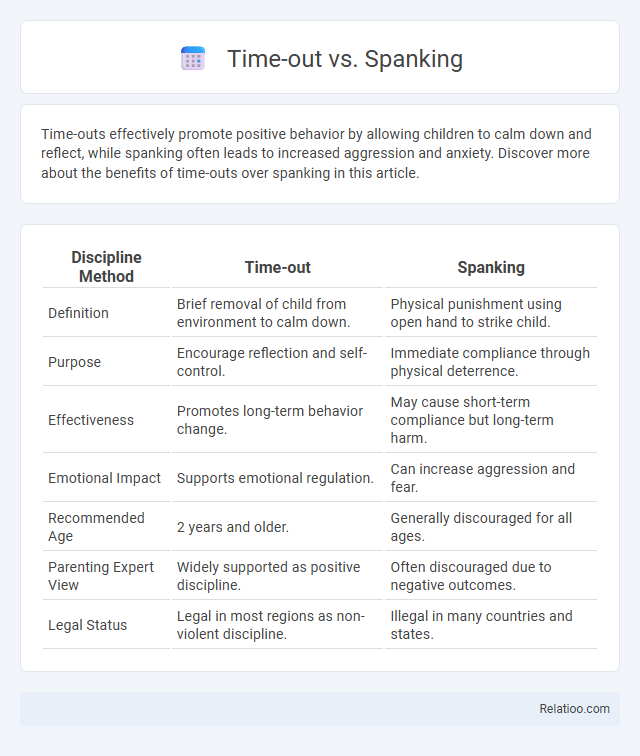
Time-outs effectively promote positive behavior by allowing children to calm down and reflect, while spanking often leads to increased aggression and anxiety. Discover more about the benefits of time-outs over spanking in this article.
Table of Comparison
| Discipline Method | Time-out | Spanking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Brief removal of child from environment to calm down. | Physical punishment using open hand to strike child. |
| Purpose | Encourage reflection and self-control. | Immediate compliance through physical deterrence. |
| Effectiveness | Promotes long-term behavior change. | May cause short-term compliance but long-term harm. |
| Emotional Impact | Supports emotional regulation. | Can increase aggression and fear. |
| Recommended Age | 2 years and older. | Generally discouraged for all ages. |
| Parenting Expert View | Widely supported as positive discipline. | Often discouraged due to negative outcomes. |
| Legal Status | Legal in most regions as non-violent discipline. | Illegal in many countries and states. |
Understanding Disciplinary Techniques: Time-Out vs Spanking
Time-out and spanking represent distinct disciplinary techniques, with time-out emphasizing removal of attention to reduce unwanted behavior, while spanking relies on physical punishment to deter misbehavior. Research consistently shows that time-out, when applied with discipline consistency, promotes better emotional regulation and long-term behavior improvement compared to spanking, which may lead to increased aggression and anxiety in children. Understanding the effectiveness of these methods highlights that consistent application of non-violent discipline techniques fosters healthier child development and stronger parent-child relationships.
Historical Context of Child Discipline
Time-out, spanking, and consistent discipline have evolved significantly within the historical context of child-rearing practices, reflecting shifts from corporal punishment to more structured behavioral strategies. Spanking, once widely accepted across cultures as a primary disciplinary method, faces increasing scrutiny due to psychological research linking it to negative outcomes, whereas time-outs emerged in the mid-20th century as a non-violent method promoting self-regulation. Your approach to discipline benefits from understanding these historical shifts, emphasizing consistency to foster secure and positive behavioral development in children.
Psychological Impact of Time-Out
Time-out as a disciplinary technique helps children regulate emotions by providing a structured pause that encourages self-reflection and calming, reducing immediate stress and promoting better long-term behavioral control. Unlike spanking, which may increase aggression and anxiety, consistent use of time-out supports emotional development by reinforcing boundaries without physical punishment. Psychological studies indicate that discipline consistency in applying time-outs enhances a child's sense of security and trust, contributing positively to their emotional resilience and mental health.
Psychological Impact of Spanking
Spanking, unlike time-outs and consistent discipline strategies, can lead to increased aggression and anxiety in children due to its punitive nature. Psychological studies indicate that spanking may undermine your child's sense of security and trust, potentially causing long-term emotional harm. Consistent discipline methods such as time-outs promote self-regulation and healthier behavioral outcomes by teaching accountability without the negative psychological impact of physical punishment.
Short-term vs Long-term Behavioral Outcomes
Time-out, spanking, and discipline consistency each influence short-term and long-term behavioral outcomes differently. Time-out promotes immediate behavior correction without physical harm, while spanking may yield quick compliance but risks fostering aggression and fear over time. Your consistent use of structured, non-violent discipline strategies is crucial for cultivating lasting positive behaviors and emotional regulation in children.
Parental Perspectives and Cultural Influences
Parental perspectives on time-out versus spanking vary significantly across cultures, impacting discipline consistency and child behavior outcomes. Time-out is often favored in Western societies for promoting self-regulation and emotional control, while spanking persists in some cultures emphasizing immediate obedience and traditional authority. Cultural values shape parental discipline strategies, affecting both the frequency and perceived effectiveness of these methods in fostering long-term behavior management.
Expert Opinions: Pediatricians and Psychologists
Pediatricians and psychologists emphasize that consistent discipline strategies, such as time-outs, are more effective and less harmful than spanking, as they promote self-regulation and understanding of consequences. Experts caution that spanking can increase aggression and anxiety in children, while regular, calm time-outs help reinforce boundaries without emotional damage. Consensus among specialists highlights consistency and positive reinforcement as crucial components for healthy child development and behavior management.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Discipline
Time-out methods align with legal frameworks emphasizing non-physical discipline, reducing risks of physical abuse allegations and promoting ethical child-rearing practices. Spanking, while legally permitted in some regions, raises significant ethical concerns due to potential physical and psychological harm and increasing scrutiny under child protection laws. Consistency in discipline, grounded in clear boundaries and non-violent methods, enhances ethical compliance and supports positive behavioral outcomes without infringing legal standards or children's rights.
Alternatives to Spanking for Effective Discipline
Time-out offers a structured, non-physical alternative to spanking, promoting reflection and self-regulation in children, while discipline consistency ensures clear expectations and predictable consequences that reinforce positive behavior. Alternatives to spanking, such as time-out, positive reinforcement, and natural consequences, emphasize teaching rather than punishment, leading to improved long-term behavioral outcomes and stronger parent-child relationships. Research supports consistent discipline strategies combined with non-violent approaches as essential for effective behavior management and emotional development.
Choosing the Best Approach for Your Child
Time-out, spanking, and discipline consistency each impact child behavior differently, with time-outs promoting self-regulation and spanking often linked to increased aggression. Consistent discipline establishes clear expectations and boundaries, fostering long-term positive behavior. Your choice should prioritize nurturing respect and emotional growth while maintaining consistent, age-appropriate consequences.
Infographic: Time-out vs Spanking
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com