Parental rights emphasize guardians' authority to make decisions for their minors, while children's rights prioritize the child's autonomy and protection under international law. Explore the balance and conflicts between these rights in this article.
Table of Comparison
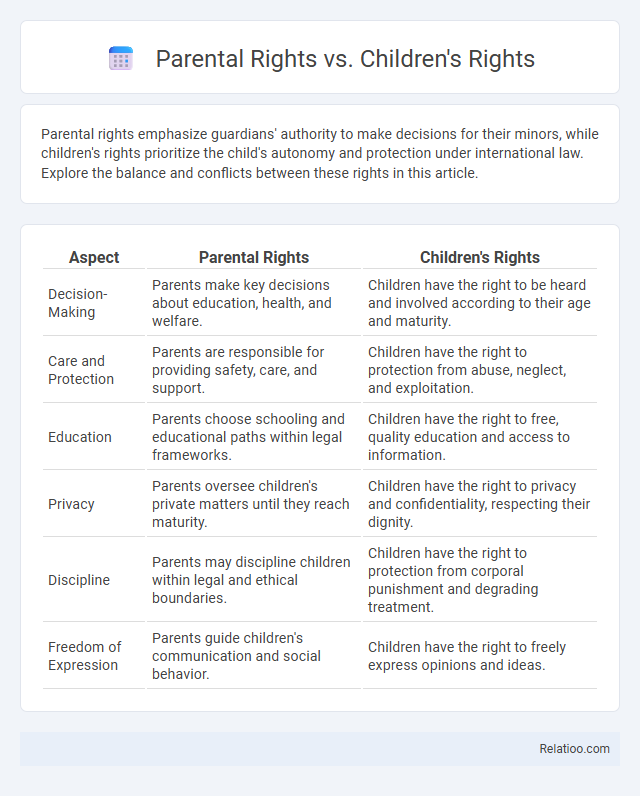
| Aspect | Parental Rights | Children's Rights |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Parents make key decisions about education, health, and welfare. | Children have the right to be heard and involved according to their age and maturity. |
| Care and Protection | Parents are responsible for providing safety, care, and support. | Children have the right to protection from abuse, neglect, and exploitation. |
| Education | Parents choose schooling and educational paths within legal frameworks. | Children have the right to free, quality education and access to information. |
| Privacy | Parents oversee children's private matters until they reach maturity. | Children have the right to privacy and confidentiality, respecting their dignity. |
| Discipline | Parents may discipline children within legal and ethical boundaries. | Children have the right to protection from corporal punishment and degrading treatment. |
| Freedom of Expression | Parents guide children's communication and social behavior. | Children have the right to freely express opinions and ideas. |
Understanding Parental Rights: Definition and Scope
Parental rights define the legal responsibilities and privileges parents hold over their children, including decisions about education, healthcare, and welfare. These rights coexist with children's rights, which protect the child's best interests and autonomy as they grow. Your understanding of parental authority clarifies how these rights balance parental control with the child's evolving rights and freedoms within the family structure.
Exploring Children’s Rights: Key Concepts
Children's rights encompass fundamental protections and freedoms designed to ensure their well-being, development, and participation in society, as outlined in international frameworks like the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child. Balancing these rights with parental rights and parental authority involves recognizing children as independent rights holders while maintaining parents' responsibility for care and guidance. Key concepts include the child's right to express their views, access education and healthcare, protection from abuse, and the state's role in safeguarding these rights when parental authority conflicts with the child's best interests.
Historical Evolution of Parental and Children’s Rights
The historical evolution of parental rights, children's rights, and parental authority reflects a gradual shift from absolute parental control toward recognizing children's individual rights within legal frameworks. Over centuries, laws have transitioned from viewing children solely as parental property to acknowledging their autonomy and protection, influenced by landmark legislations such as the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (1989). Your understanding of these evolving rights informs how modern legal systems balance parental authority with the safeguarding of children's well-being and freedoms.
Legal Frameworks: National and International Perspectives
National and international legal frameworks establish a balance between parental rights, children's rights, and parental authority by emphasizing the best interests of the child as a primary consideration. You must recognize that conventions such as the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC) provide comprehensive standards ensuring children's protection and participation, while national laws define the scope and limits of parental authority to safeguard welfare and development. Jurisdictions vary in how they interpret and enforce these rights, but the consensus prioritizes protecting children's fundamental rights without unduly undermining parental responsibilities.
Education Decisions: Parents’ Authority vs. Child Autonomy
Parental rights grant parents the legal authority to make education decisions based on their child's best interests, while children's rights emphasize autonomy and the right to participate in decisions affecting their learning. Parental authority is often upheld in legal systems, allowing parents to guide educational pathways, but courts increasingly recognize a child's evolving capacity to express preferences. You must balance respecting parental guidance with supporting your child's voice in educational choices to foster both development and rights protection.
Healthcare Choices: Balancing Consent and Protection
Balancing parental rights, children's rights, and parental authority in healthcare choices requires navigating legal and ethical frameworks that ensure your child's best interests while respecting their emerging autonomy. Healthcare consent laws often grant parents authority to make medical decisions for minors, yet as children mature, their rights to participate in healthcare decisions increase, emphasizing the need for collaborative communication. Protecting your child involves understanding age-specific consent regulations and prioritizing their well-being without undermining parental responsibility or the child's evolving capacity for informed consent.
Religious and Cultural Influences on Rights
Religious and cultural influences significantly shape the balance between parental rights, children's rights, and parental authority by dictating moral frameworks and decision-making processes within families. In many societies, religious doctrines empower parental authority to govern children's upbringing, often prioritizing parental rights over children's individual autonomy. Legal systems in these contexts may accommodate such traditions, creating complex intersections where children's rights, particularly in education and freedom of belief, intersect and occasionally conflict with parental authority grounded in religious and cultural norms.
Child Welfare Interventions: When Authorities Step In
Child welfare interventions prioritize children's rights to safety and well-being, often leading authorities to override parental rights and parental authority when neglect or abuse is suspected. Legal frameworks balance parental authority with state responsibility to protect children, ensuring interventions are justified and aimed at safeguarding the child's best interests. Cases involving child protection services highlight the tension between preserving family integrity and enforcing children's rights through mandated reporting and court-ordered custody changes.
Resolving Conflicts: Mediation and Legal Approaches
Resolving conflicts between parental rights, children's rights, and parental authority often involves mediation and legal approaches that prioritize the child's best interests while respecting familial roles. Family courts and child welfare agencies employ mediation to facilitate agreements that balance protection, autonomy, and parental responsibilities, aiming to reduce adversarial disputes. Legal frameworks emphasize child-centered outcomes, ensuring that decisions uphold children's rights to safety and participation alongside parental authority and rights.
Future Trends: Evolving Views on Family Rights
Future trends in family rights show a shift toward balancing parental rights, children's rights, and parental authority through more child-centric legal frameworks. Increasing recognition of children's autonomy influences reforms that prioritize the child's best interests while still respecting parental roles in decision-making. Digital advancements and global human rights movements drive evolving legislation to harmonize these rights in diverse cultural and legal contexts.
Infographic: Parental rights vs Children’s rights
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com