In relationships, the subject represents the individual with agency and emotions, while the object often embodies the recipient of interactions or feelings. Explore deeper insights into the dynamics of subject versus object roles in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
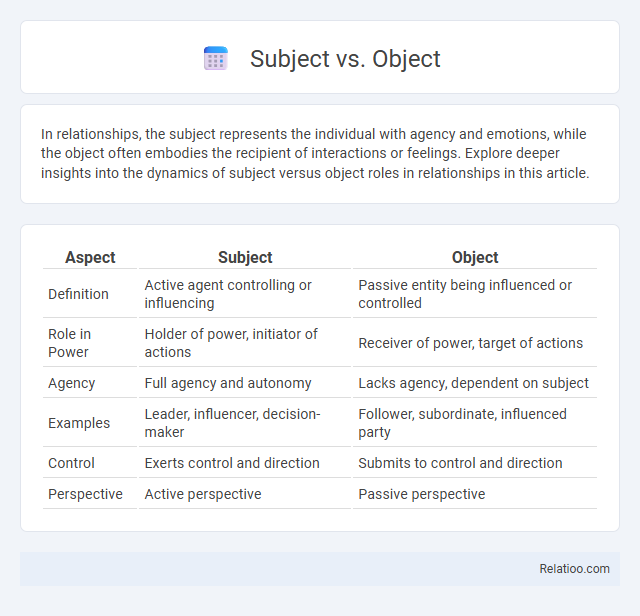
| Aspect | Subject | Object |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active agent controlling or influencing | Passive entity being influenced or controlled |
| Role in Power | Holder of power, initiator of actions | Receiver of power, target of actions |
| Agency | Full agency and autonomy | Lacks agency, dependent on subject |
| Examples | Leader, influencer, decision-maker | Follower, subordinate, influenced party |
| Control | Exerts control and direction | Submits to control and direction |
| Perspective | Active perspective | Passive perspective |
Understanding the Concepts: Subject vs Object
Understanding the concepts of subject and object is essential in analyzing relationships and perspectives in various disciplines, including philosophy, linguistics, and social sciences. The subject refers to the entity that experiences, perceives, or performs an action, while the object is the entity that is acted upon or observed. Your ability to distinguish between subject and object enhances critical thinking and promotes a deeper awareness of how meaning and agency are assigned in communication and social interactions.
Definitions: What is a Subject?
A subject is the entity performing an action or being described in a sentence, typically the focus of a clause that controls the verb. In grammar and philosophy, the subject is the conscious agent or observer experiencing or initiating actions, distinguished from objects that receive actions. Understanding the role of the subject in language and thought helps clarify how your perspective and agency shape interactions with the world.
Definitions: What is an Object?
An object is a noun or pronoun that receives the action of a verb or shows the result of the action in a sentence, serving as the target of the verb's effect. In grammar, objects can be direct, receiving the action directly, or indirect, benefiting from or affected by the action. Understanding what an object is helps clarify sentence structure and improve your communication skills by accurately identifying who or what is involved in the action.
Grammatical Roles: Subject and Object in Sentences
The subject in a sentence typically performs the action and is often the noun or pronoun before the verb, while the object receives the action and usually follows the verb. Understanding the distinction between subject and object is fundamental in grammar to determine sentence structure, clarity, and meaning. Objectification occurs when an object is treated as a subject, altering the focus or agency within the sentence, especially in semantic or syntactic analyses.
Subject vs Object: Key Differences
Subjects perform actions or experience states in a sentence, typically serving as the doer or focus of the action, while objects receive the action or are affected by it, functioning as the target or recipient. The subject usually appears before the verb and determines verb agreement, whereas the object follows the verb and often answers questions like "whom?" or "what?". Understanding the distinction between subject and object clarifies sentence structure and enhances grammatical accuracy in both spoken and written language.
Types of Objects: Direct and Indirect Objects
Direct objects receive the action of a verb directly, answering "what?" or "whom?" in a sentence, while indirect objects indicate to whom or for whom the action is performed. Your understanding of grammar improves by distinguishing these objects, as the direct object clarifies the focus of the verb and the indirect object adds recipient or beneficiary context. Mastering how subjects relate to objects and how objectification transforms entities into objects enhances sentence structure and meaning precision.
Identifying Subjects and Objects in Examples
Identifying subjects and objects involves recognizing that the subject performs the action while the object receives it, such as in "The cat (subject) chased the mouse (object)." In sentences like "She gave him a gift," "she" is the subject, "him" is the indirect object, and "a gift" is the direct object. Objectification occurs when a person or group is treated as an object, stripping away agency or subjectivity, often analyzed in social and linguistic contexts.
Common Mistakes: Subject vs Object Confusion
Common mistakes in distinguishing subject vs object often arise from misunderstanding their grammatical roles; the subject performs the action, while the object receives it. Confusing these roles leads to errors in sentence clarity, such as misusing pronouns like "he" instead of "him" when referring to objects. Correct identification of subjects and objects is crucial for constructing grammatically sound and semantically clear sentences.
Importance of Subjects and Objects in Language
Subjects and objects are foundational elements in language structure, defining who performs an action and who receives it, which clarifies meaning and ensures effective communication. Understanding the distinction between subjects and objects allows you to construct sentences that accurately convey intent and relationships. Objectification occurs when objects are deprived of their agency, making awareness of these roles essential for maintaining respect and clarity in language use.
Subject vs Object: Tips for Mastery
Mastering the difference between Subject and Object enhances your understanding of sentence structure by recognizing that the Subject performs the action while the Object receives it. Identifying clear Subjects and Objects in your writing improves clarity and precision, helping you construct impactful statements. Practice locating Subjects and Objects in varied sentences to solidify your grammatical skills effectively.
Infographic: Subject vs Object
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com