Mastery in relationships emphasizes mutual growth, respect, and empowerment, while subjugation involves control, dominance, and imbalance. Discover how to cultivate mastery and avoid subjugation for healthier connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
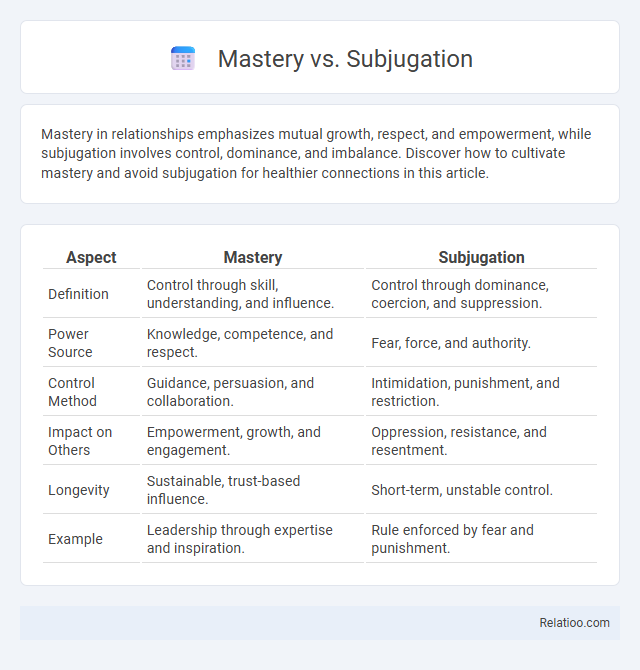
| Aspect | Mastery | Subjugation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Control through skill, understanding, and influence. | Control through dominance, coercion, and suppression. |
| Power Source | Knowledge, competence, and respect. | Fear, force, and authority. |
| Control Method | Guidance, persuasion, and collaboration. | Intimidation, punishment, and restriction. |
| Impact on Others | Empowerment, growth, and engagement. | Oppression, resistance, and resentment. |
| Longevity | Sustainable, trust-based influence. | Short-term, unstable control. |
| Example | Leadership through expertise and inspiration. | Rule enforced by fear and punishment. |
Understanding Mastery and Subjugation
Mastery involves exerting control through deep knowledge and skill, enabling influence without erasing the subject's identity. Subjugation enforces dominance by suppressing autonomy, often resulting in compliance through fear or coercion. Understanding mastery highlights the power of respect and expertise, while subjugation reveals the impact of enforced control and loss of freedom.
Historical Perspectives on Power Dynamics
Historical perspectives on power dynamics reveal Mastery as the ability to skillfully control and influence others through authority and respect. Subjugation describes the enforced domination where power suppresses opposition, often leading to social stratification and resistance movements. Obliteration, representing total annihilation of adversaries or cultures, marks the most extreme and destructive form of power, challenging Your understanding of dominance and control throughout history.
Psychological Foundations of Mastery
Mastery is grounded in psychological principles such as self-efficacy, intrinsic motivation, and cognitive control, enabling individuals to effectively regulate their actions and adapt to complex environments. This state contrasts with subjugation, which often involves external control and diminished autonomy, leading to decreased psychological resilience. Obliteration represents a total loss of agency, where mastery is absent, resulting in profound psychological disempowerment and disengagement.
The Roots and Consequences of Subjugation
Subjugation originates from systemic power imbalances where one group enforces control over another through political, economic, or social dominance, often rooted in historical colonization or oppression. The consequences of subjugation include loss of cultural identity, restricted access to resources, and entrenched inequality, perpetuating cycles of marginalization. These long-term effects hinder societal cohesion and fuel resistance movements aimed at reclaiming autonomy and rights.
Mastery in Personal Development
Mastery in personal development represents the pursuit of deep understanding and skill refinement to achieve self-mastery and optimize performance across various life domains. It involves intentional practice, continuous learning, and emotional regulation, enabling individuals to harness their potential and overcome limitations without resorting to dominance or suppression of others. Unlike subjugation or obliteration, mastery fosters sustainable growth, resilience, and empowerment through self-discipline and mindful awareness.
Subjugation in Social Structures
Subjugation in social structures signifies the systematic domination where one group enforces control over another through laws, economic disparity, and cultural hegemony, maintaining unequal power dynamics. This mechanism often results in marginalized communities experiencing restricted access to resources, political representation, and social mobility. The persistent nature of subjugation perpetuates cycles of inequality, reinforcing hierarchies that resist transformative change.
Balancing Authority and Empowerment
Mastery, Subjugation, and Obliteration represent distinct approaches to authority where Mastery emphasizes skillful control and expertise, Subjugation relies on dominance and coercion, and Obliteration aims at complete destruction or erasure of opposition. Achieving balance between authority and empowerment involves fostering your ability to guide and inspire others without suppressing their autonomy or resorting to harsh measures. This equilibrium ensures sustainable leadership, encouraging growth, collaboration, and resilience within any organizational or social structure.
Societal Impacts: From Oppression to Progress
Mastery, subjugation, and obliteration represent distinct societal dynamics with profound impacts on social structures and human rights. Mastery, when exercised ethically, can lead to leadership and progress by empowering communities and fostering innovation, whereas subjugation perpetuates systemic oppression, limiting individual freedoms and deepening social inequalities. Understanding these forces helps you recognize how eliminating oppressive practices can drive societal transformation towards justice and equity.
Cultivating Mastery over Subjugation in Leadership
Cultivating mastery in leadership emphasizes empowering teams through skill development, emotional intelligence, and adaptive strategies rather than relying on control or suppression of others. Mastery fosters collaboration and innovation by building trust and encouraging autonomy, contrasting sharply with subjugation's focus on dominance and obedience. Leaders who prioritize mastery create sustainable growth and resilience, avoiding the destructive outcomes associated with obliteration of dissent or diversity.
Fostering Mastery-Oriented Communities
Mastery-oriented communities thrive by emphasizing continuous learning, intrinsic motivation, and the valuing of effort over innate talent, fostering a growth mindset among members. Your role in promoting open feedback, collaboration, and recognition of progress helps shift focus away from subjugation, which enforces control and obedience, or obliteration, which seeks to erase individuality. Prioritizing mastery cultivates resilience, innovation, and long-term engagement within any community or organization.
Infographic: Mastery vs Subjugation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com