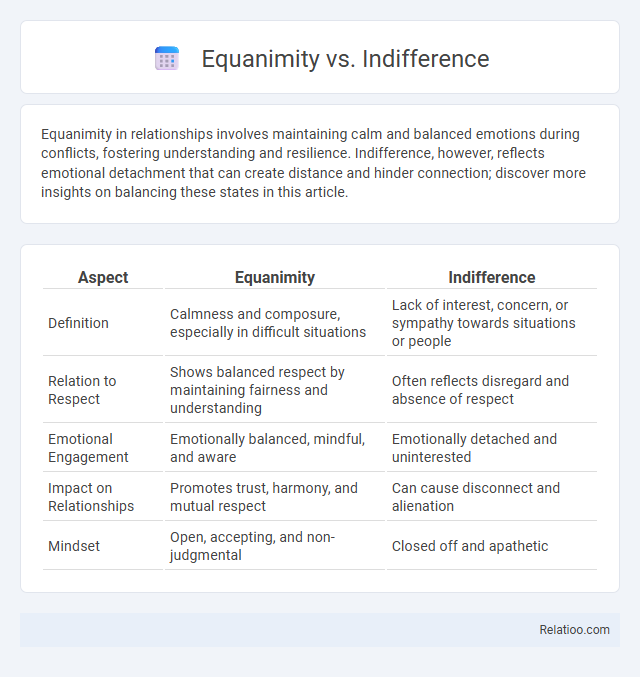
| Aspect | Equanimity | Indifference |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Calmness and composure, especially in difficult situations | Lack of interest, concern, or sympathy towards situations or people |
| Relation to Respect | Shows balanced respect by maintaining fairness and understanding | Often reflects disregard and absence of respect |
| Emotional Engagement | Emotionally balanced, mindful, and aware | Emotionally detached and uninterested |
| Impact on Relationships | Promotes trust, harmony, and mutual respect | Can cause disconnect and alienation |
| Mindset | Open, accepting, and non-judgmental | Closed off and apathetic |
Understanding Equanimity: Definition and Core Principles
Equanimity is a mental state characterized by calmness, composure, and even-mindedness, especially in difficult situations, distinguishing it clearly from indifference, which implies a lack of concern or emotional engagement. Core principles of equanimity include acceptance, non-reactivity, and balance, enabling you to maintain inner peace without detachment or apathy. Understanding these nuances helps in cultivating emotional resilience and improving your ability to respond thoughtfully rather than react impulsively.
What is Indifference? Key Characteristics Explained
Indifference is a state of emotional detachment where you remain unaffected by positive or negative events, showing a lack of interest or concern. Unlike equanimity, which involves balanced and mindful acceptance of experiences without being overwhelmed, indifference reflects apathy or disengagement. Key characteristics of indifference include emotional numbness, avoidance of conflict or discomfort, and an absence of motivation to act or respond.
The Emotional Landscape: Equanimity vs Indifference
Equanimity embodies a balanced emotional state marked by calmness and resilience, allowing individuals to face challenges without excessive reactivity. Indifference reflects a lack of emotional engagement or concern, often leading to emotional detachment or apathy. Unlike indifference, equanimity nurtures mindful awareness and acceptance, fostering emotional stability rather than emotional disengagement.
Psychological Benefits of Equanimity
Equanimity fosters emotional resilience by allowing you to maintain mental calmness and composure in the face of stress or adversity, unlike indifference, which implies a lack of concern or emotional engagement. Its psychological benefits include enhanced stress management, improved emotional regulation, and increased mindfulness, leading to better overall mental health. Cultivating equanimity enables balanced responses to life's challenges without the apathy associated with indifference, supporting sustained psychological well-being.
The Hidden Risks of Indifference
Indifference, unlike equanimity, signals a lack of emotional engagement that can obscure critical ethical and social responsibilities, leading to disengagement from important issues. Equanimity maintains balanced emotional regulation, promoting resilience without apathy, while indifference risks neglecting empathy and active problem-solving. The hidden risks of indifference include erosion of social cohesion and impaired decision-making in both personal and organizational contexts.
Why Equanimity is Not Emotional Detachment
Equanimity is a balanced mental state characterized by calmness and clarity, allowing one to experience emotions without being overwhelmed, unlike indifference, which involves a lack of concern or emotional engagement. Unlike emotional detachment that often implies suppression or avoidance of feelings, equanimity embraces emotions with mindful awareness and acceptance. Research in psychology highlights that equanimity supports resilience and emotional regulation by fostering an open, non-judgmental attitude toward experiences rather than emotional numbness.
Indifference: A Barrier to Compassion and Connection
Indifference serves as a significant barrier to compassion and connection by creating emotional detachment and apathy towards others' experiences, preventing genuine empathy from forming. Unlike equanimity, which fosters balanced awareness and acceptance of emotions without judgment, indifference dismisses the importance of others' feelings, leading to social isolation and weakened relationships. Cultivating equanimity promotes emotional resilience and compassionate engagement, contrasting sharply with the disengagement inherent in indifference.
Cultivating Equanimity in Daily Life
Cultivating equanimity in daily life involves maintaining mental calmness and emotional balance despite external challenges, distinguishing it from indifference, which implies a lack of concern or engagement. Practices such as mindfulness meditation, gratitude journaling, and conscious breathing enhance equanimity by fostering a non-reactive awareness and acceptance of present experiences. Developing equanimity supports resilience, reduces stress, and promotes well-being through balanced responses to both positive and negative events.
Recognizing and Overcoming Indifference
Recognizing and overcoming indifference is crucial for cultivating true equanimity, which involves maintaining mental calmness and emotional balance without detachment or apathy. Indifference reflects a lack of concern or emotional engagement, whereas equanimity allows you to face challenges with clear awareness and compassion. Developing this mindset improves your emotional resilience, enabling you to respond thoughtfully rather than react passively.
Embracing Equanimity for Personal Growth and Well-Being
Embracing equanimity involves maintaining mental calmness and emotional balance during life's challenges, which fosters personal growth and well-being by reducing stress and enhancing resilience. Unlike indifference, which implies a lack of concern or emotional detachment, equanimity promotes mindful awareness and balanced engagement with experiences. Practicing equanimity supports emotional regulation and clarity, offering a foundation for sustainable mental health and meaningful self-improvement.
Infographic: Equanimity vs Indifference
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com