Parental burnout is a state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion caused by prolonged parenting stress, while exhaustion refers to general fatigue without the extended emotional toll. Explore this article to understand the key differences and ways to manage parental burnout effectively.
Table of Comparison
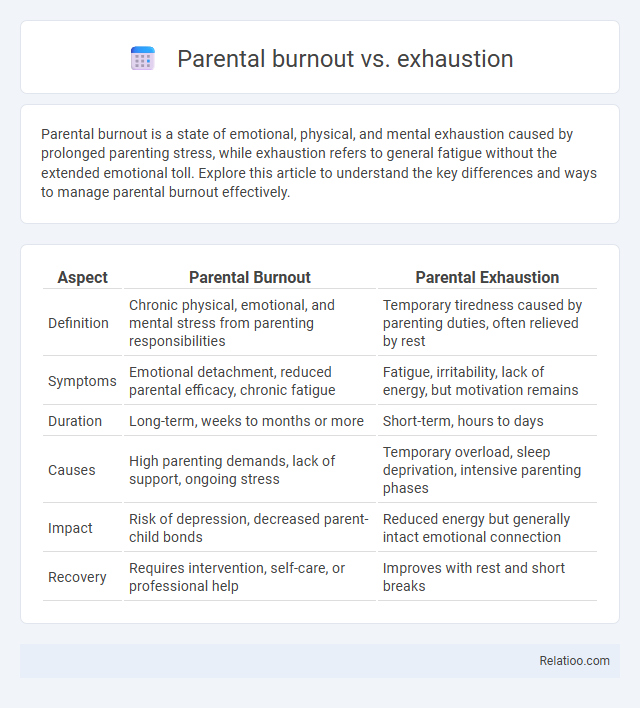
| Aspect | Parental Burnout | Parental Exhaustion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic physical, emotional, and mental stress from parenting responsibilities | Temporary tiredness caused by parenting duties, often relieved by rest |
| Symptoms | Emotional detachment, reduced parental efficacy, chronic fatigue | Fatigue, irritability, lack of energy, but motivation remains |
| Duration | Long-term, weeks to months or more | Short-term, hours to days |
| Causes | High parenting demands, lack of support, ongoing stress | Temporary overload, sleep deprivation, intensive parenting phases |
| Impact | Risk of depression, decreased parent-child bonds | Reduced energy but generally intact emotional connection |
| Recovery | Requires intervention, self-care, or professional help | Improves with rest and short breaks |
Understanding Parental Burnout: Definition and Symptoms
Parental burnout is a state of chronic physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion caused by prolonged and overwhelming parenting stress, characterized by feelings of detachment from one's children and a sense of reduced parental accomplishment. Unlike general exhaustion, parental burnout specifically arises from the demands of parenting roles, leading to emotional distancing and a loss of motivation in caregiving tasks. Recognizing symptoms such as persistent fatigue, irritability, and emotional numbness is crucial for differentiating parental burnout from temporary tiredness or stress.
What is Parental Exhaustion? Key Differences
Parental exhaustion is a state of physical and emotional depletion caused by the demands of parenting, characterized by fatigue, irritability, and reduced motivation, but it is less severe and often temporary compared to parental burnout. Parental burnout involves a chronic condition marked by overwhelming exhaustion, emotional distancing from children, and feelings of incompetence, whereas parental exhaustion may not include the profound detachment and pervasive sense of failure found in burnout. Key differences between parental exhaustion and burnout lie in intensity, duration, and psychological impact, with burnout requiring more intensive intervention due to its long-term effects on mental health and family dynamics.
Causes of Parental Burnout and Exhaustion
Parental burnout arises from chronic stress due to overwhelming caregiving demands, lack of support, and persistent feelings of incompetence, while exhaustion primarily results from physical and mental fatigue linked to insufficient rest and high caregiving load. Key causes include prolonged exposure to parenting stressors, unrealistic expectations, and a mismatch between parental resources and demands. Both conditions share overlapping symptoms but differ in intensity and underlying psychological impacts, with burnout reflecting emotional detachment and exhaustion emphasizing depletion of energy.
Signs You’re Experiencing Burnout vs Exhaustion
Parental burnout manifests through emotional detachment, overwhelming fatigue, and a sense of ineffectiveness in your parenting role, while exhaustion primarily involves physical and mental tiredness without the deep emotional impact. Signs you're experiencing burnout include persistent feelings of hopelessness, irritability, and a loss of fulfillment from parenting activities, contrasting with exhaustion, which typically resolves with rest. Recognizing these distinctions helps you address your symptoms appropriately, whether through self-care strategies or seeking professional support.
Emotional and Physical Effects on Parents
Parental burnout manifests in intense emotional exhaustion, chronic stress, and feelings of detachment from children, whereas general exhaustion might result from temporary fatigue without deeper emotional impact. Emotional effects include irritability, anxiety, depression, and a sense of failure, while physical effects range from persistent fatigue to headaches and sleep disturbances. Understanding these distinctions helps in addressing parental burnout with targeted interventions focusing on both mental health support and physical well-being restoration.
The Impact on Family Dynamics
Parental burnout significantly disrupts family dynamics by increasing emotional distance between parents and children, reducing parental responsiveness, and amplifying household stress. Exhaustion, a primary symptom of parental burnout, impairs parents' ability to engage effectively, often leading to decreased communication and unresolved conflicts within the family unit. The cumulative effects of parental burnout compromise overall family cohesion, escalating tension and diminishing the quality of parent-child relationships.
Risk Factors and Vulnerable Groups
Parental burnout differs from general exhaustion by its chronic nature and emotional depletion, often triggered by prolonged stress without adequate support. Risk factors include high parenting demands, lack of social support, and pre-existing mental health conditions, making single parents, parents of children with special needs, and those facing socioeconomic hardships particularly vulnerable. Recognizing these early signs can help you seek targeted interventions to prevent severe consequences on parental well-being.
Prevention Strategies for Burnout and Exhaustion
Parental burnout and exhaustion share symptoms such as overwhelming fatigue and emotional depletion, but burnout involves a deeper sense of detachment and reduced accomplishment. Prevention strategies for your parental burnout and exhaustion include establishing consistent self-care routines, seeking social support, and setting realistic expectations to manage daily stresses. Prioritizing adequate rest, engaging in mindfulness practices, and communicating openly with partners or support networks can significantly reduce the risk of long-term burnout.
Coping Mechanisms and Recovery Tips
Parental burnout, characterized by overwhelming exhaustion, emotional distancing, and reduced accomplishment, requires focused coping mechanisms such as establishing boundaries, practicing self-care, and seeking social support. Differentiating it from general exhaustion, which may stem from temporary fatigue, parental burnout demands long-term recovery strategies including professional counseling and mindfulness techniques to rebuild emotional resilience. Your ability to recognize these signs early and implement tailored recovery tips can significantly enhance mental well-being and parenting effectiveness.
When to Seek Professional Help
Parental burnout manifests as chronic physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion due to prolonged parenting stress, distinct from ordinary fatigue or temporary exhaustion. Seek professional help when overwhelming feelings of detachment, irritability, or hopelessness persist for weeks, impairing daily functioning and parent-child relationships. Early intervention from mental health experts can prevent exacerbation and support recovery through tailored coping strategies and therapeutic guidance.
Infographic: Parental burnout vs exhaustion
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com