Kinship foster care places children with relatives, promoting emotional stability and cultural continuity, while non-kinship foster care involves placement with unrelated caregivers, often emphasizing specialized support services. Explore this article to understand the key differences and impacts on child well-being in both foster care types.
Table of Comparison
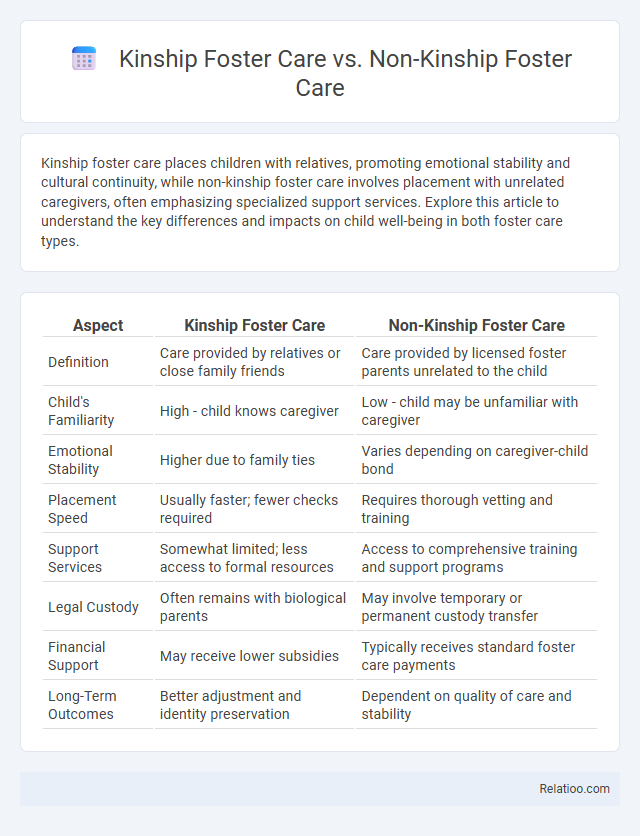
| Aspect | Kinship Foster Care | Non-Kinship Foster Care |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Care provided by relatives or close family friends | Care provided by licensed foster parents unrelated to the child |
| Child's Familiarity | High - child knows caregiver | Low - child may be unfamiliar with caregiver |
| Emotional Stability | Higher due to family ties | Varies depending on caregiver-child bond |
| Placement Speed | Usually faster; fewer checks required | Requires thorough vetting and training |
| Support Services | Somewhat limited; less access to formal resources | Access to comprehensive training and support programs |
| Legal Custody | Often remains with biological parents | May involve temporary or permanent custody transfer |
| Financial Support | May receive lower subsidies | Typically receives standard foster care payments |
| Long-Term Outcomes | Better adjustment and identity preservation | Dependent on quality of care and stability |
Understanding Kinship Foster Care
Kinship foster care places children with relatives or close family friends, providing a familiar environment that supports emotional stability and cultural continuity. Non-kinship foster care involves caregivers without familial ties, emphasizing professional training and resources to meet children's needs. Understanding kinship foster care helps you recognize its benefits in maintaining family connections while addressing the challenges that may arise in caregiving dynamics.
What Is Non-Kinship Foster Care?
Non-kinship foster care involves placing children with certified caregivers who have no biological or legal relationship to them, providing a stable and nurturing environment when family members are unavailable or unsuitable. Unlike kinship foster care, which places children with relatives or close family friends, non-kinship foster parents undergo specialized training and licensing to address diverse behavioral and emotional needs. Foster parenting encompasses both kinship and non-kinship care, emphasizing the commitment to safeguard children's welfare through structured support and care.
Key Differences Between Kinship and Non-Kinship Care
Kinship foster care places children with relatives or close family friends, providing stability through familiar relationships and cultural continuity, whereas non-kinship foster care involves placement with licensed caregivers without familial ties, offering professional support and resources. Kinship caregivers often face fewer licensing requirements and maintain stronger emotional bonds, while non-kinship foster parents receive extensive training and access to formal support systems. These differences impact placement stability, child well-being, and the type of services available to both the child and the caregiver.
Benefits of Kinship Foster Care
Kinship foster care provides children with a stable environment by placing them with relatives who share cultural background and values, enhancing emotional security and identity formation. It reduces trauma associated with separation from familiar caregivers and improves placement stability compared to non-kinship foster care. Foster parenting, while crucial, often requires additional adjustments, whereas kinship care leverages existing family bonds to promote quicker emotional recovery and maintain family continuity.
Advantages of Non-Kinship Foster Care
Non-Kinship Foster Care offers the unique advantage of providing children with access to a broader range of resources and specialized support services that may not be available within kinship settings. Your child benefits from caregivers who are often extensively trained and experienced in managing diverse behavioral and emotional needs. This form of fostering enhances socialization opportunities by exposing children to new environments and networks beyond their family circle.
Challenges in Kinship Placements
Kinship foster care faces unique challenges such as limited access to resources, increased emotional strain due to pre-existing family dynamics, and legal complexities surrounding custody and guardianship. In contrast, non-kinship foster care often benefits from more standardized support systems but may encounter attachment difficulties between the child and unrelated caregivers. Foster parenting overall requires navigating diverse challenges including trauma-informed care, behavioral management, and fostering long-term stability for the child.
Obstacles in Non-Kinship Foster Care
Non-kinship foster care faces significant obstacles such as emotional bonding challenges, increased placement disruptions, and lower retention rates compared to kinship foster care, where children are placed with relatives and often experience greater stability. Non-kinship foster parents frequently encounter difficulties navigating complex child welfare systems, securing adequate training, and managing behavioral issues without the familial support network that kinship caregivers naturally possess. These challenges contribute to greater stress and turnover among non-kinship foster parents, impacting the overall quality of care and permanency outcomes for children.
Child Outcomes in Kinship vs Non-Kinship Care
Children placed in kinship foster care often experience greater stability, stronger cultural connections, and improved emotional wellbeing compared to those in non-kinship foster care. Research indicates kinship care placements lead to lower rates of behavioral problems and higher permanency outcomes due to familiar family environments. Foster parenting in both contexts requires specialized training, but kinship caregivers typically provide a more nurturing and consistent support system, enhancing long-term child development.
Support Services for Foster Families
Support services for kinship foster care prioritize family preservation through tailored financial assistance, counseling, and legal aid to maintain existing family bonds. Non-kinship foster care support includes comprehensive training, mental health resources, and respite care to address the unique challenges faced by unrelated caregivers. Foster parenting programs offer extensive educational workshops, peer support networks, and access to child development experts to empower all foster families in creating stable, nurturing environments.
Choosing the Best Foster Care Option
Choosing the best foster care option depends on the needs and stability of the child, with kinship foster care offering the advantage of familiar family connections that promote emotional security. Non-kinship foster care provides access to trained foster parents who can offer specialized support when family members are unavailable or unsuitable. Your decision should prioritize the child's well-being, considering factors like relational bonds, caregiver experience, and the ability to provide a safe, nurturing environment.
Infographic: Kinship Foster Care vs Non-Kinship Foster Care
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com