Excessive screen time significantly reduces reading comprehension and critical thinking skills, while regular reading enhances vocabulary and cognitive development. Explore this article to understand how balancing screen time and reading can improve your relationships.
Table of Comparison
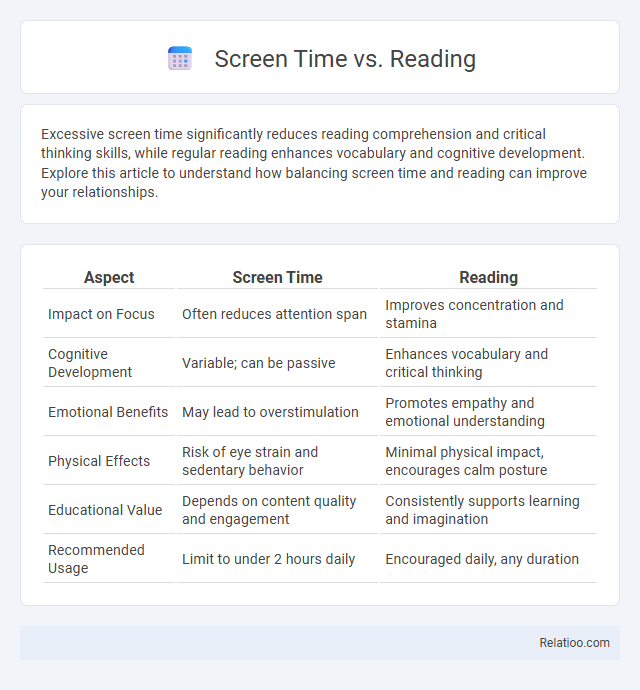
| Aspect | Screen Time | Reading |
|---|---|---|
| Impact on Focus | Often reduces attention span | Improves concentration and stamina |
| Cognitive Development | Variable; can be passive | Enhances vocabulary and critical thinking |
| Emotional Benefits | May lead to overstimulation | Promotes empathy and emotional understanding |
| Physical Effects | Risk of eye strain and sedentary behavior | Minimal physical impact, encourages calm posture |
| Educational Value | Depends on content quality and engagement | Consistently supports learning and imagination |
| Recommended Usage | Limit to under 2 hours daily | Encouraged daily, any duration |
Understanding Screen Time and Reading
Understanding screen time requires analyzing its impact on cognitive functions, eye health, and attention span, with research highlighting increased risks of digital eye strain and reduced focus during prolonged use. Reading, both print and digital, enhances vocabulary acquisition and comprehension skills while promoting deeper cognitive engagement compared to passive screen time activities. Balancing screen time with focused reading sessions optimizes mental stimulation, minimizes fatigue, and supports overall brain development.
Cognitive Impacts: Digital vs Print
Excessive screen time can strain your cognitive functions, reducing attention span and impairing memory retention compared to traditional reading. Reading print materials engages deep comprehension and critical thinking by minimizing distractions and promoting sustained focus. Balancing digital screen time with print reading optimizes cognitive health and enhances learning effectiveness.
Effects on Attention Span
Excessive screen time negatively impacts attention span by promoting rapid, fragmented information processing that reduces focus and patience for sustained tasks. In contrast, reading enhances cognitive engagement and concentration by requiring deeper mental immersion and sustained attention to comprehend complex narratives or arguments. Balancing screen exposure with regular reading practices supports healthier attention regulation and cognitive resilience.
Screen Time and Eye Health
Excessive screen time significantly contributes to digital eye strain, causing symptoms such as dry eyes, blurred vision, and headaches due to prolonged exposure to blue light emitted by screens. Reading physical books reduces the risk of eye fatigue by allowing natural focus shifts and minimizing harmful light exposure. Limiting daily screen time and incorporating regular breaks using the 20-20-20 rule can help maintain optimal eye health and prevent long-term vision problems.
Reading and Language Development
Reading significantly enhances language development by expanding vocabulary, improving syntax comprehension, and strengthening critical thinking skills. Unlike passive screen time, interactive reading sessions foster deeper cognitive engagement and better retention of language structures. Research shows that children exposed to regular reading experiences develop stronger language skills compared to those who primarily consume screen-based content.
Emotional Well-being: Books vs Devices
Reading books offers significant benefits for your emotional well-being by reducing stress and enhancing empathy through immersive storytelling and deep cognitive engagement. Excessive screen time, particularly on social media or digital devices, often correlates with increased anxiety, depression, and disrupted sleep patterns due to constant notifications and blue light exposure. Balancing screen time with regular reading can improve emotional regulation, promote mindfulness, and foster a healthier mental state.
Academic Performance: Comparing Outcomes
Screen time and reading have distinct impacts on your academic performance, with reading consistently linked to improved vocabulary, comprehension, and critical thinking skills. Excessive screen time, especially passive consumption, may hinder academic outcomes by reducing focus and increasing distractions. Balancing interactive screen use with dedicated reading time optimizes cognitive development and overall educational achievement.
Social Skills and Communication
Excessive screen time can impede social skills development by reducing face-to-face interactions and nonverbal communication cues critical for empathy and emotional understanding. Reading, particularly literature and narrative texts, enhances vocabulary, perspective-taking, and critical thinking, fostering more effective communication and social awareness. Balancing screen time with reading activities supports the growth of verbal and nonverbal communication competencies essential for successful social engagement.
Strategies for Balanced Media Use
Balancing screen time and reading requires setting clear limits on digital device usage while encouraging daily reading habits to promote cognitive development and reduce eye strain. Implementing scheduled breaks, using apps that monitor screen exposure, and creating tech-free zones or times can effectively manage media consumption for children and adults alike. Prioritizing educational and quality content during screen time complements traditional reading, fostering a well-rounded approach to media use.
Expert Recommendations and Guidelines
Experts recommend limiting screen time to no more than two hours per day for children to promote healthy development and reduce eye strain. Reading, particularly physical books, is encouraged as it enhances cognitive skills and fosters imagination without the negative impact of screen exposure. Guidelines from organizations like the American Academy of Pediatrics emphasize balancing screen time with offline activities such as reading to support overall well-being and academic success.
Infographic: Screen time vs Reading
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com