Understanding the difference between entitlement and rights is crucial for healthy relationships, as entitlement implies an expectation without basis, while rights are legitimate claims based on mutual respect and fairness. Explore this article to learn how recognizing these distinctions can improve communication and trust in your relationships.
Table of Comparison
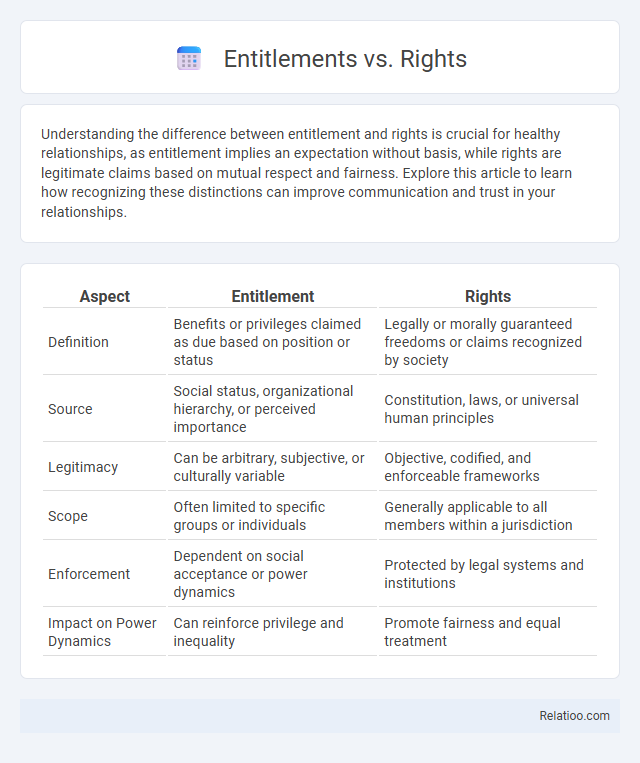
| Aspect | Entitlement | Rights |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Benefits or privileges claimed as due based on position or status | Legally or morally guaranteed freedoms or claims recognized by society |
| Source | Social status, organizational hierarchy, or perceived importance | Constitution, laws, or universal human principles |
| Legitimacy | Can be arbitrary, subjective, or culturally variable | Objective, codified, and enforceable frameworks |
| Scope | Often limited to specific groups or individuals | Generally applicable to all members within a jurisdiction |
| Enforcement | Dependent on social acceptance or power dynamics | Protected by legal systems and institutions |
| Impact on Power Dynamics | Can reinforce privilege and inequality | Promote fairness and equal treatment |
Understanding the Concepts: Entitlement vs Rights
Entitlement refers to the guaranteed access to benefits or privileges based on legal or policy provisions, while rights represent fundamental freedoms or claims inherently possessed by individuals as recognized by law or moral principles. Understanding the distinction between entitlement and rights is crucial in legal and social contexts, as entitlements often depend on specific qualifications or conditions, whereas rights are universal and inalienable. This conceptual clarity helps in navigating policy frameworks, ensuring proper allocation of resources, and protecting individual freedoms within society.
Historical Evolution of Rights and Entitlements
The historical evolution of rights and entitlements reflects the gradual recognition of individual freedoms and social justice, marked by events such as the Magna Carta, the Enlightenment, and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Rights originated as legal guarantees protecting individuals from state power, while entitlements evolved as specific benefits or services granted by governments or institutions to support welfare and citizenship. Over time, the distinction between rights as inherent claims and entitlements as granted provisions has shaped modern legal and social frameworks.
Legal Definitions: Clarifying Entitlements and Rights
Entitlements refer to specific benefits or privileges granted by law, often tied to eligibility criteria such as social security or unemployment benefits. Rights are fundamental legal guarantees protected by constitutional or statutory laws, including freedom of speech or the right to a fair trial. Understanding the distinction empowers you to accurately assert your legal protections and access your entitled benefits.
Cultural Perspectives on Entitlement and Rights
Cultural perspectives on entitlement and rights vary widely, shaping how societies define and prioritize individual and collective claims. In some cultures, rights are viewed as universal principles, whereas entitlements are linked to social roles and responsibilities within community frameworks. Your understanding of these distinctions can influence how you navigate legal, social, and ethical environments across different cultural contexts.
Common Misconceptions Between Entitlement and Rights
Entitlement and rights are often confused, but they differ fundamentally: rights are legally or morally guaranteed claims inherent to individuals, while entitlements are benefits granted by institutions based on specific criteria. Common misconceptions arise when people perceive entitlements as universal rights, leading to disputes over what is considered fair or justified. Clarity in distinguishing legal rights from socially or economically defined entitlements helps prevent misunderstandings in policy and personal expectations.
Social Impacts of Confusing Entitlements with Rights
Confusing entitlements with rights often leads to social discord as individuals may perceive guaranteed benefits as inherent freedoms, undermining mutual respect and societal trust. This misinterpretation fosters entitlement mentalities where people expect benefits without corresponding responsibilities, destabilizing social cohesion and increasing resource conflicts. Your awareness of the distinction between legal rights and conditional entitlements enhances social harmony by promoting fair expectations and encouraging responsible citizenship.
Entitlement in the Workplace vs Employee Rights
Entitlement in the workplace refers to the specific benefits or privileges employees expect based on company policies or employment contracts, such as paid leave or flexible hours, while employee rights are legally protected guarantees, including workplace safety and non-discrimination. Understanding the distinction is crucial, as entitlements can vary by employer and role, whereas rights are enforceable by law and provide a baseline of employee protection. Employers must balance honoring entitlements with ensuring compliance with labor laws that safeguard employee rights to foster a fair and productive work environment.
Government Policies: Rights Granted vs Entitlements Allowed
Government policies distinguish rights as fundamental guarantees protected by law, whereas entitlements represent benefits or services your government allows based on eligibility criteria. Rights, such as freedom of speech or voting, are inalienable and enforceable, while entitlements like social security or unemployment benefits depend on meeting specific requirements. Understanding this distinction helps you navigate what is guaranteed versus what is conditional in government provisions.
Balancing Individual Rights and Social Entitlements
Balancing individual rights and social entitlements requires understanding that rights are inherent freedoms protected by law, while entitlements are benefits granted by social systems or governments. Individual rights ensure personal autonomy and freedom, whereas entitlements provide necessary resources or services like healthcare and education to support social welfare. Effective policy frameworks harmonize these concepts to uphold personal liberties while promoting equitable access to communal benefits.
Moving Forward: Fostering Responsible Rights Awareness
Promoting responsible rights awareness involves distinguishing between entitlements, legal rights, and social entitlements, emphasizing their respective roles in society. Clear understanding of legal rights ensures individuals know their protections under law, while recognizing social entitlements encourages equitable access to resources and opportunities. Moving forward, education and policy must focus on integrating these concepts to foster informed citizens who respect both their privileges and responsibilities.
Infographic: Entitlement vs Rights
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com